Core peripherals PM0214
256/262 PM0214 Rev 9
Bit 28 V: Overflow condition code flag. Floating-point comparison operations update this flag. For more
details on the result, refer to Table 57.
0: Operation did not result in an overflow
1: Operation resulted in an overflow.
Bit 27 Reserved.
Bit 26 AHP: Alternative half-precision control bit:
0: IEEE half-precision format selected.
1: Alternative half-precision format selected.
Bit 25 DN: Default NaN mode control bit:
0: NaN operands propagate through to the output of a floating-point operation.
1: Any operation involving one or more NaNs returns the Default NaN.
Bit 24 FZ: Flush-to-zero mode control bit:
0: Flush-to-zero mode disabled. Behavior of the floating-point system is fully compliant with the
IEEE 754 standard.
1: Flush-to-zero mode enabled.
Bits 23:22 RMode: Rounding Mode control field. The specified rounding mode is used by almost all
floating-point instructions:
0b00: Round to nearest (RN) mode
0b01: Round towards plus infinity (RP) mode
0b10: Round towards minus infinity (RM) mode
0b11: Round towards zero (RZ) mode.
Bit 21:8 Reserved.
Bit 7 IDC: Input denormal cumulative exception bit. Cumulative exception bit for floating-point
exception.
1: Indicates that the corresponding exception occurred since 0 was last written to it.
Bit 6:5 Reserved
Bit 4 IXC: Inexact cumulative exception bit. Cumulative exception bit for floating-point exception.
1: Indicates that the corresponding exception occurred since 0 was last written to it.
Bit 3 UFC: Underflow cumulative exception bit. Cumulative exception bit for floating-point exception.
1: Indicates that the corresponding exception occurred since 0 was last written to it.
Bit 2 OFC: Overflow cumulative exception bit. Cumulative exception bit for floating-point exception.
1: Indicates that the corresponding exception occurred since 0 was last written to it.
Bit 1 DZC: Division by zero cumulative exception bit. Cumulative exception bit for floating-point
exception. 1: Indicates that the corresponding exception occurred since 0 was last written to it.
Bit 0 IOC: Invalid operation cumulative exception bit. Cumulative exception bit for floating-point
exception. 1: Indicates that the corresponding exception occurred since 0 was last written to it.
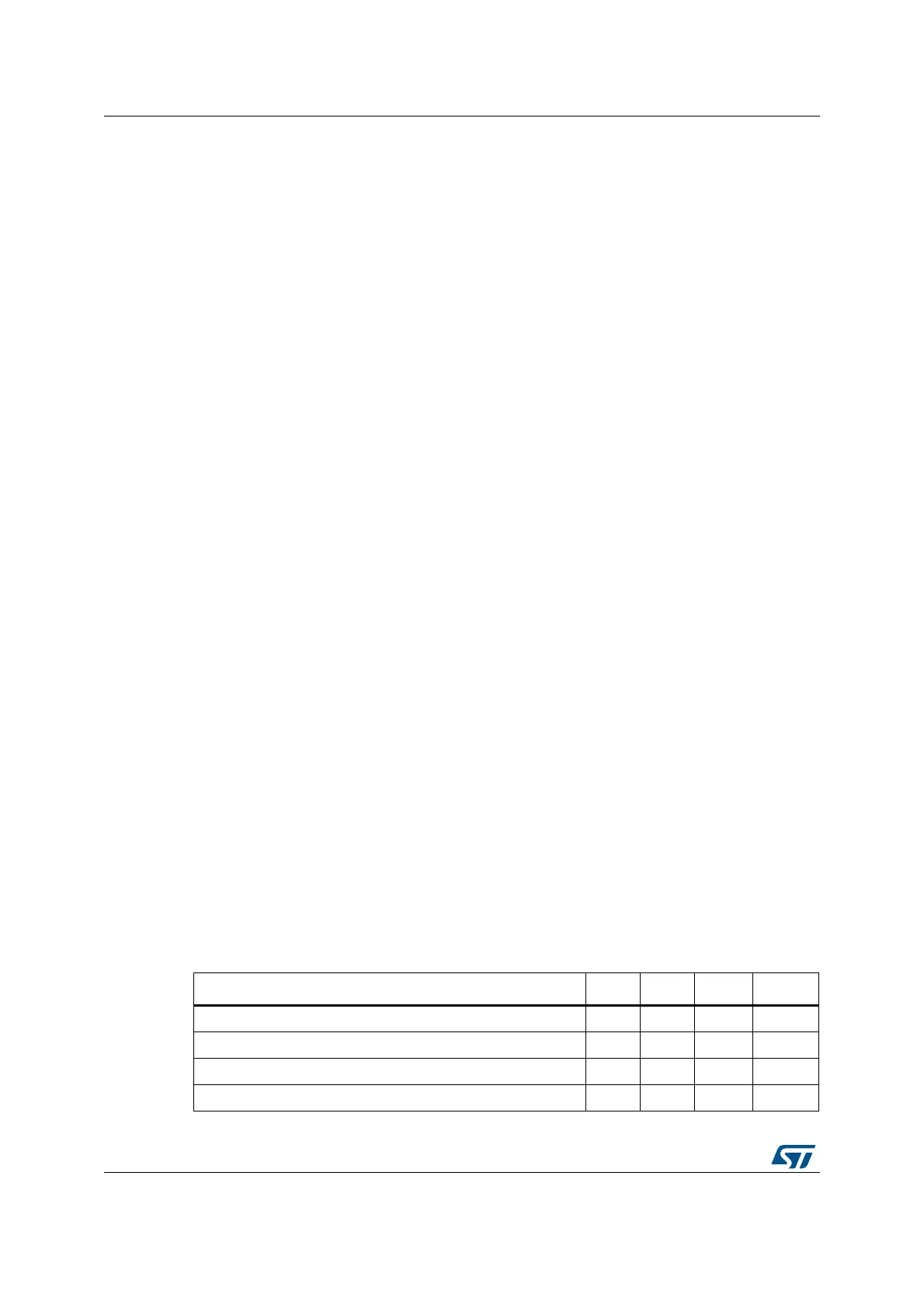
Table 57. Effect of a Floating-point comparison on the condition flags
Comparison result N Z C V
Equal 0 1 1 0
Less than 1 0 0 0
Greater than 0 0 1 0
Unordered 0 0 1 1

 Loading...
Loading...