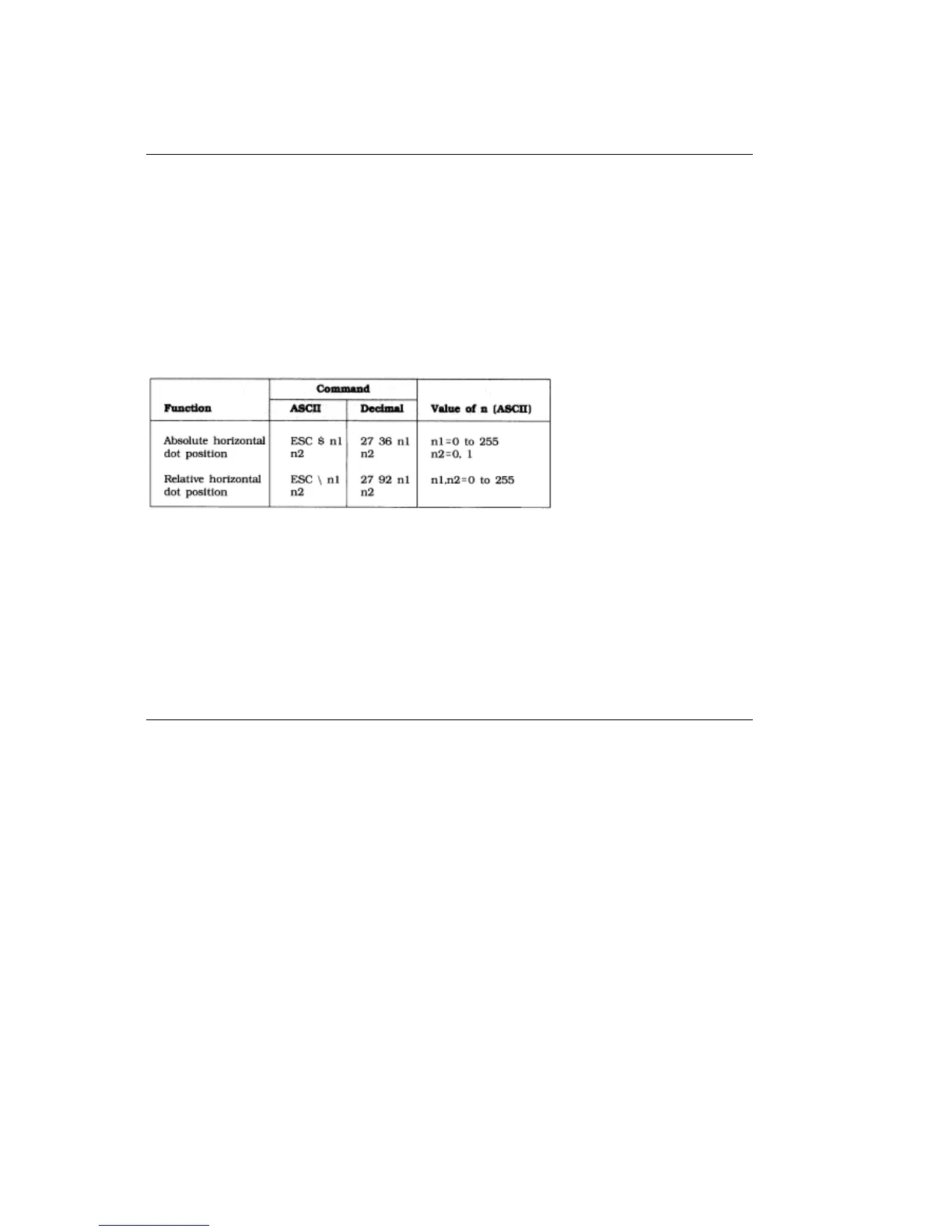
%Horizontal Dot Placement Commands
Horizontal Dot Placement Commands
These commands let you place text or graphics very precisely on the page. (For precise vertical
positioning, see the description of the fine line feed and line spacing on pages 92 and 91.) The ESC $ n1
n2 command uses the left margin as a reference point and moves the print position horizontally in
1/60-inch increments, regardless of the pitch. To determine how many dots you wish to move, multiply
the number of inches you wish to move the print position by 60, the number of dots per inch.Example
Suppose you want to set an absolute horizontal dot position of six inches over from the left margin. First,
multiply 6 inches by 60 dots/inch to obtain 360 dots. Then divide the number of dots by 256: this yields a
value of 1 (n2) with a remainder of 104 (n1). Therefore, the command you would send would be ESC $ h
SOH (ASCII) or 27 36 104 01 (decimal).For values above 99, you can use hexadecimal for n1; in this
case n1 would be 68 hexadecimal.
The ESC \ n1 n2 command lets you move the print position to either the right or the left of the current
print position. To determine the values of the two variables (n1 and n2), first determine how many dots
over you wish to move. To do this, divide the number of inches you wish to move by the number of dots
per inch. For this command, the number of dots per inch depends on the print mode you have engaged.
The "Horizontal Position Units" table below gives the number of dots per inch for each of the print modes,
to be used in calculating how many dots you wish to move.If you want to move the print position to the
right, divide the number of dots to be moved by 256, then assign the whole number result to n2 and the
remainder to n1. If you want to move the print position to the left, subtract the number of dots to be
moved from 65,536, then divide the result by 256: assign the whole number result to n2 and the
remainder to n1.
ML 380 ( 96-02-03 )
 Loading...
Loading...











