ACT6000 User Guide – January 2021 Page 49 of 52
At the complete loading, when appeared “You Can Now Restart”, it is necessary to restart
the instrument by Power-Off and Power-On.
In any case, it is suggested to follow all the instructions enclosed on the .zip updating packet downloadable
from https://tescomusa.com/pages/act6000-applications.
ATTENTION ! After every software update it is suggested to set the instrument to the
original (default) configuration: from the Main Menu select and enter into “7 - Config &
Utility” menu, then select push F1 “Default” and “Enter”.
The instrument is ready to work!
Pressing from the Main Menu it is possible to verify the installed software release.
8. CABLE SETUP
By this menu it is possible to select from
the wide Cables data-base the cable type to
be test:
usual Name (dielectric type), typical
Capacitance/km, Wires Diameter (with
typical resistance/km), and typical PVF.
Selecting the preponderant cable by
arrows and pushing “Enter” the reference
cable will be automatically pre-configured
for various measurements or functions as
TDR, Capacitance length, Resistance,
Fault location etc.
To create a new cable type, use the F5 “New” key typing and saving the related
parameters into the proper fields of the new record named “Custom Cable Type”.
If necessary to update the “Cable data-base” with the new externally re-edited, i.e. by the
specific ACT6000 PC Utility (compatible only with Windows XP and downloadable from
https://tescomusa.com/pages/act6000-applications), it is before necessary to erase the
actual data-base pushing F1 “Clr Mem”, then pushing the F4 “Import” key selecting 1 from
PC or 2 from Pen-drive.
If desired to export the currently cabledat.csv file it is enough to push the key and
select 1 from PC or 2 from Pen-drive.
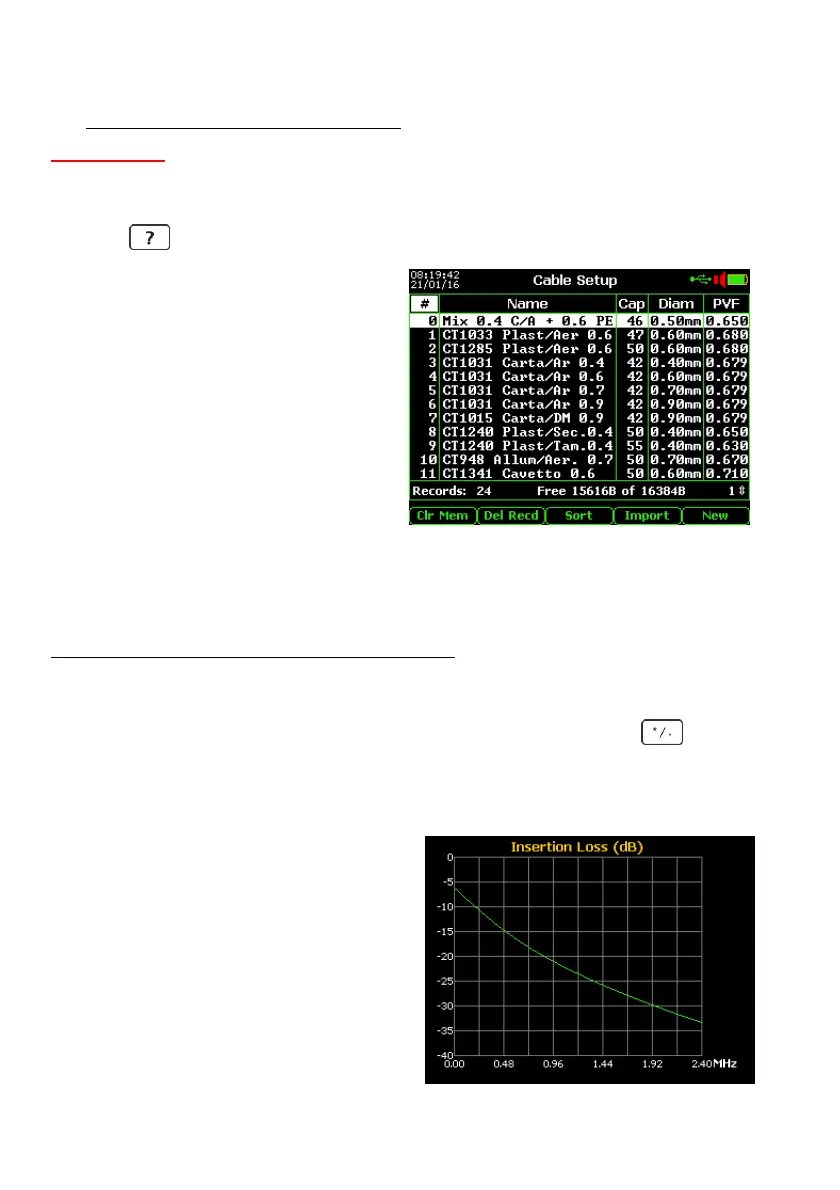
If desire to verify the typical Insertion-Loss (frequency response) of a line of 1 km with
specific dielectric, specific wires diameter and specific capacitance/km, proceed as follows:
- Highlight the cable type by the arrows:
- push 1 for the response up to 0.9 MHz;
- push 2 for the response up to 2.4 MHz;
- push 3 for the response up to 6 MHz;
- push 4 for the response up to 12 MHz;
- push 5 for the response up to 18 MHz;
- push 6 for the response up to 30 MHz.
 Loading...
Loading...