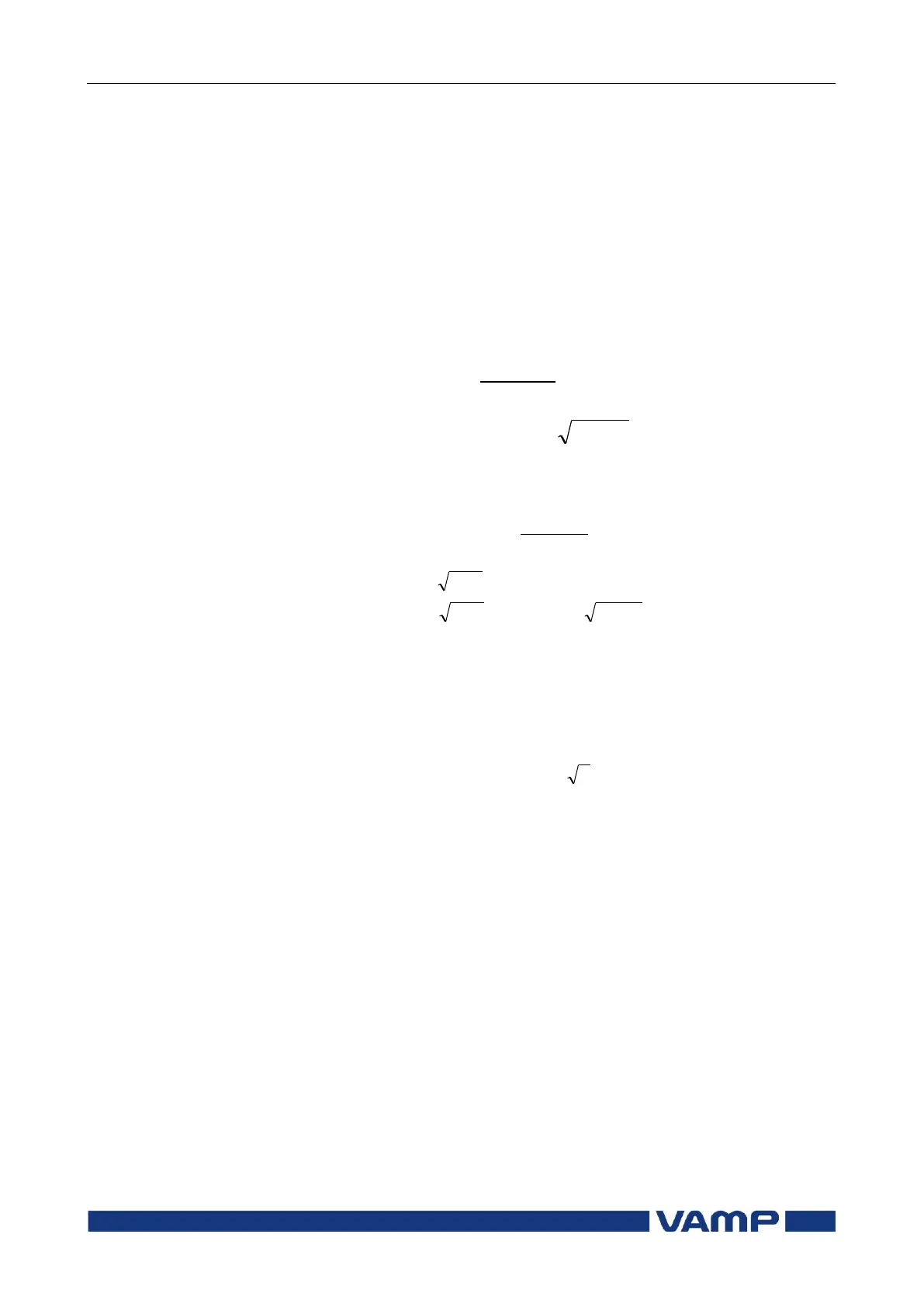2.13 Thermal overload protection T>
(49)
VAMP 24h support phone +358 (0)20 753 3264
2.13. Thermal overload protection T> (49)
The thermal overload function protects the cables in the feeder
mode against excessive heating due to overloading conditions.
Thermal model
The temperature is calculated using rms values of phase
currents and a thermal model according IEC 60255-8. The rms
values are calculated using harmonic components up to the
15
th
.
