4.11 Primary, secondary and per unit
scaling
VAMP 24h support phone +358 (0)20 753 3264
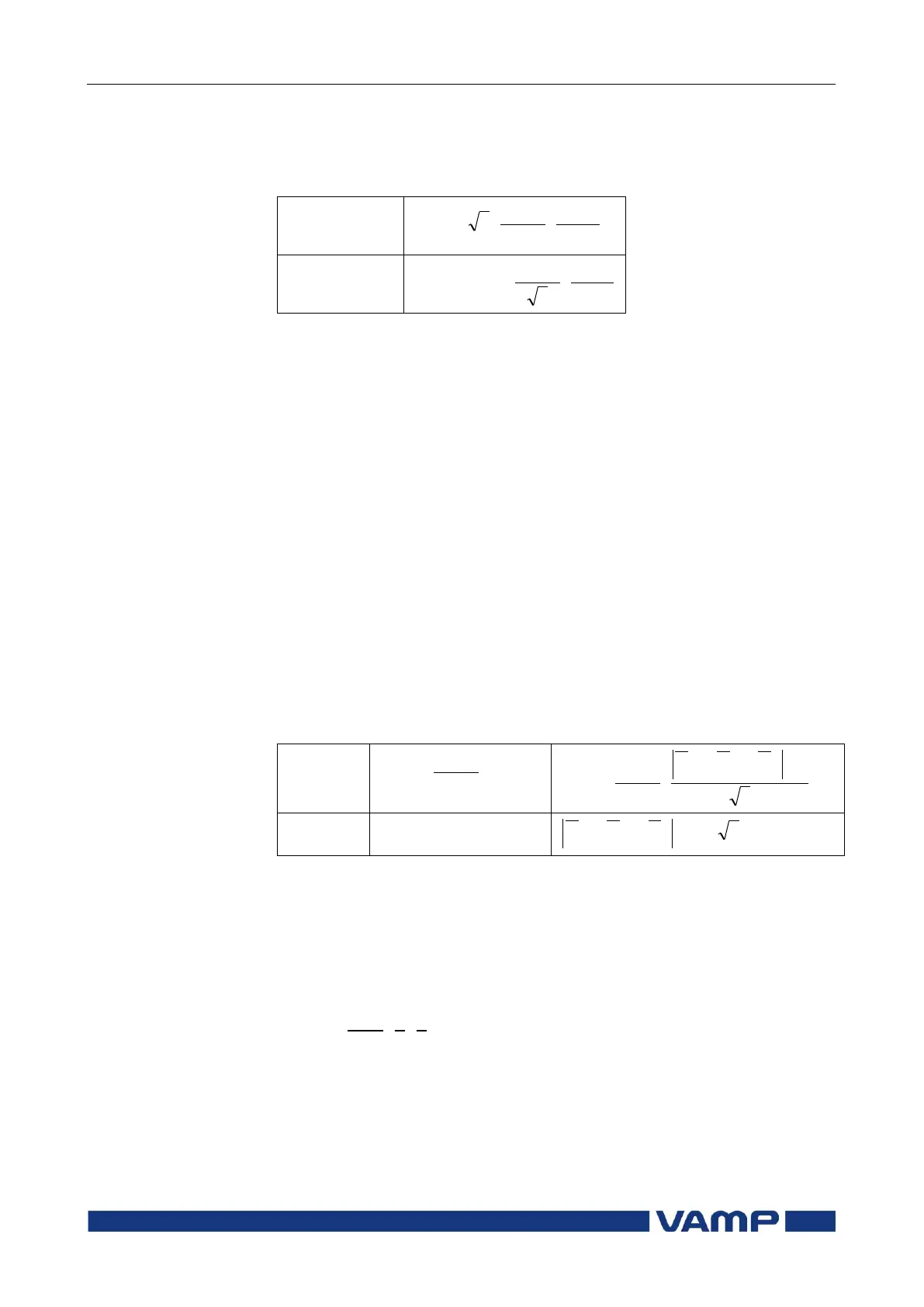
Per unit [pu] scaling of line-to-line voltages
One per unit = 1 pu = 1xU
N
= 100 %, where U
N
= rated voltage
of the VT.
N
PRI
SEC
SEC
PU
U
VT
VT
U
U 3
Example 1: Secondary to per unit.
VT = 12000/110
Three symmetric phase-to-neutral voltages connected to the
device's inputs U
a
,U
b
and U
c
are 63.5 V
Per unit voltage is
U
PU
= 3x63.5/110x12000/11000 = 1.00 pu = 1.00xU
N
= 100 %
Example 2: Per unit to secondary.
VT = 12000/110
U
N
= 11000 V
The device displays 1.00 pu = 100 %.
Three symmetric phase-to-neutral voltages connected to the
device 's inputs U
a
,U
b
and U
c
are.
U
SEC
= 1.00x110/3x11000/12000 = 58.2 V
Per unit [pu] scaling of zero sequence voltage
SECPU
SEC
cba
VTUUUU 3
Example 1: Secondary to per unit.
VT = 12000/110
Voltage connected to the device's input U
a
is 38.1 V, while
U
a
= U
b
= 0.
Per unit voltage is
U
PU
= (38.1+0+0)/(3x110) = 0.20 pu = 20 %
Example 2: Per unit to secondary.
VT = 12000/110
The device displays U
0
= 20 %.
If U
b
= U
c
= 0, then secondary voltages at U
a
is
U
SEC
= 3x0.2x110 = 38.1 V
 Loading...
Loading...