72 Previews
3. Using the sample data below, enter the
population in column 1.
Pop. (in 1000s) Bldgs > 12 stories
150 4
500 31
800 42
250 9
500 20
750 55
950 73
Press 150 ¸ 500 ¸ 800 ¸ 250
¸ 500 ¸ 750 ¸ 950 ¸
4. Move the cursor to row 1 in column 2 (r1c2).
Then enter the corresponding number of
buildings.
8 C moves the cursor to the top of the
page. After typing data for a cell, you can
press ¸ or D to enter the data and
move the cursor down one cell. Pressing C
enters the data and moves the cursor up
one cell.
@B 8 C 4 ¸ 31 ¸ 42 ¸ 9
¸ 20 ¸ 55 ¸ 73 ¸
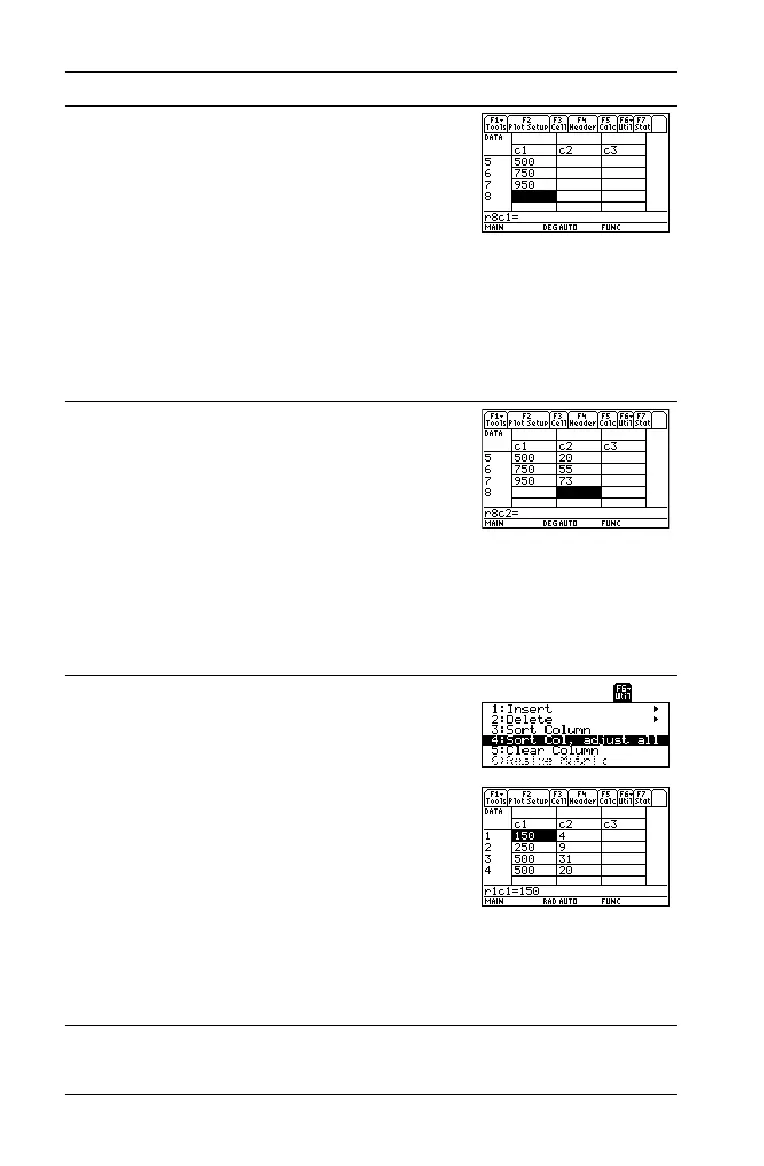
5. Move the cursor to row 1 in column 1 (r1c1).
Sort the data in ascending order of
population.
This sorts column 1 and then adjusts all
other columns so that they retain the same
order as column 1. This is critical for
maintaining the relationships between
columns of data.
To sort column 1, the cursor can be
anywhere in column 1. This example has
you press
@8C
so that you can see the first four rows.
@A 8 C 2 ˆ 4
Steps and keystrokes Display

 Loading...
Loading...











