MPC-385 SERIES OPERATION MANUAL – REV. 3.21K (20201120)
Turn ON
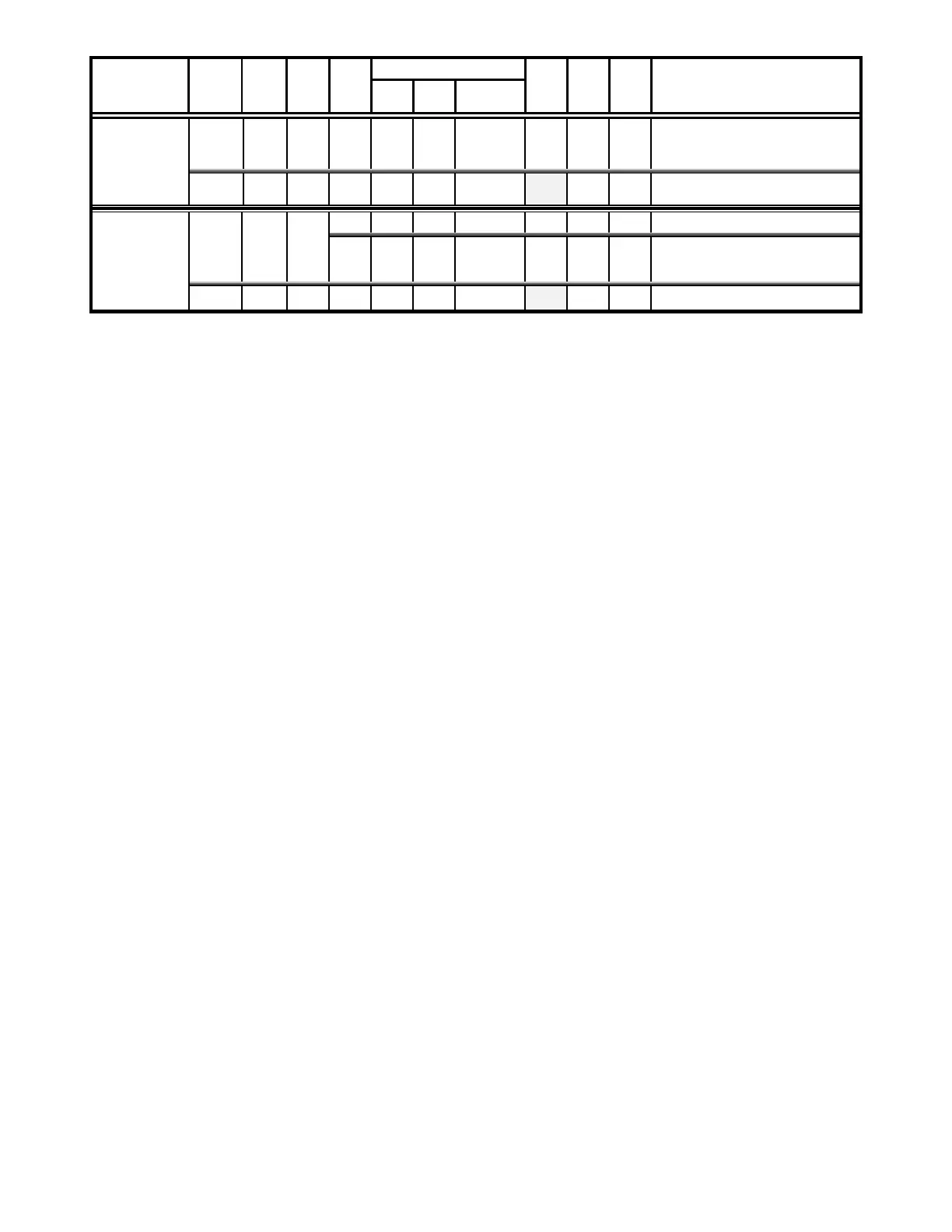
S-Move
command
streaming
data (‘O’)
‘S’ Command’s
am
ing Return Data for Current
Position
note)
-
–
Mode 0 - 9 (coarsest/fastest to
fi
nest/slowest)
Task-completion indicator
NOTES:
1. Task-Complete Indicator: All commands will send back to the
computer the “Task-Complete Indicator” to signal the
command and its associated function in controller is complete.
