31
User’s manual
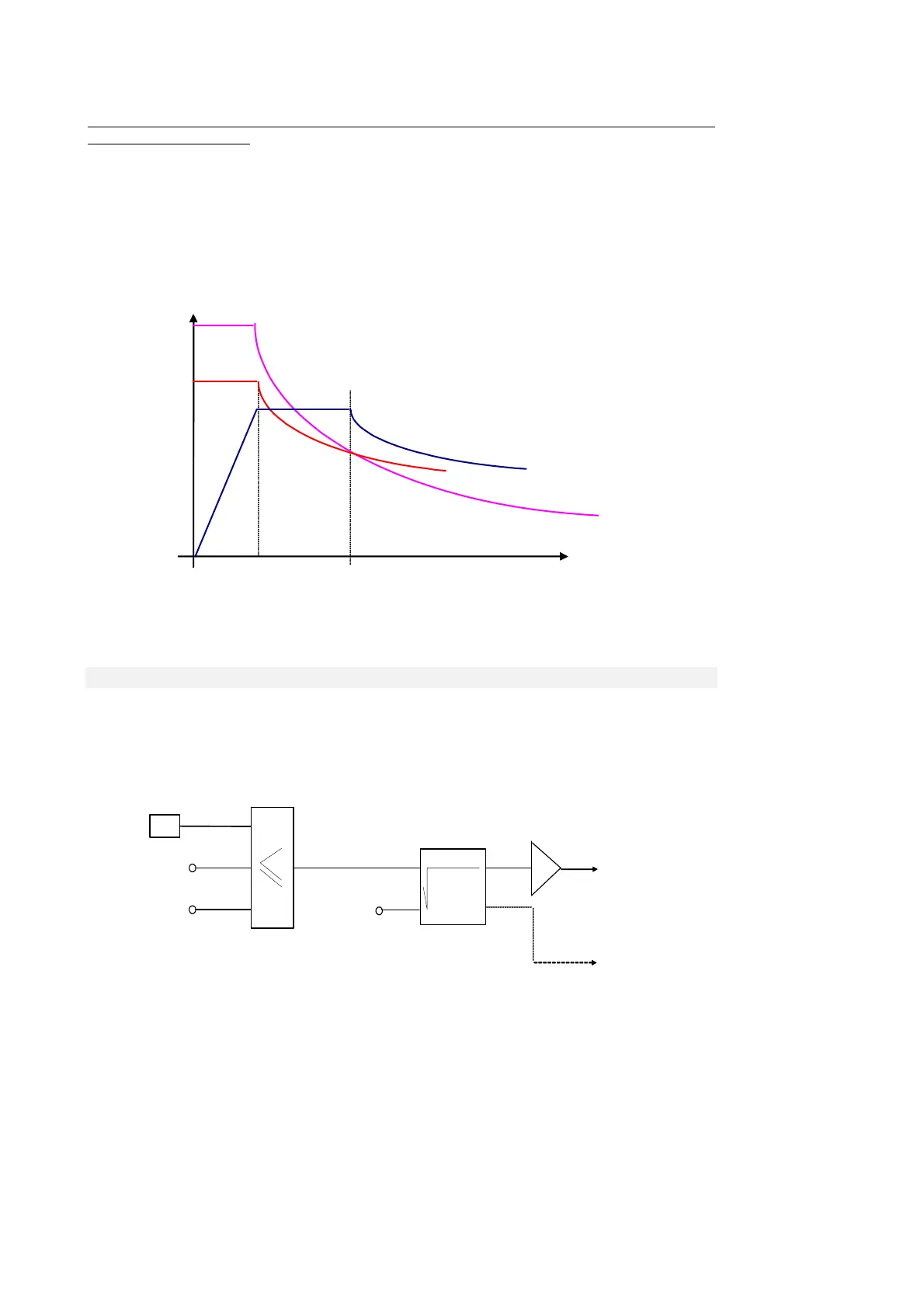
It is proved that the maximum motor torque decreases during flux weakening in proportion to the
square of the φ/φnom ratio. Thus the motor has three working areas:
Constant torque: the maximum torque is available up to the rated speed (as long as the
current to deliver it is available);
Constant power: over the rated speed, flux is reduced proportionally to speed, the
available torque also drops in proportion to speed, the power delivered is constant;
Maximum torque: after reaching the maximum torque, which decreases with the square
of the speed, the available torque will start to drop with the square of the speed and the
power delivered will decrease in proportion to the speed.
Speed
Nominal speed
0
Available torque
Max. torque
Power
delivered
MAXIMUM TORQUE
ZONE
CONSTANT
POWER
ZONE
CONSTANT
TORQUE
ZONE
To ensure regulation stability, P41 must be set with the Maximum torque divided by Rated motor
torque. This limit will decrease during flux weakening with the square of the speed.
2.2.3.3 MAXIMUM CURRENT LIMIT
The drive is fitted with a maximum current limiting circuit that cuts in if exceeded, restricting the
maximum current delivered to the lowest value from among parameter P40, the value calculated by
the drive thermal image circuit, and the motor thermal protection circuit.
P40 is used to programme the maximum current limit delivered by the drive from 0% to the maximum
authorised value, which depends on the type of overload chosen with connection C56.
P40
I
LIMITE
I
Q MAX
I
LIM
- I
FLUSSO
Drive thermal
image
Motor thermal
protection
I
FLUSSO
Maximum torque set
by current limit
Possibile limit on
flux current
If the current limit exceeds the flux current, then only the torque current will be limited and thus the
maximum torque delivered is limited. Otherwise, the delivered torque is set to zero and the flux
current is also limited
 Loading...
Loading...