3 Directions of Movement, Dimensioning 01.93
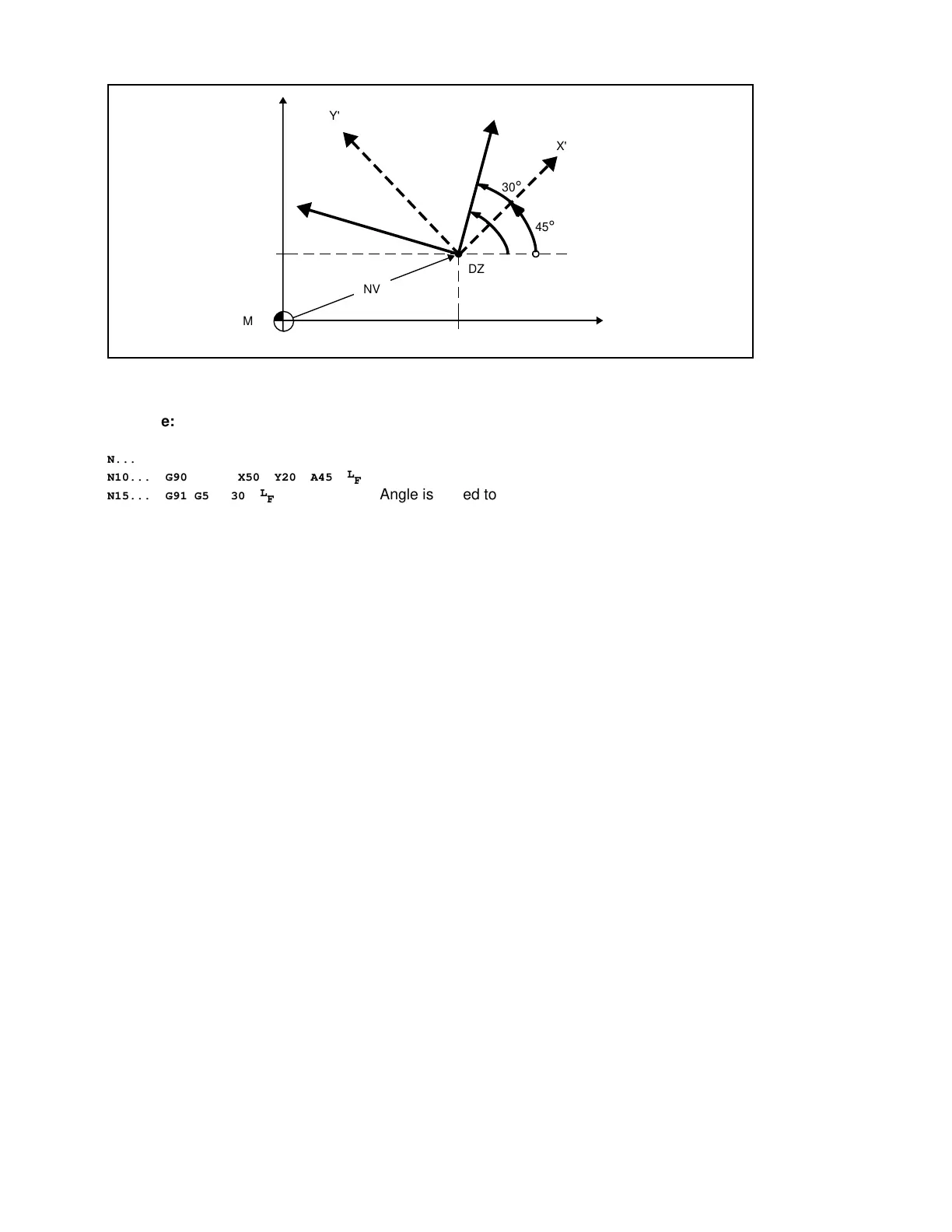
3.10 Coordinate rotation
X
Y
20
50
a
a
a
45°
Y'
X'
DZ
NV
M
a
a
a
30°
a
a
a
75°
Example:
N...
N10... G90 G58 X50 Y20 A45
L
F
N15... G91 G58 A30
L
F
Angle is added to the angle already programmed in
block N10 (sum = 75°)
:
:
Characteristics of coordinate rotations
• Coordinate rotations are channel specific.
• Coordinate rotations are active in the current plane.
• Coordinate rotations are suppressed modally if G53 or @706 was programmed.
• Circular interpolation must not be programmed immediately after coordinate rotation.
• If cutter radius compensation is active the angle of rotation can be changed but not the
position of the coordinate zero.
• If an angle of rotation is changed with @ commands while G54 ... G57 are active, @715
must first be programmed. If the settable zero offset is also changed, the command @714
is to be used. Commands @714 or @715 must be in a block of their own.
• Block search or program start must always begin at a block containing all the required
information. This especially applies to shortened block notation (i.e. only those axes are
programmed which are to move).
• If a coordinate rotation and a zero offset are active, neither a transition to another
coordinate rotation or zero offset nor a plane change are permitted.
3–24
© Siemens AG 1991 All Rights Reserved 6ZB5 410-0HD02
SINUMERIK 880, (PG)

 Loading...
Loading...











