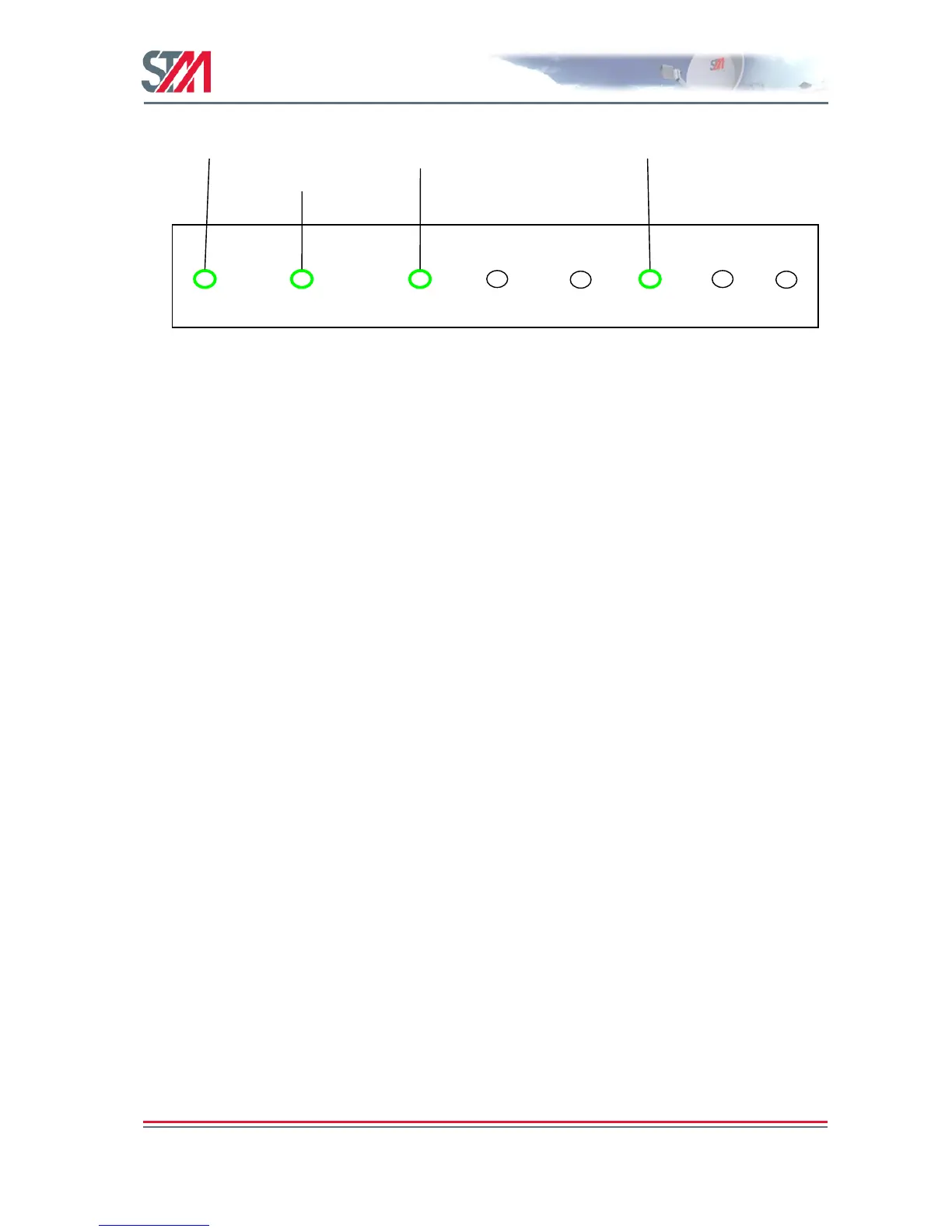
Figure 42: J1 Connector Pin Mapping
19.2 GPS Interface
The SatLink 1910 and SatLink 2900 with a mobile license key set can automatically read their GPS
position from an external GPS via the NMEA-0183 protocol and hence constantly have available the
correct GPS position for use in calculating correct delay to the satellite to enable the logon burst to be sent
with correct timing when the mobile VSAT wants to enter a SatLink network.
The SatLink 2900 can automatically read its GPS position from the GPS input received via the J1
connector (uses pin 2 and common GND on pin 6 in Figure 42) . On the SatLink 1910 the GPS input is
read via the DSUB connector using a special adapter cable.
Two NMEA-0183 GPS strings, GPGLL and GPGGA, are supported by the SatLink mobile VSATs.
The GPGLL GPS string concerns the geographic position. STM supports the following string:
$GPGLL,4916.45,N,12311.12,W,225444,A,*31
This string indicates a latitude of 49 degrees, 16.45 minutes North and a longitude of 123 degrees, 11.12
minutes West, with a fix taken at 22:54:44 UTC. Data status is set to A, or active (can be set to V, or
void). Checksum data is indicated by the 31 at the end of the string.
The GPGGA GPS string concerns the global positioning system fix data. STM supports the following
string:
$GPGGA,123519,4807.038,N,01131.000,E,1,08,0.9,545.4,M,46.9,M,,*47
Parsing out the fields sequentially in the string, we find that this string indicates a fix taken at 12:35:19
UTC, for the latitude 48 degrees, 7.038 seconds North and the longitude 11 degrees, 31 seconds East.
The ―1‖ following the ―E‖ indicates a selection from one of 9 possible options for fix quality, 0-8. These
options are:
0: Invalid
1: GPS Fix (SPS)
2: DGPS Fix
3: PPS Fix
4: Real Time Kinematic
5: Float RTK
6: Estimated (Dead Reckoning)
7: Manual Input Mode
8: Simulation Mode
 Loading...
Loading...