Functions
6-1117SA6 Manual
C53000-G1176-C156-2
In the event of an earth fault the induced longitudinal voltage must neither exceed
60 % of the isolation voltage of the pilot wires nor 60 % of the isolation of the device.
The pilot wire comparison is therefore only suited for short lines.
6.6.1.9 Reverse Interlocking
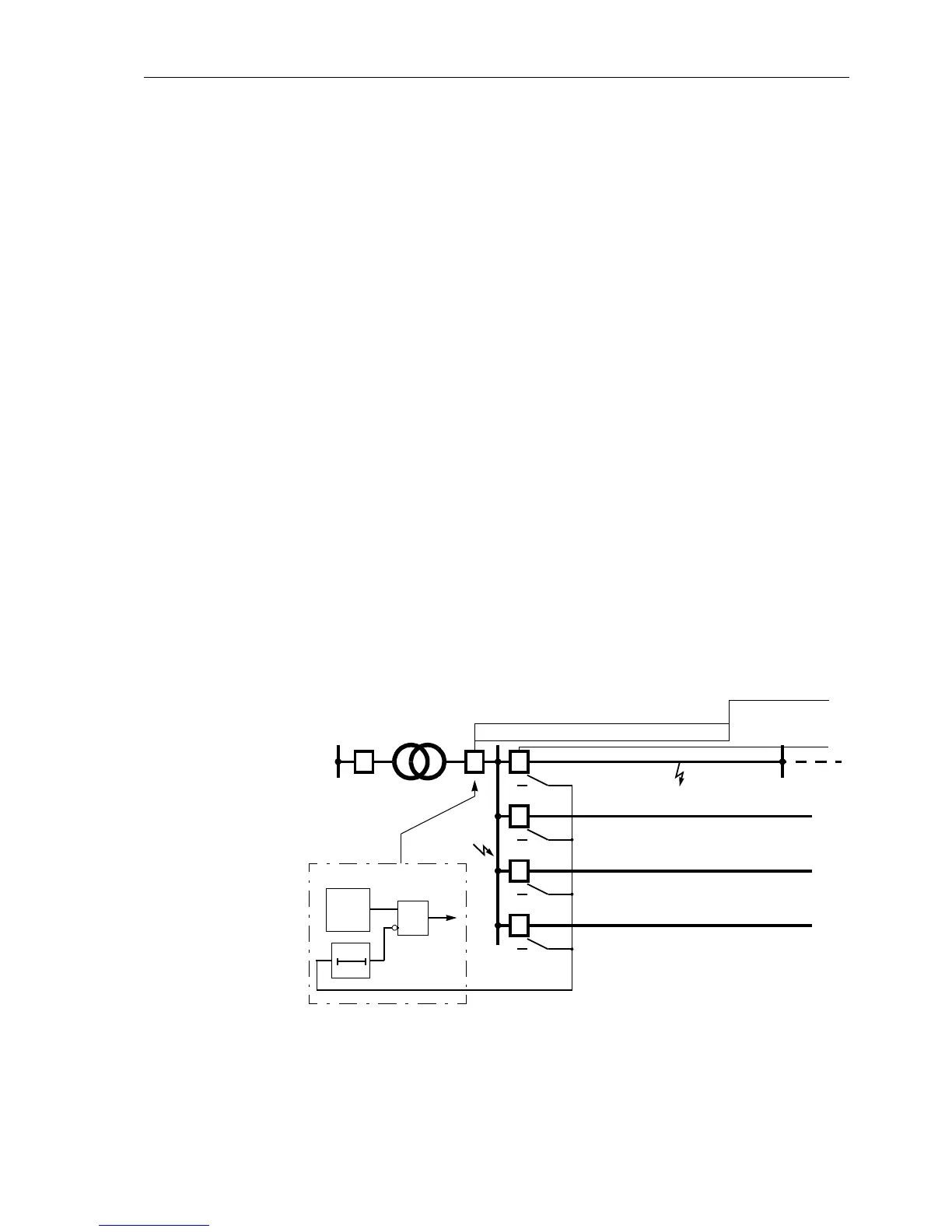
If the Distance Protection 7SA6 is used as back-up protection in single-end fed trans-
former feeders, the reverse interlocking function ensures a fast protection of the bus-
bar without endangering the selectivity for faults on the outgoing feeders.
According to Figure 6-65 the distance zones Z1 and Z2 serve as back-up stages for
faults on the outgoing lines, for example a fault in
F2. For distance grading the shortest
outgoing line is to be used.
The overreach zone Z1B, whose delay time T1B must be set longer than the pickup
time Ta of the protection devices of the outgoing lines, is blocked after the pickup of
an inferior protection. The pickup signal is sent (according to Figure 6-65) via the re-
ceive input of the Distance Protection.
If no signal is received this zone guarantees fast tripping of the busbar for
- faults on the busbar, such as for example in
F1,
- failure of the line protection during a fault, such as for example in
F2.
The reverse interlocking of the Distance Protection is performed by specific release or
blocking of the overreach zone Z1B. It can be realized by the blocking mode (see Fig-
ure 6-65) or the release mode.
To avoid transient false signals after clearance of external faults, the blocking condi-
tion of the reverse interlocking is extended by a transient blocking time (TB in Figure
6-65).
Figure 6-65 Reverse interlocking — functional principle and grading example
F1
F2
Z1
Z1B
T1
T1B
T2
Ta
Pickup
L+
Pick.
L+
Pick.
L+
Pick.
L+
Shortest Line
&
TB0
Z1B
T1B
Direc
.
7SA6
Tripping

 Loading...
Loading...











