Feedback Controlyzer DigiLock 110
Page 60
Status: 5.12.17
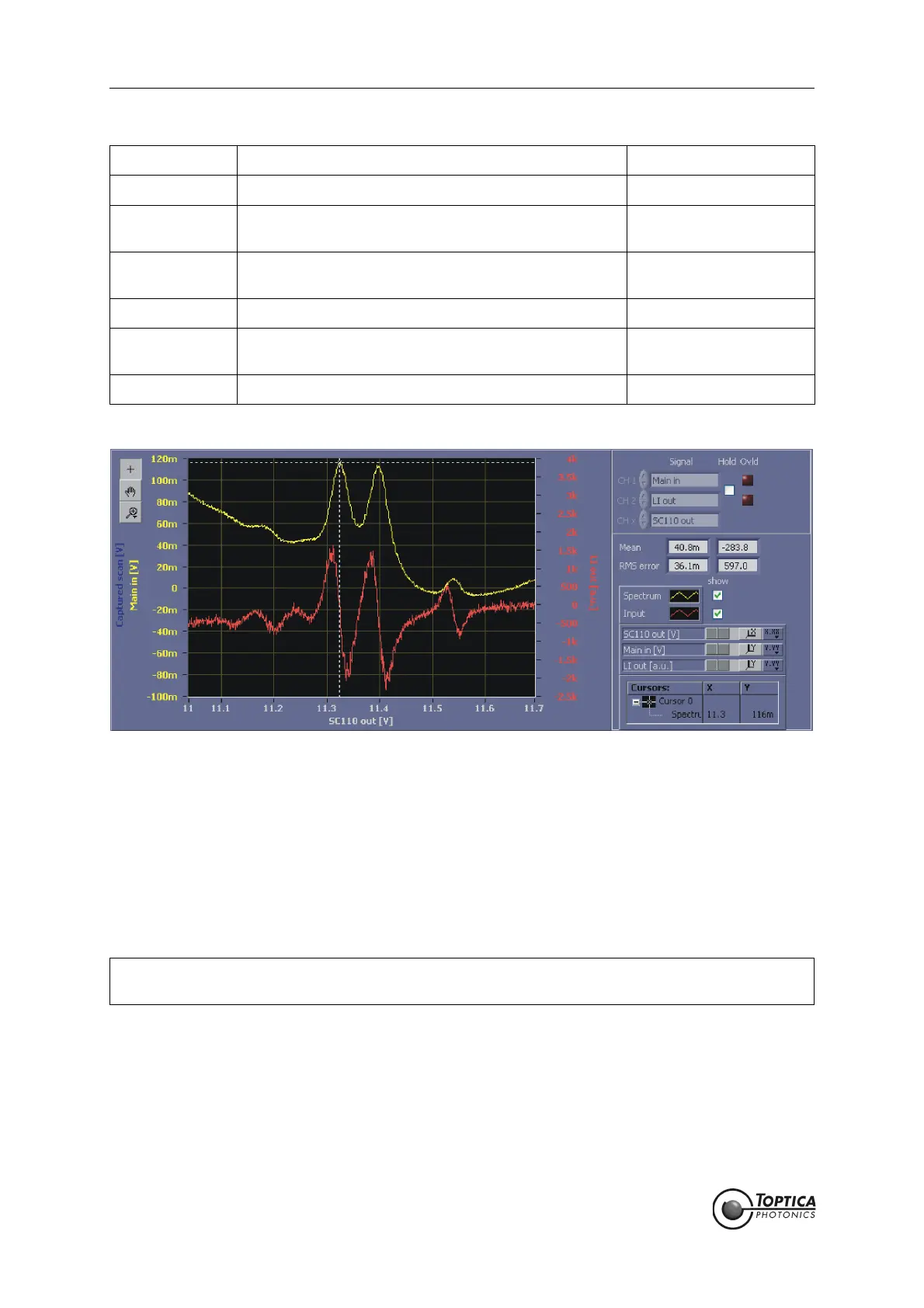
Figure 49 AutoLock display of the Doppler-free Rb-spectrum (upper yellow trace) with the correspond-
ing Lock-in signal (lower red trace)
Note that the sign/phase of the error signal is chosen to be the derivative of the absorption
signal, i.e. it is positive (negative) on positive (negative) slopes, respectively.
24. The phase between the modulation and the reference signal must be adjusted to obtain a large
error signal with steep slopes and zero crossings at the maxima of the spectral signal. The sign of
the error signal can be inverted by changing the phase by 180°. The sign should be adjusted such,
that the lock-in signal is the derivative of the input signal, i.e. positive error signal on positive signal
slope and vice versa.
Please see section 9.2 on how to manually adjust the phase.
25. Once the phase is adjusted, turn off the modulation of the Lock-In module. Check the parameters
of the PID controllers. Now you can position the crosshairs to either a peak or a valley and it will
automatically track the lock point. To find the correct settings of the sign for each PID controller,
please see section 9.4
14
. Here, we assume the following AutoLock settings:
Cursor: Track on, Snap to setpoint on,
Smart Assistance: Engage on, Setpoint off.
When the error signal offset is compensated, the PID set point can be set to zero.
Name Description Value to set to
Input Signal input to be demodulated <Main In>
Set freq Modulation set frequency is the user selected
modulation frequency
100 [kHz]
Act freq Modulation act frequency is automatically set to the
nearest possible discrete frequency
(automatically set)
Mod amplitude Amplitude of the modulation 0.01 [V
pp
]
Phase shift Phase shift of the local oscillator with respect to the
applied modulation
0 [°]((to be optimized,
see text)
Mod Output Output to which the modulation is added <Main out>
NOTE ! As of software versions 1.5.4.70 the DigiLock 110 frequency modulation modules feature
an automatic phase adjust (see section 8.2.1.7 and 8.2.1.8 for details).
 Loading...
Loading...