Trip time:
Alarm:
(Alarm 60% = 0.6)
Trip:
Release time:
Trip release:
Start release:
(Alarm 60% = 0.6)
Thermal time constant tau (Setting value)
Natural logarithm function
Measured rms phase current (the max. value of
three phase currents)
(If temperature rise
is 120%
). This parameter is the memory of
the algorithm and corresponds to the actual
temperature rise.
Overload factor (Maximum continuous current), i.e.
service factor. (Setting value)
Ambient temperature factor (Permitted current due
to tamb) Figure 2.13-1.
The rated current (I
n
or I
mot
)
Cooling time coefficient (cooling time constant =
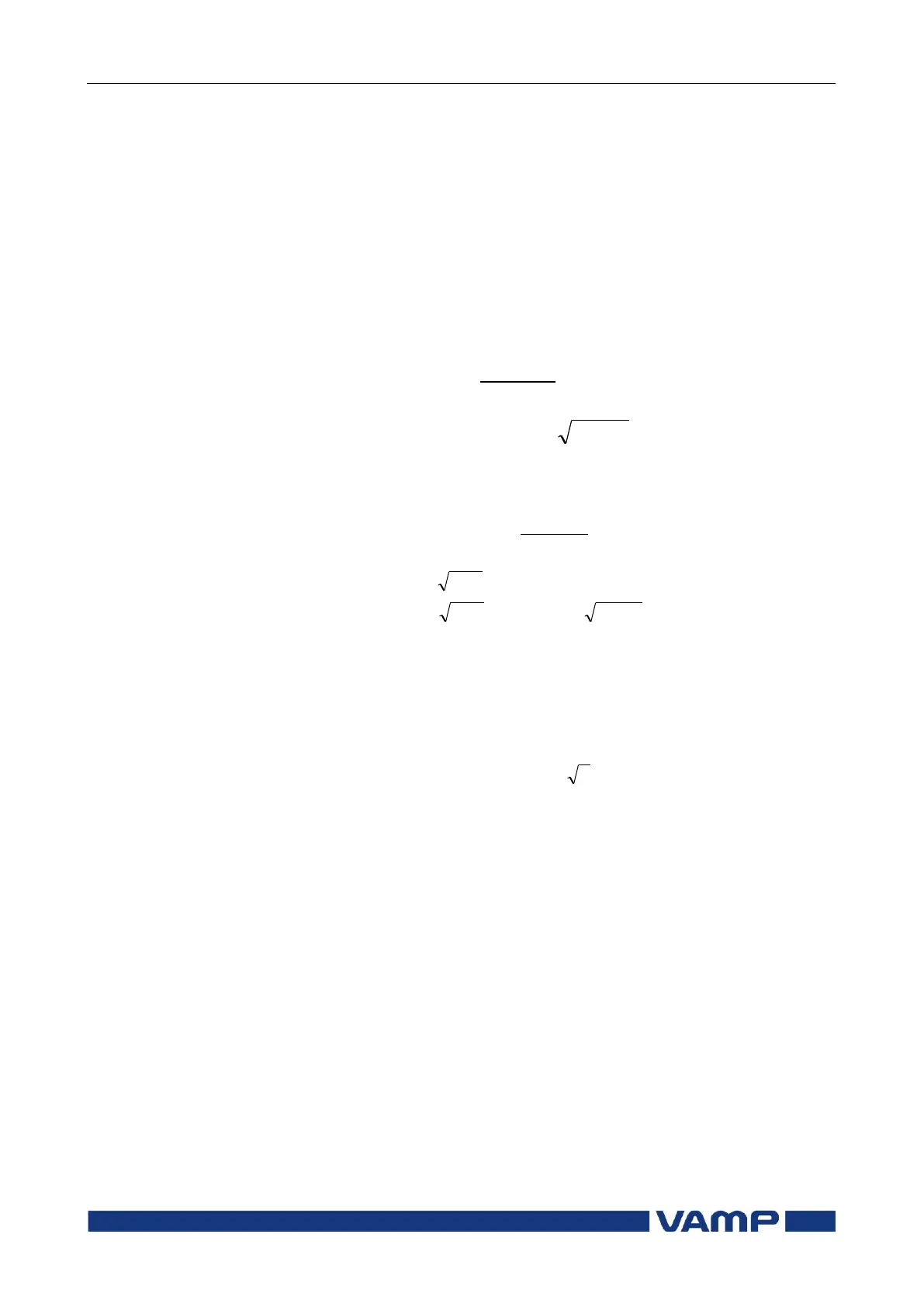 Loading...
Loading...