274 Appendix A: Functions and Instructions
ô
(radian)
MATH/Angle menu
expression1
ô ⇒
expression
list1
ô ⇒
list
matrix1
ô ⇒
matrix
In Degree angle mode, multiplies
expression1
by
180/p. In Radian angle mode, returns
expression1
unchanged.
This function gives you a way to use a radian
angle while in Degree mode. (In Degree angle
mode,
sin(), cos(), tan(), and polar-to-
rectangular conversions expect the angle
argument to be in degrees.)
Hint: Use ô if you want to force radians in a
function or program definition regardless of the
mode that prevails when the function or program
is used.
In Degree or Radian angle mode:
cos((p/4)ô ) ¸
‡2
2
cos({0ô,(p/12)ô,ë pô }) ¸
{1
(
3
+1)ø
2
4
ë 1}
¡
(degree)
2“ key
expression
¡ ⇒
value
list1
¡ ⇒
list
matrix1
¡ ⇒
matrix
In Radian angle mode, multiplies
expression
by
p/180. In Degree angle mode, returns
expression
unchanged.
This function gives you a way to use a degree
angle while in Radian mode. (In Radian angle
mode,
sin(), cos(), tan(), and polar-to-
rectangular conversions expect the angle
argument to be in radians.)
In Radian angle mode:
cos(45¡) ¸
‡2
2
cos({0,p/4,90¡,30.12¡}) ¥ ¸
{1 .707
... 0 .864...}
o (angle) 2’ key
[
radius,
oq_
angle
] ⇒
vector
(polar input)
[
radius,
oq_
angle,Z_coordinate
] ⇒
vector
(cylindrical input)
[
radius,
oq_
angle,
o
f_angle
] ⇒
vector
(spherical input)
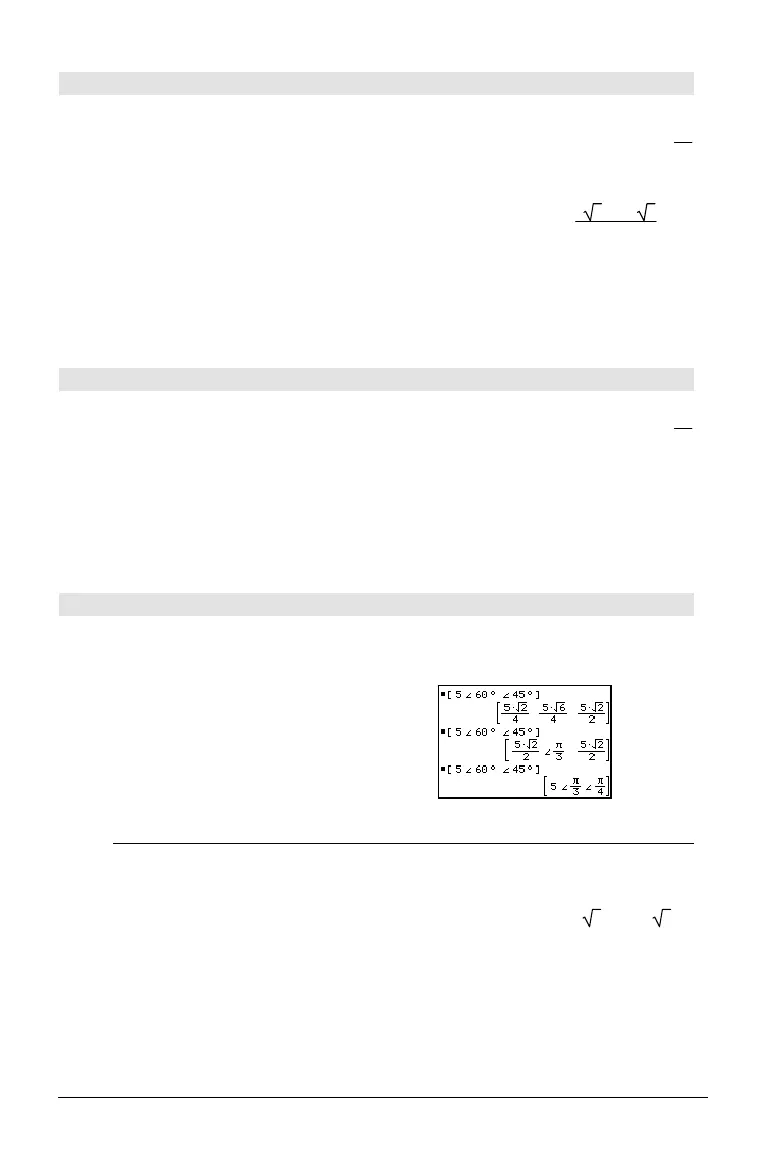
Returns coordinates as a vector depending on the
Vector Format mode setting: rectangular,
cylindrical, or spherical.
[5,o60¡,o45¡] ¸
In Radian mode and vector format set to:
(
magnitude
o
angle
) ⇒
complexValue
(polar input)
Enters a complex value in (roq) polar form. The
angle
is interpreted according to the current Angle
mode setting.
In Radian angle mode and Rectangular
complex format mode:
5+3
i
ì (10op/4) ¸
5ì 5ø
2+(3ì 5ø 2)ø
i
¥¸ ë 2.071…ì 4.071…ø
i
rectangular
cylindrical
spherical
 Loading...
Loading...











