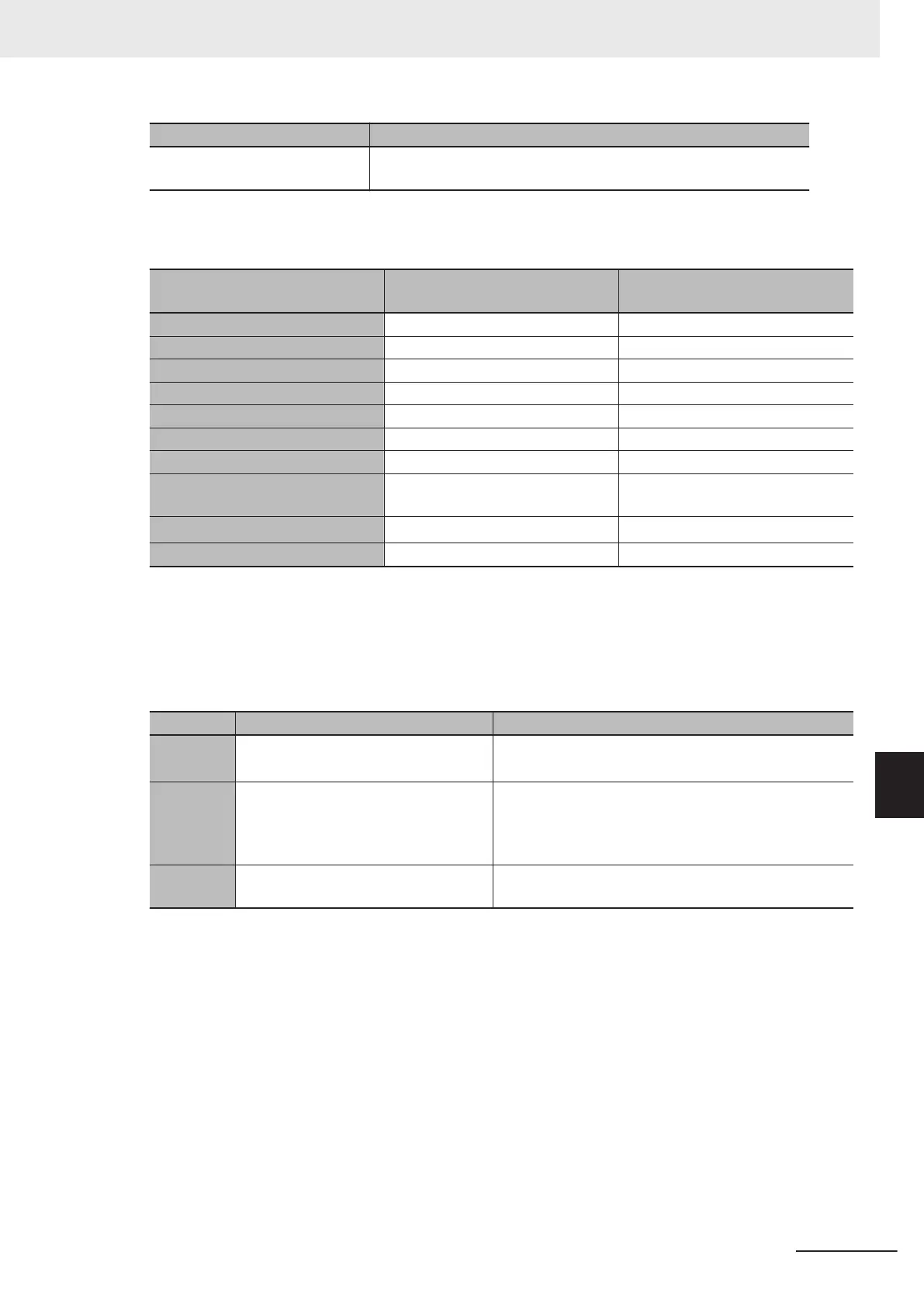
Item Specification
Locations in memory At an integral multiple of the alignment starting from the start of the
variable in memory
.
The alignments and the amounts of memory that are allocated for the basic data types and enumera-
tions are given below
.
Data type Alignment [bytes]
Amount of memory that is allo-
cated [bytes]
BOOL 2 2
BYTE, USINT, or SINT 1 1
WORD, UINT, or INT 2 2
DWORD, UDINT, or DINT 4 4
LWORD, ULINT, or LINT 8 8
REAL 4 4
LREAL 8 8
TIME, DATE, TIME_OF_DAY, or
DA
TE_AND_TIME
8 8
STRING[N+1]
*1
1 N+1
Enumerations 4 4
*1. N is the maximum number of characters handled. For example, if a maximum of 10 single-byte characters
are handled, the NULL character is added, so memory for 1
1 characters must be reserved.
The elements of arrays and the members of structures and unions are located in memory for the most
ef
ficient access. The alignments and the amounts of memory that are allocated for arrays, structures,
and unions are determined by the variable declarations, as described below.
Data type Alignment Amount of memory that is allocated
Array Same as alignment of the data type of
the elements
(Amount of memory that is allocated for the data type of
the elements) × Number of elements
*1
Structure The largest alignment of all of the
members
The integral multiple of the alignment that is larger than
the total amount of memory that is allocated when the
members are arranged in order at integral multiples of
the alignment of the data types of the members
Union The largest alignment of all of the
members
The largest amount of memory that is allocated for any
of the members
*1. BOOL arrays are an exception. Refer to Precautions for Correct Use, below
, for the amount of memory that
is allocated for BOOL arrays.
Appendices
A-47
NJ/NX-series CPU Unit Built-in EtherNet/IP Port User’s Manual (W506)
A-5 Variable Memory Allocation Methods
A
A-5-1 Variable Memory Allocation Rules

 Loading...
Loading...