2.4 Distance protection Z<
VAMP 24h support phone +358 (0)20 753 3264
2.4. Distance protection Z<
2.4.1. Short circuit distance protection Z< (21)
The distance protection function calculates the impedance Z =
U/I of the short circuit fault loops.
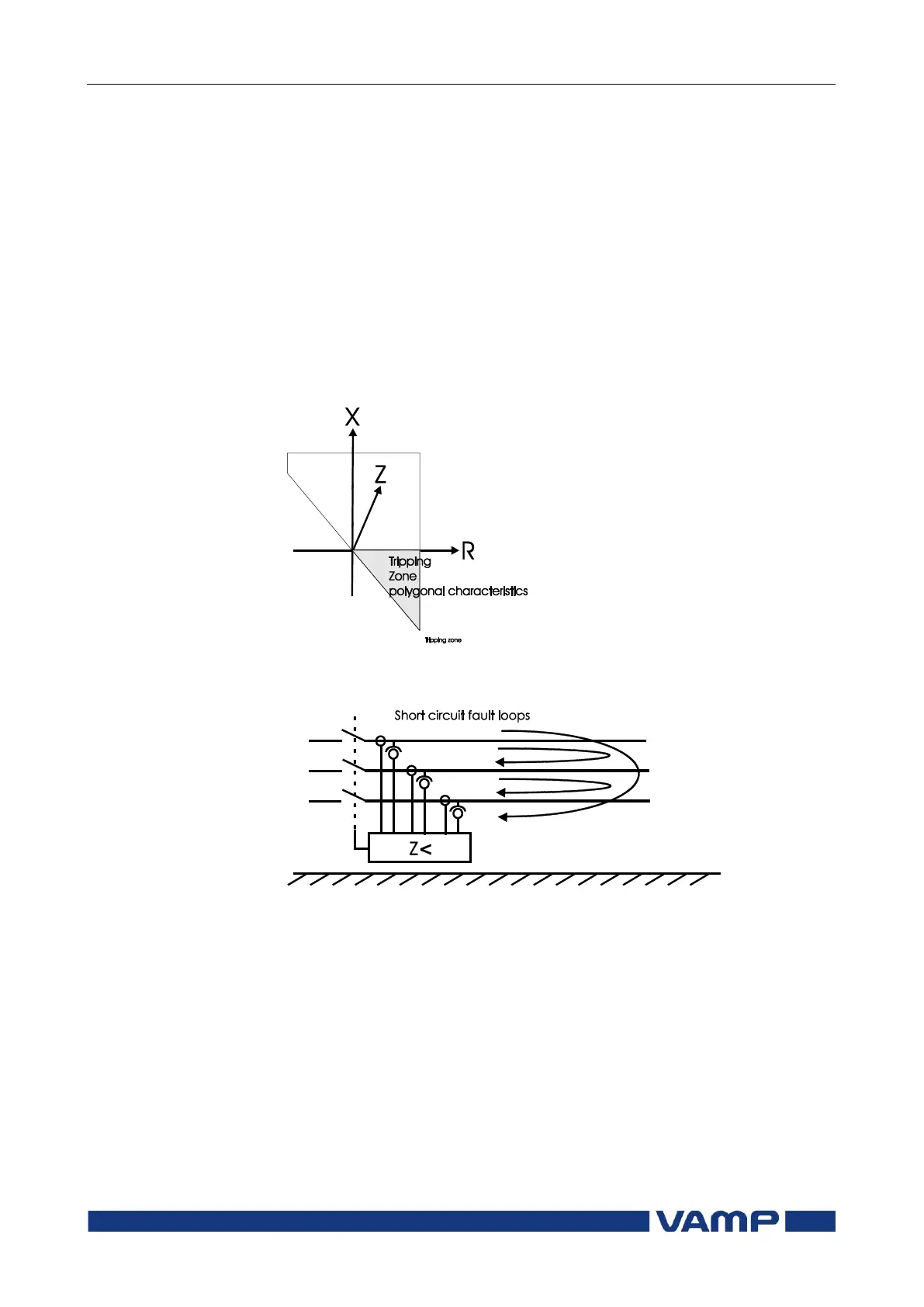
If impedance is inside the tripping zone (normally presented in
R-X plane), the distance function operates. In short circuit
faults there are 3 possible fault loops. The VAMP distance
protection function calculates the impedances of the fault loops
continuously and thus separate pick-up conditions are not
needed.
Figure 2.4.1-1 An example of tripping zone. Gray area is the tripping zone,
polygonal characteristics.
Figure 2.4.1-2 Short circuit fault loops and formulas to calculate the fault
impedances.
Zones and characteristics
There are 5 zones (Z1, Z2, Z3, Z4 and Z5) for short circuit
protection. These are implemented as protection stages Z1<,
Z2<, Z3<, Z4< and Z5<. Z1 extension can be implemented by
applying second setting group to cover the extension zone in
auto-reclosing.
The distance protection‘s zones implement a polygonal
characteristics as shown in Figure 2.4.1-3.

 Loading...
Loading...