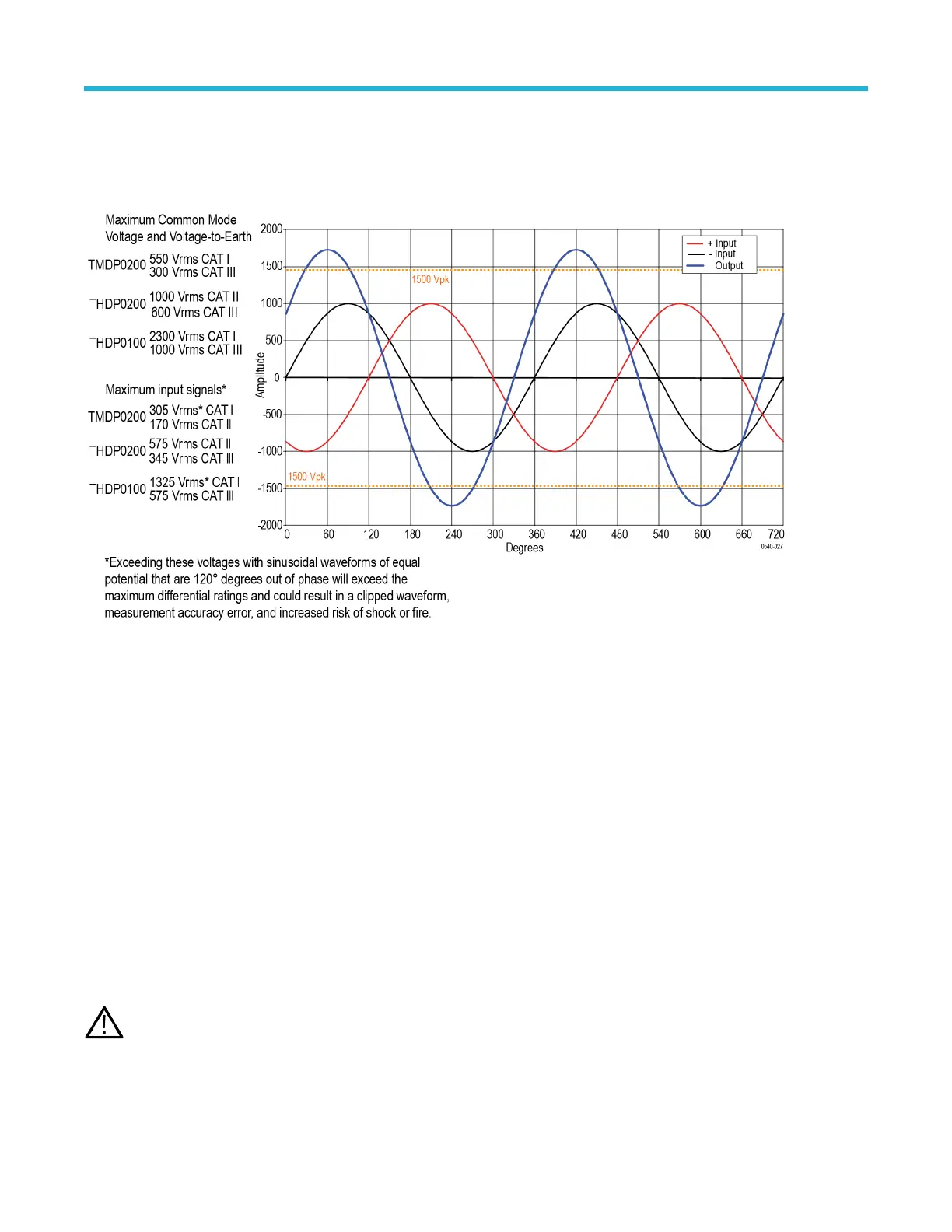
Example 2
Next, assume that the same waveforms from the previous example are 120° out of phase with each other
. This phase relationship yields a
maximum differential of 1.732 times the individual signal inputs, or 1732 V
pk
. Although this is a lower potential between the inputs than in
example 1, it exceeds the differential voltage ratings of the THDP0200 and TMDP0200 probes, so you must use the THDP0100 probe.
Figure 7: Measuring two equal-amplitude waveforms that are 120 degrees out of phase
Example 3
Y
our task is to measure two AC waveforms of the same phase, each with an amplitude of 300 V. However, one waveform is centered
on ground (– input), and the other is centered on an offset of 400 VDC (+ input). The common mode voltage is the 300 V
rms
, but the
maximum voltage-to-earth (the common mode voltage plus the signal waveform) must also be taken into account for both inputs. The
voltage-to-earth is 300 V
rms
on the (– input), but on the (+ input), the voltage-to-earth is 700 V
rms
(the 300 VAC
rms
plus the 400 VDC
rms
).
Thus the (+ input) exceeds the maximum input voltage-to-earth rating of the THDP0200 probe, so it cannot be used for taking this
measurement. In this case, you must use either the TMDP0200 or THDP0100 probe.
Overrange detection
Differential voltage outside the operating range will overdrive the circuitry of the probe and distort the output signal. When this differential
overrange occurs, the probe detects the condition and lights the overrange indicator. With the Audible Overrange ON, the probe will also
emit an audible alarm.
WARNING: The Overrange indicator does not detect an overrange condition of common-mode voltages or voltage-to-earth
potential at the probe inputs. The Overrange indicator only detects dif
ferentially between the + and – inputs (not relative to
ground). Do not exceed the Common-Mode Voltage or Input Voltage-to-Earth ratings of the probe when taking measurements.
If you are not sure, first take a single-ended measurement of each point that you are intending to measure differentially. Take a
single-ended measurement by tying one input lead to ground (the – input) and then connecting the other lead (the + input) to the
points of interest, one at a time.
Operating basics
High Voltage Differential Probes THDP0100/0200 and TMDP0200 User Manual 37

 Loading...
Loading...











