Functions
6-266 7SA6 Manual
C53000-G1176-C156-2
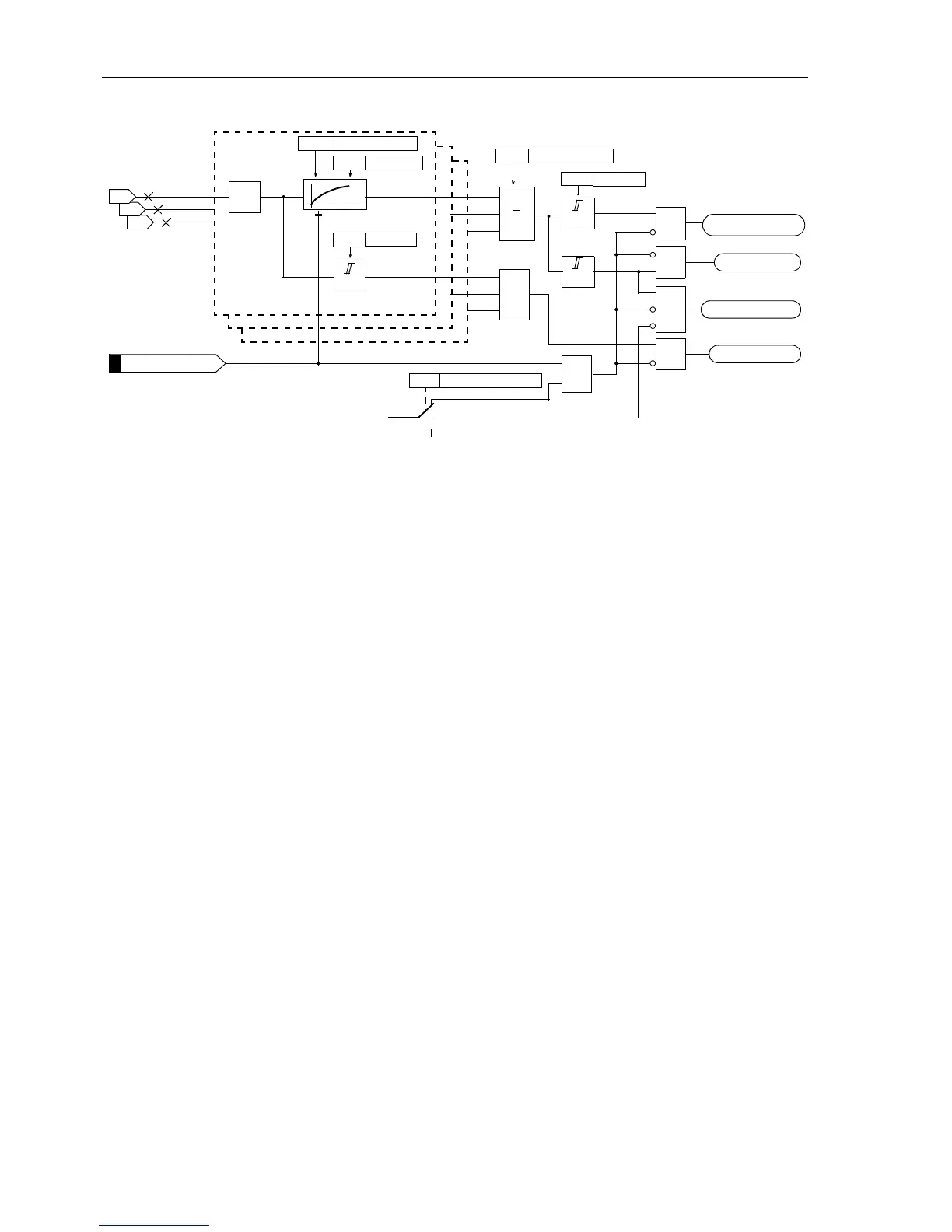
Figure 6-138Logic diagram of the thermal overload protection
6.19.2 Applying the Function Parameter Settings
General Informa-
tion
A precondition for the use of the thermal overload protection is that Overload =
Enabled was configured under address 142 (Section 5.1). It can be switched On or
Off under address 4201 Ther. OVERLOAD.FurthermoreAlarm Only canbeset.
With that latter setting the protection function is active but only outputs an alarm when
the tripping temperature is reached, i.e. the output function “
Th.O/L TRIP” is not ac-
tive.
k–factor The rated current of the device is taken as the base current for detecting an overload.
The setting factor k is set under address
4202 K-FACTOR. It is determined by the re-
lation between the permissible thermal continuous current and this rated current:
The permissible continuous current is at the same time the current at which the e-func-
tion of the overtemperature has its asymptote. It is not necessary to determine the trip-
ping temperature since it results automatically from the final rise temperature at k ·
I
N
.
Manufacturers of electrical machines usually state the permissible continuous current.
If no data are available, k is set to 1.1 times the rated current of the protected object.
For cables, the permissible continuous current depends on the cross section, the in-
sulation material, the design and the way they are laid, and can be derived from the
relevant tables.
Please note that the overload capability of electrical equipment relates to its primary
current. This has to be considered if the primary current differs from the rated current
of the current transformers.
L3
L2
L1
I
L3
I
L2
I
L1
>BLK ThOverload
&
4203 TIME CONSTANT
Θ
4202 K–FACTOR
I>
4205 I ALARM
4206 CALC. METHOD
Θ>
4204 Θ ALARM
Θ
max
Θ
Θ(I
max
)
Θ≥1
&
&
≥1
4201 Ther. OVER LOAD
Alarm Only
OFF
ON
“1“
FNo 1503
FNo 1521
FNo 1515
FNo 1516
Th.O/L Θ Alarm
Th.O/L I Alarm
Th.O/L TRIP
i
2
FNo 1517
Th.O/L Pickup
&
≥1
k
I
max
I
N
------------
=

 Loading...
Loading...











