33/317
2 - How does a typical microcontroller work?
Depending on the source of the interrupt (I/O, timer, etc.), the core fetches, from a predefined
location in memory, the address of the interrupt service routine especially written to process
that event. The vectors are always located at the end of the addressing space. When the mi-
crocontroller is reset, these interrupt vectors are fetched together with the reset vector for get-
ting the start address of the main program.
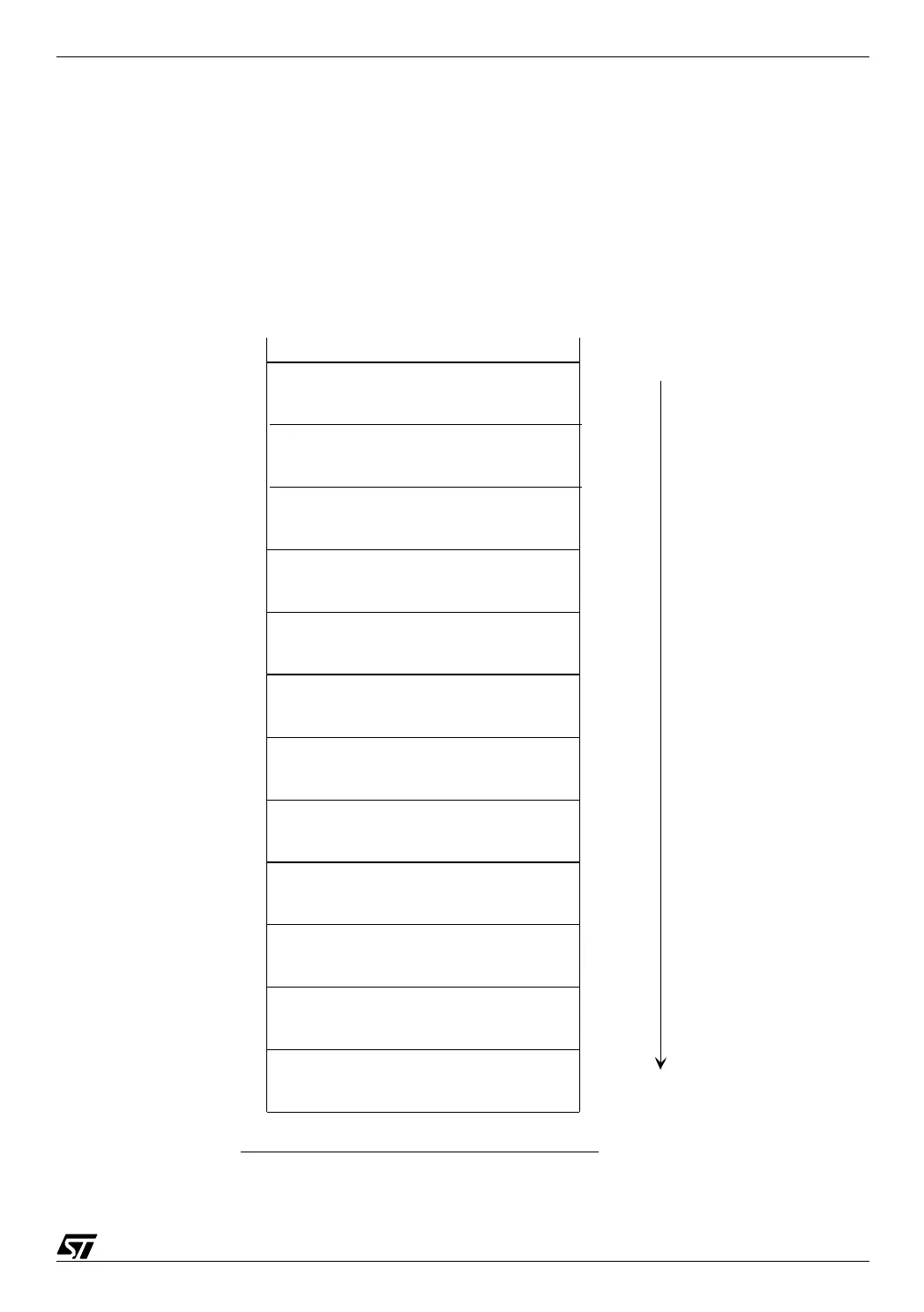
The following table shows the interrupt vectors:
02-tabv
I²C
Bus Interface
Timer B
Interrupt vector table of the ST72251
Timer A
Serial Peripheral
Interface
Ports B and C
TRAP
Software Interrupt
Reset vector
Higher priority
Lower priority
Memory
address
not used
not used
not used
not used
Port A
FFE0
FFE4
FFE6
FFEE
FFF0
FFF2
FFF4
FFF6
FFF8
FFFA
FFFC
FFFE
 Loading...
Loading...