30/317
2 - How does a typical microcontroller work?
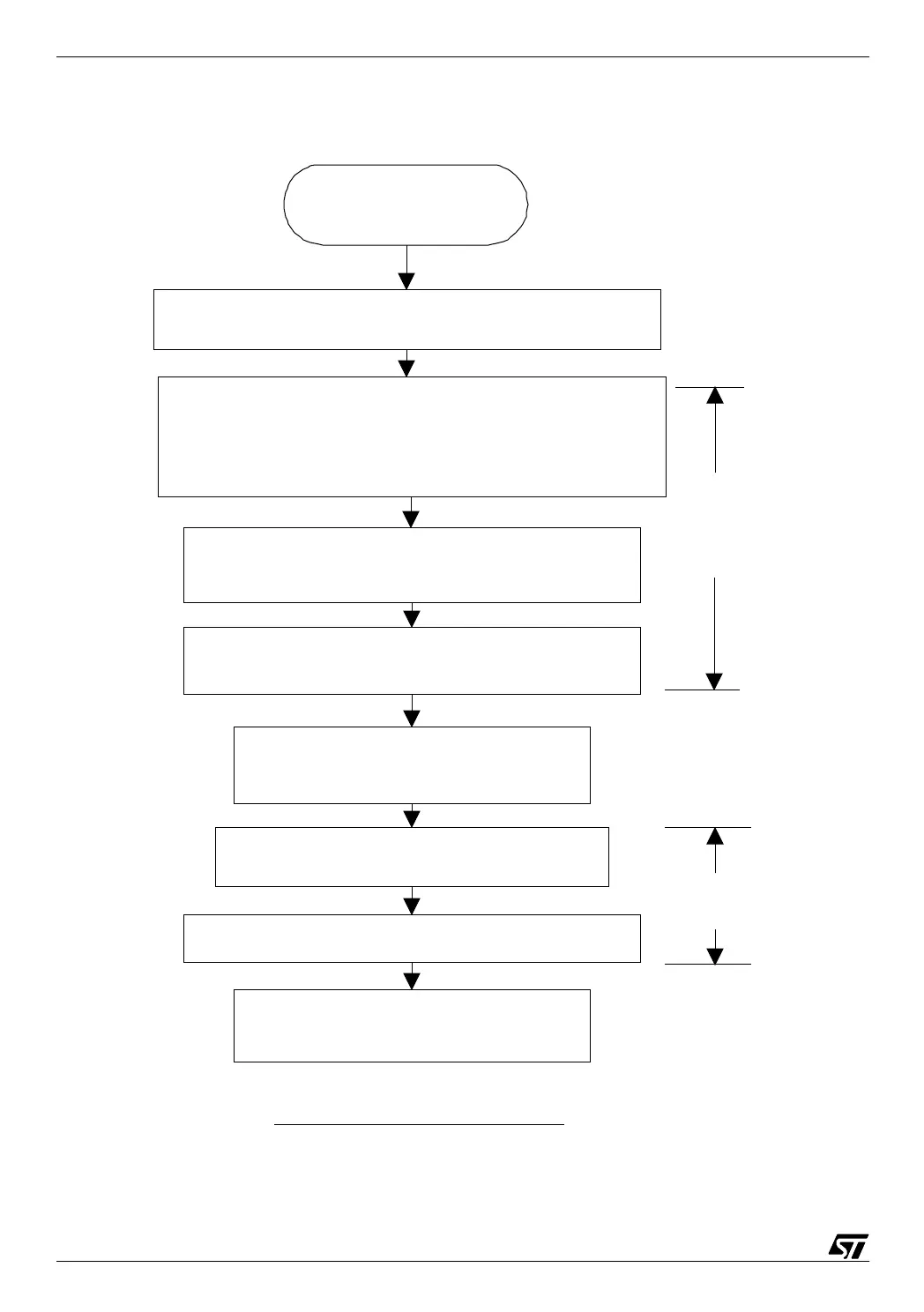
The effect of the interrupt is shown in the following diagram:
02-flow
An interrupt is requested
and authorized
The current instruction is executed, the PC is incremented
The PC and a small number of registers are saved, they are
automatically pushed onto the stack. The registers to be saved
are defined by hardware: accumulator, code condition register
etc.
Depending on the type of microcontroller, the lower
priority or all the maskable interrupt sources are masked
The PC is loaded with the interrupt vector address which
is a pointer to the address of the interrupt sub-routine
The sub-routine is executed and ends with
the 'return from interrupt' instruction
The masked interrupt sources are authorized
The PC and predefined registers are popped from stack
The next instruction of the interrupted
program is fetched and executed
Interrupt processing flowchart
Done
by
hardware
Done
by hardware
 Loading...
Loading...