WSDA
®
-2000 User Manual
users on the network from accessing the data stream . If Live Connect is disabled it will not be
available for connecting to SensorConnect unless done remotely through SensorCloud™ (
see
Remote Connectivity on page 44
). The default is for Live Connect to be enabled.
Data Logging: Data logging saves acquired data to the gateway internal memory, and also makes it
available to the CAN J1939 Bus, SensorCloud™, and a host computer through Live Connect.
Disabling data logging will prevent data only from being stored in the gateway internal memory and
from being uploaded to SensorCloud™. The data will still be available to SensorConnect through
Live Connect and for the CAN J1939 bus. The default setting is that all data logging is enabled.
When data logging is enabled the gateway waits for time synchronization (
see Time Options on
page 39
), sets the node synchronization beacon, sets the gateway wireless node communication
frequency, and then begins logging data.
WSN Beacon On Startup:The beacon is used to precisely coordinate node data acquisition and
data transmission in the wireless sensor network (WSN) during synchronized sampling.
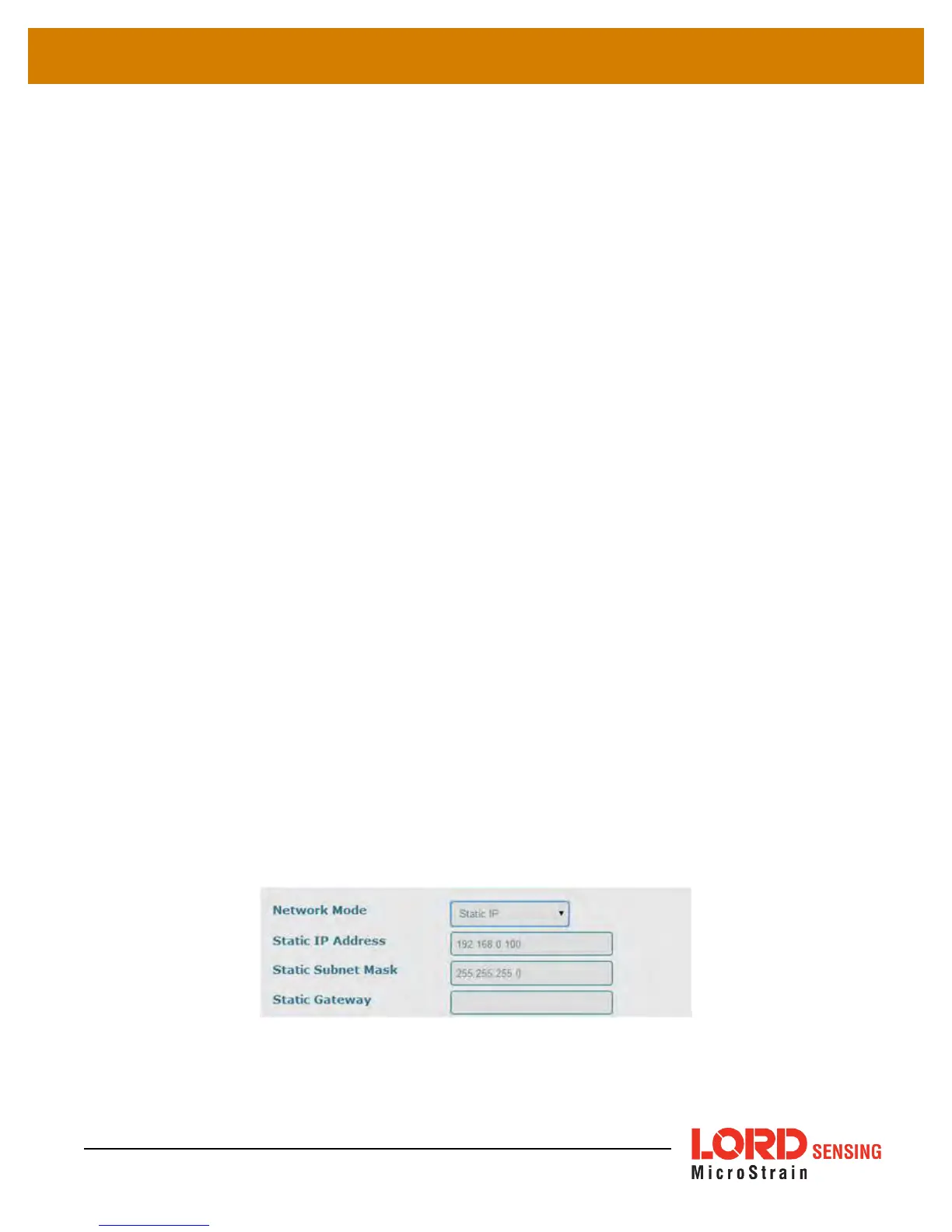
Network Mode: The network mode determines whether the gateway has a dynamic or a static IP
address, which is used to identify it on the network. A dynamic, or DHCP network, automatically
assigns the gateway an IPaddress. The static IPsetting allows manual assignment of the IP
address. A static IPaddress is required if the network does not have a DHCP server or if the
gateway will be connected directly to a host computer and not used on a network. The default
setting is for a DHCP network.
If Static IP is selected, additional menu settings will appear (
Figure 22 - Static IPSettings
). The
Static IPAddress is the IPAddress to which the gateway will be assigned. This cannot be the
network address or the broadcast address of the subnet. The Static Subnet Mask defines the
range that the gateway can communicate (on the subnet). For example, if the gateway IP Address
is 192.168.0.100, and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0 the gateway can communicate with all
addresses between 192.168.0.0 and 192.168.0.255. The Static Gateway option allows users to
define an address the gateway can communicate with outside of its subnet. This requires the
gateway to be able to access the internet on a static network.
Figure 22 - Static IPSettings
37
 Loading...
Loading...