ENGLISH
Siemens AG 610.40 064.01
15
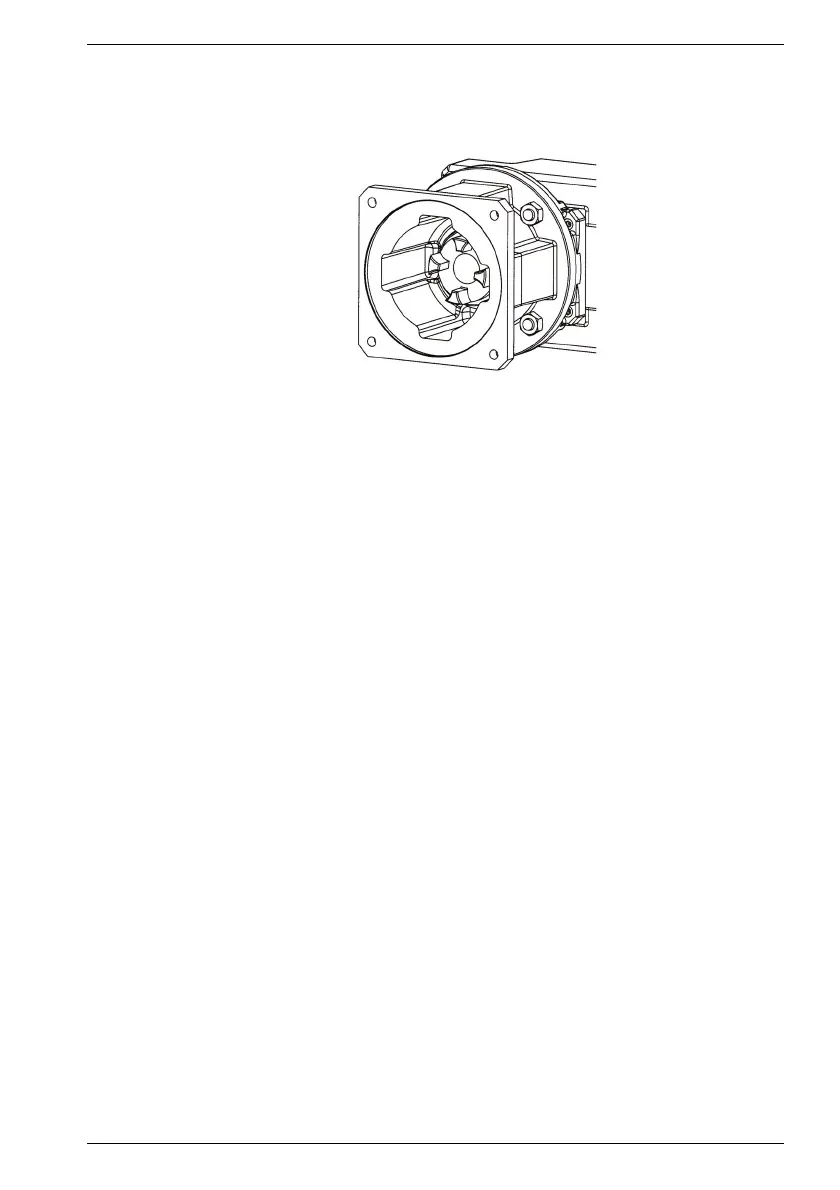
2.1.3 Motor adapter
If no direct motor gear mounting is provided, motor adapters (with a square flange) are
used for mounting servomotors (according to IEC or NEMA-C) on a gearbox.
Fig. 5 Motor adapter (example)
2.1.3.1 Motor adapter with curved tooth clutch
Servomotors are mounted on the gearbox by means of motor adapters (with a square
flange). Servomotors can be mounted if the shaft end and mounting flange have standard
true running, axial run-out deviation and coaxial qualities complying with DIN 42955-N.
The motor does not have to be oil-tight. The centering diameter must be designed with a
tolerance complying with ISO j6, the shaft end complying with tolerance ISO k6, and the
key complying with DIN 6885 sheet 1. The motor can be mounted and dismounted with-
out coming into contact with lubricant. The motor shaft is linked to the gear input shaft by
the freely movable, torsionally rigid and maintenance-free curved tooth clutch. The clutch
runs dry and has a maximum continuous operating temperature of 80°C. The motor
adapter does not require any special maintenance.
2.1.3.2 Motor adapter with plug-in connector, zero-backlash
Motor adapters with zero backlash, axially braced, plug-in metal bellows-type clutch are
used for mounting servomotors on gearboxes. The motors preferably have smooth shafts
(without key). The clutch bush mounted on the gear side has a spring-loaded metal bel-
lows. For this reason, standard true running, axial run-out deviation and coaxial qualities
complying with DIN 42955-N are adequate for the shaft ends and the mounting flange of
the mounted motor.
2.1.4 Hollow shaft with shrink disk
Shaft mounted gearboxes are inserted onto the drive shaft of the machine that is to be
driven. The reaction torque must be supported either by flange-mounting the gearbox on
the machine or by a torque bracket. In the case of flange mounting, the deviation from
perpendicularity between the flanged end surface on the machine and the shaft axis must
not exceed 0.03/100 mm because of the danger of distorting the bearing or causing an
impermissible bending load on the machine shaft.

 Loading...
Loading...