The indicator consists of one (1) byte containing a value of 13
decimal (0D hexadecimal), and which represents an ASCII CR
(Carriage Return).
2. Intercommand Delay: A short delay (usually around 2 ms) is
recommended between commands (after sending a command
sequence and before sending the next command).
3. Clearing the I/O Send & Receive Buffers: Clearing (purging) the
transmit and receive buffers of the I/O port immediately
before sending any command is recommended. Note that this
clearing of the buffers affects only the computer-side I/O; it
does not (necessarily) clear the buffers on the controller side,
requiring, when necessary, to reset/power-cycle the controller.
Following the rules described will generally avoid problems
with getting garbage data in the I/O buffers of both the
computer and controller (i.e., using exact number of bytes for
both command sequences and return data (as per the
Commands
table), never sending a command before the
previous command is finished with its task, etc.).
4. Positions in Microsteps: All positions sent to and received
from the controller are in microsteps (µsteps). See
Microns/microsteps conversion
table) for conversion between
µsteps and microns (micrometers (µm)).
Declaring position variables in C/C++:
/* current position for X, Y, & Z */
unsigned long cp_x_us, cp_y_us, cp_z_us; /*
microsteps */
double cp_x_um, cp_y_um, cp_z_um; /*
microns */
/* specified (move-to) position for X, Y, & Z */
unsigned long sp_x_us, sp_y_us, sp_z_us; /*
microsteps */
double sp_x_um, sp_y_um, sp_z_um; /*
microns */
Use the same convention for other position variables the
application might need.
Declaring the microsteps/microns conversion factors in C/C++:
/* conversion factors for MP-225/M, MP-285/M, or
MP-265/M based config. */
double us2umCF = 0.0625; /* microsteps to microns
*/
double um2usCF = 16; /* microns to microsteps
*/
/* conversion factors for MP-245[S]/M, MP-
845[S]/M, or MP-865/M based config. */
double us2umCF = 0.046875; /* microsteps to
microns */
double um2usCF = 21.333333333; /* microns to
microsteps */
/* conversion factors for MT-800 config. */
double us2umCF = 0.078125; /* microsteps to
microns */
double um2usCF = 12.8; /* microns to microsteps */
Converting between microsteps and microns in C/C++:
/* converting X axis current position */
cp_x_um = cp_x_us * us2umCF; /* microsteps to
microns */
cp_x_us = cp_x_um * um2usCF; /* microns to
microsteps */
Do the same for Y and Z, and for any other position sets used in the
application.
5. Ranges and Bounds: See Ranges and Bounds table for exact
minimum and maximum values for each axis of each
compatible device that can be connected. All move commands
must include positive values only for positions – negative
positions must never be specified. All positions are absolute as
measured from the physical beginning of travel of a device’s
axis. In application programming, it is important that
positional values be checked (>= 0 and <= max.) to ensure
that a negative absolute position is never sent to the controller
and that end of travel is not exceeded. All computational
relative positioning must always resolve to accurate absolute
positions.
Declaring minimum and maximum absolute position variables in
C/C++:
/* minimum and maximum positions for X, Y, & Z */
double min_x_um, min_y_um, min_z_um; /* minimum
microns */
double max_x_um, max_y_um, max_z_um; /* maximum
microns */
Set minimum and maximum absolute positions for each axis – see
Ranges & Bounds table.
/* initialize all minimum positions in microns*/
min_x_um = 0;
min_y_um = 0;
min_z_um = 0;
/* initialize all maximum positions in microns*/
/* MP-225/M, MP-285/M, MP-845[S]/M, MP-245[S]/M,
etc. */
max_x_um = 25000;
max_y_um = 25000;
max_z_um = 25000;
/* MP-865/M */
max_x_um = 50000;
max_y_um = 12500;
max_z_um = 25000;
/* MP-265/M */
max_x_um = 25000;
max_y_um = 12500;
max_z_um = 25000;
6. Absolute Positioning System Origin: The Origin is set to a
physical position of travel to define absolute position 0. The
 Loading...
Loading...