OPERATION
OUTER SHIED OUTER SHIED
HI O- HI O-
TOSOURCE TOSOURCE
loo loo
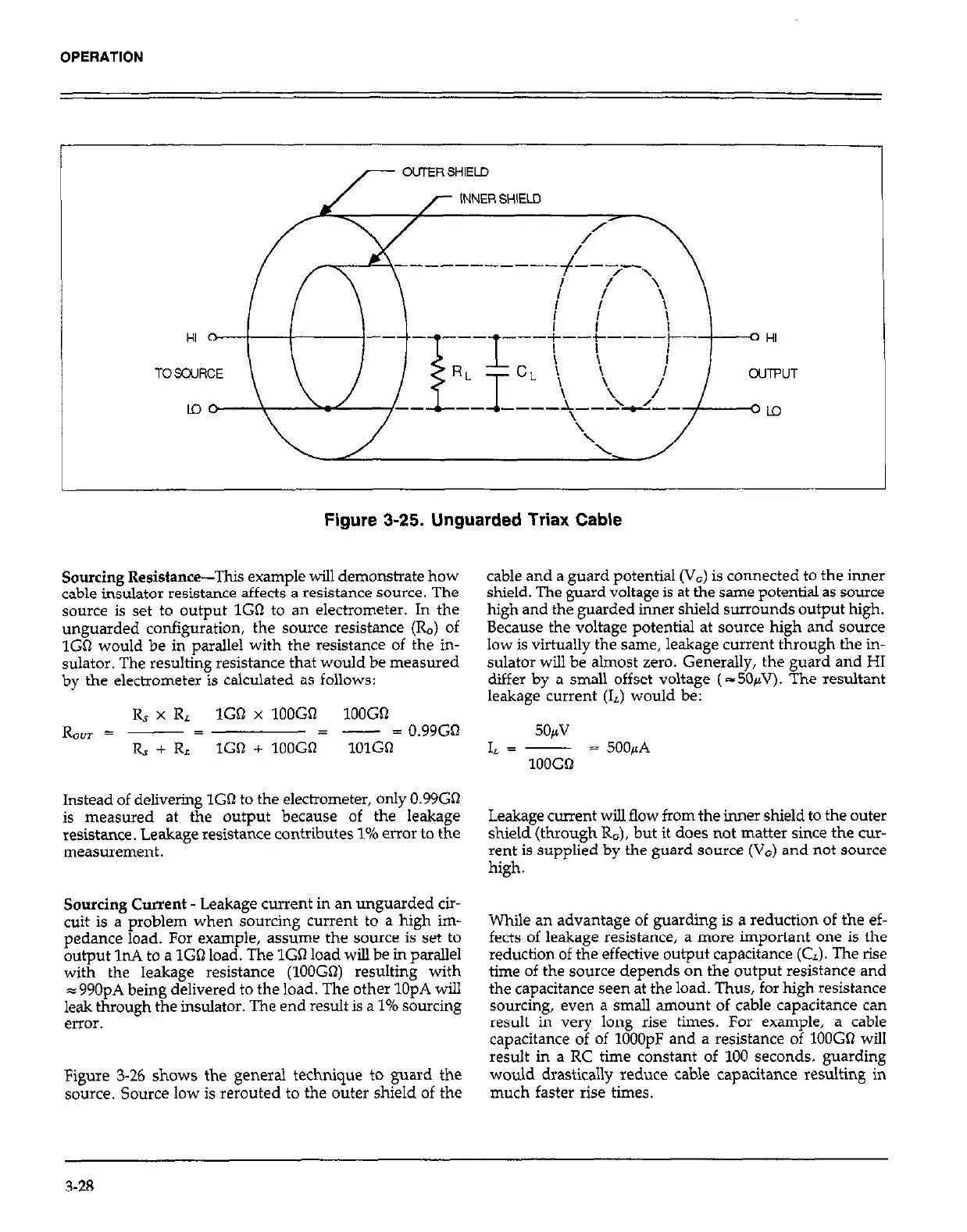
Figure 3-25. Unguarded Triax Cable
Sourcing Resistance-This example will demonstrate how
cable insulator resistance affects a resistance source. The
source is set to output 1GQ to an electrometer. In the
unguarded configuration, the source resistance (Ro) of
1Gn would be in parallel with the resistance of the in-
sulator. The resulting resistance that would be measured
by the electrometer is calculated as follows:
Rs x R,
1GQ x lOOGil 100Gfl
R
o”T = - =
= - = 0.99GO
Q + R,
1Gll + 100GR 101GR
Instead of delivering 1GR to the electrometer, only 0.99GQ
is measured at the output because of the leakage
resistance. Leakage resistance contributes 1% error to the
measurement.
Sourcing Current - Leakage current in an unguarded cir-
cuit is a problem when sourcing current to a high im-
pedance load. For example, assume the source is set to
output 1nA to a 1GQ load. The 1GQ load will be in parallel
with the leakage resistance (100GQ resulting with
z 990pA being delivered to the load. The other 10pA will
leak through the insulator. The end result is a 1% sourcing
error.
Figure 3-26 shows the general technique to guard the
source. Source low is rerouted to the outer shield of the
cable and a guard potential (V,) is connected to the inner
shield. The guard voltage is at the same potential as source
high and the guarded inner shield surrounds output high.
Because the voltage potential at source high and source
low is virtually the same, leakage current through the in-
sulator will be almost zero. Generally, the guard and HI
differ by a small offset voltage (=SOpV). The resultant
leakage current (Id would be:
5ojJv
I, = ~ = 500pA
lOOGO
Leakage current will flow from the inner shield to the outer
shield (through RO), but it does not matter since the cm=
rent is supplied by the guard source (V,) and not source
high.
Whiie an advantage of guarding is a reduction of the ef-
fects of leakage resistance, a more important one is the
reduction of the effective output capacitance (C,). The rise
time of the source depends on the output resistance and
the capacitance seen at the load. Thus, for high resistance
sourcing, even a small amount of cable capacitance can
result in very long rise times. For example, a cable
capacitance of of 1000pF and a resistance of 1OOGQ will
result in a RC time constant of 100 seconds. guarding
would drastically reduce cable capacitance resulting in
much faster rise times.
3-28
 Loading...
Loading...