4
Configuring The Meter
26
4.3.2 Scaling Without Known Loads
To scale without known inputs, calculate input values based on the transducer
specifications and manually enter them on the front-panel push buttons. The following
example assumes load cells with these specifications:
Maximum Load: 100.0 lbs
Output: 3.1 mV/V
Sensor Excitation: 10 Vdc
Output: 31mV = (3.1 mV/V) x (10 V)
1.
Determine the correct values for IN1 and IN!2 based on the load cell specifications.
In most cases, RD1 and RD!2 are equal to the minimum and maximum of the
transducer output span. The example assumes RD1 and RD!2 are equal to the
range of the load (RD1 = 0 and RD!2 = 100.0). Calculate IN1 and IN!2 using the
loadcell output span and the following equation:
IN = (Sensor Output) x (Natural Gain) x (Multiplier).
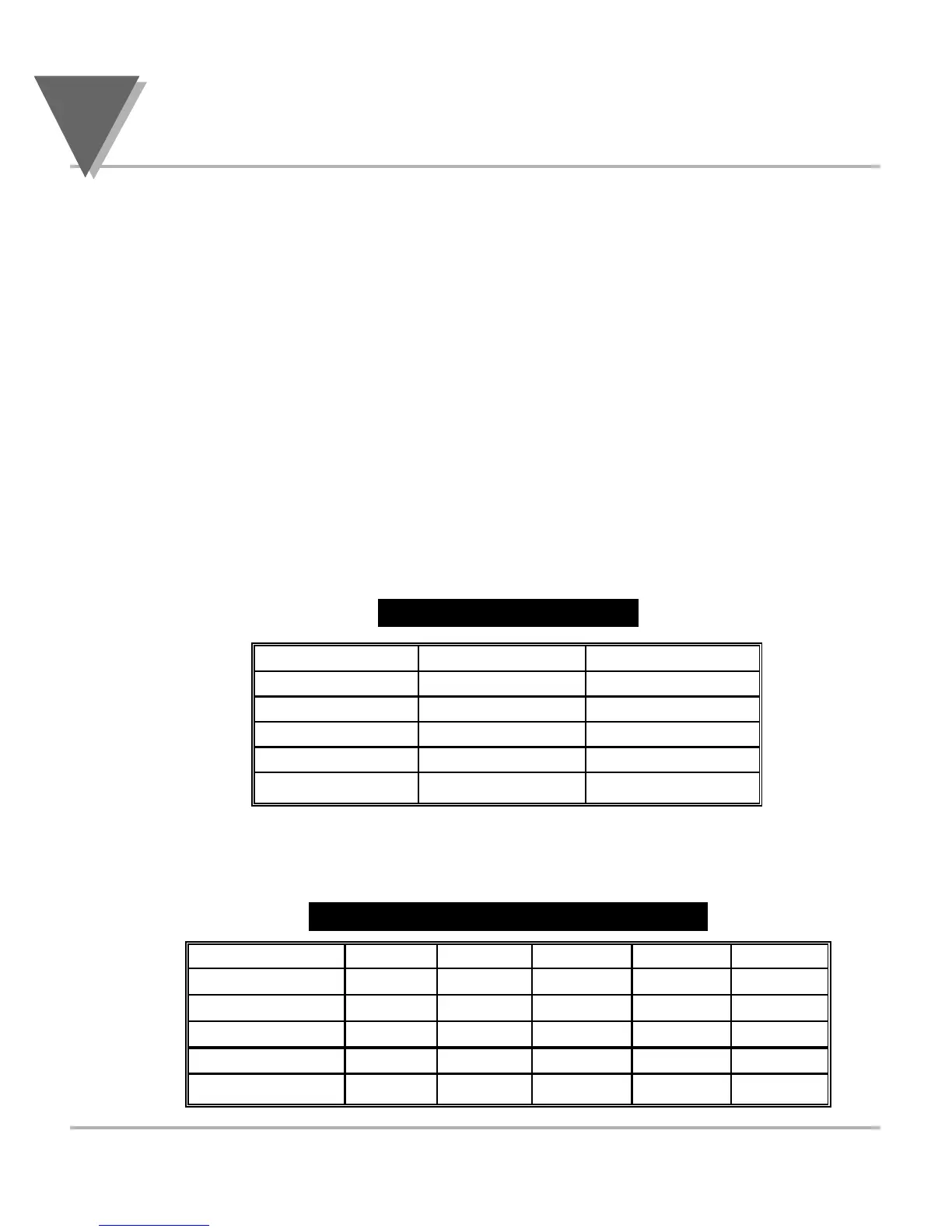
Table 4-3. Natural Gain
2. Determine the multiplier by the Input Resolution setting (R.2 in the RD.CF menu)
and the input range selected. Typically R.2=4 is suitable for most applications.
Table 4-4. Input Resolution Multiplier
Input Range R.2=4 R.2=3 R.2=2 R.2=1 R.2=0
0 to 100 mV 1.000 2.000 3.333 5.000 10.00
0 to 10 V 1.000 2.000 3.333 5.000 10.00
0 to 20 mA 1.000 2.000 3.333 5.000 10.00
± 50 mV 1.000 1.000 1.667 2.500 5.000
± 5 V 1.000 1.000 1.667 2.500 5.000
Input Range Span Units Natural Gain
0 to 100 mV Millivolts 100 cts/mV
±50 mV Millivolts 40 cts/mV
0 to 10 V Volts 1000 cts/V
± 5 V Volts 400 cts/V
0 to 20 mA Milliamps 500 cts/mA

 Loading...
Loading...