PM0214 Rev 9 47/262
PM0214 The Cortex-M4 processor
261
2.4.3 Fault status registers and fault address registers
The fault status registers indicate the cause of a fault. For bus faults and memory
management faults, the fault address register indicates the address accessed by the
operation that caused the fault, as shown in Table 20.
2.4.4 Lockup
The processor enters a lockup state if a hard fault occurs when executing the NMI or hard
fault handlers. When the processor is in lockup state it does not execute any instructions.
The processor remains in lockup state until either:
• It is reset
• An NMI occurs
• It is halted by a debugger
If lockup state occurs from the NMI handler a subsequent NMI does not cause the
processor to leave lockup state.
2.5 Power management
The STM32 and Cortex-M4 processor sleep modes reduce power consumption:
• Sleep mode stops the processor clock. All other system and peripheral clocks may still
be running.
• Deep sleep mode stops most of the STM32 system and peripheral clocks. At product
level, this corresponds to either the Stop or the Standby mode. For more details, please
refer to the “Power modes” Section in the STM32 reference manual.
The SLEEPDEEP bit of the SCR selects which sleep mode is used, as described in System
control register (SCR) on page 230. For more information about the behavior of the sleep
modes see the STM32 product reference manual.
This section describes the mechanisms for entering sleep mode, and the conditions for
waking up from sleep mode.
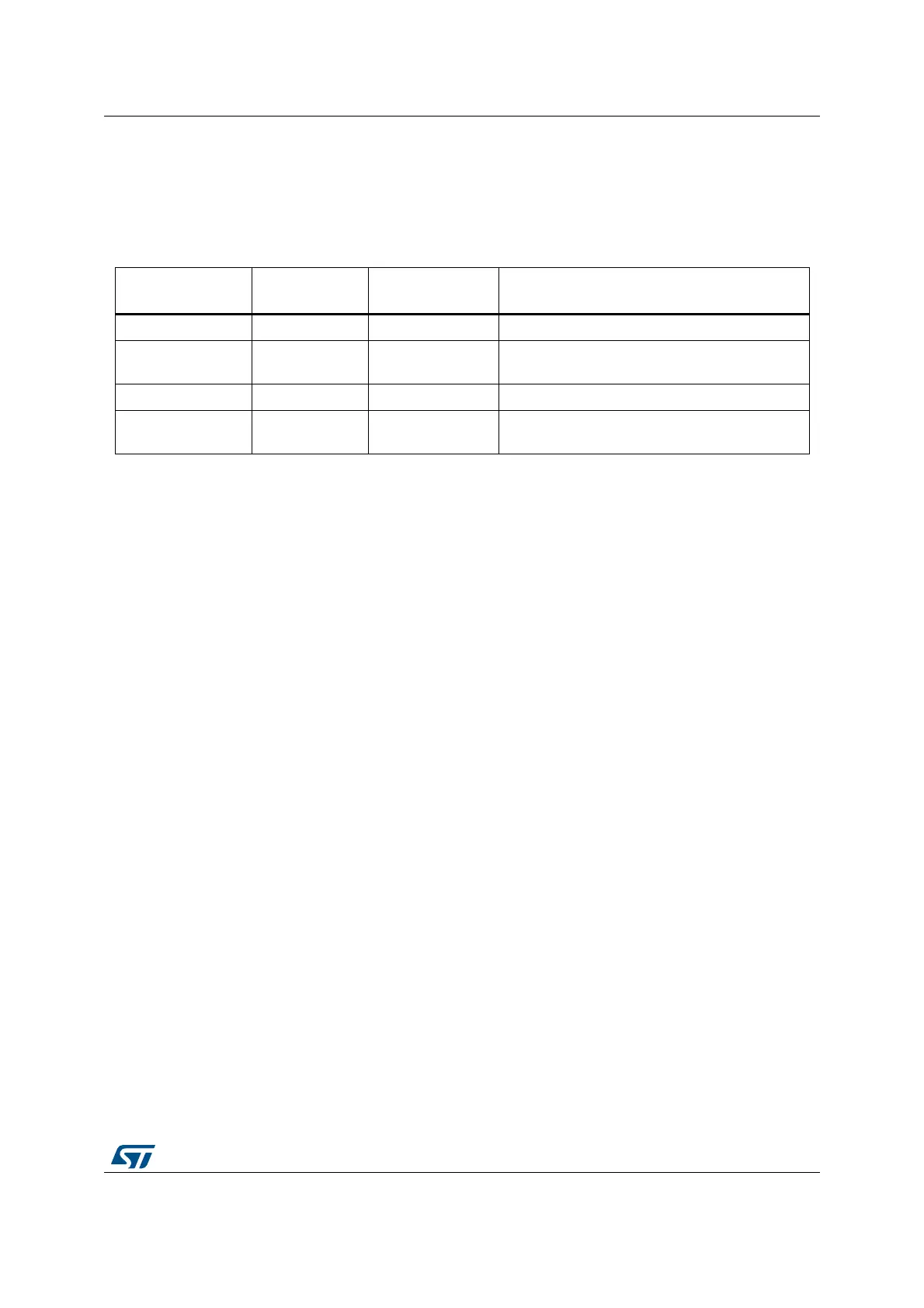
Table 20. Fault status and fault address registers
Handler Status register
name
Address register
name
Register description
Hard fault HFSR - Hard fault status register (HFSR) on page 241
Memory
management fault
MMFSR MMFAR
Memory management fault address register
(MMFAR) on page 242
Bus fault BFSR BFAR Bus fault address register (BFAR) on page 242
Usage fault UFSR -
Configurable fault status register (CFSR;
UFSR+BFSR+MMFSR) on page 237

 Loading...
Loading...