214 Eluent Considerations
Adapted from Godfrey, Norman B., Solvent Selection via Miscibility Number, CHEMTECH, 359-363 (1972).
B.3.2 Using Miscibility Numbers (M-Numbers)
Miscibility numbers (M-numbers) are used to predict the miscibility of a liquid with one
of the standard eluents (see Table B-1).
A liquid is classified in the M-number system by testing for miscibility with a sequence of
standard eluents. A correction term of 15 units is then either added or subtracted from the
cutoff point for miscibility.
To predict the miscibility of two liquids, subtract the smaller M-number value from the
larger.
• If the difference between the two M-numbers equals 15 or less, the two liquids are
miscible in all proportions at 15 °C.
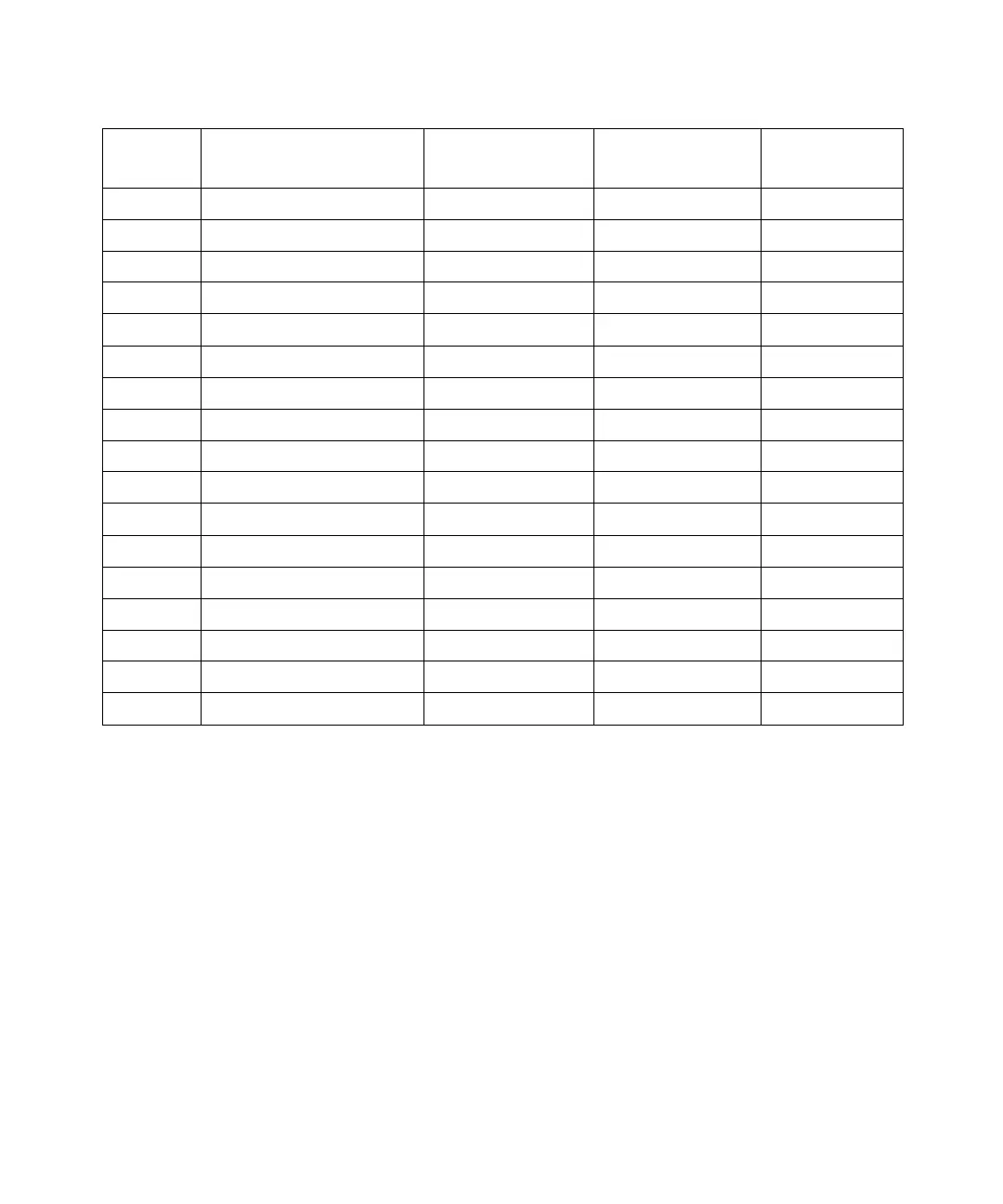
4.5 Cyclohexanone 2.24 155.7 17
4.5 Nitrobenzene 2.03 210.8 14, 20
4.6 Benzonitrile 1.22 191.1 15, 19
4.8 p-Dioxane 1.54 101.3 17
5.2 Ethanol 1.20 78.3 14
5.3 Pyridine 0.94 115.3 16
5.3 Nitroethane 0.68 114.0 13, 20
5.4 Acetone 0.32 56.3 15, 17
5.5 Benzyl alcohol 5.80 205.5 13
5.7 Methoxyethanol 1.72 124.6 13
6.2 Acetonitrile 0.37 81.6 11, 17
6.2 Acetic acid 1.26 117.9 14
6.4 Dimethylformamide 0.90 153.0 12
6.5 Dimethyl sulfoxide 2.24 189.0 9
6.6 Methanol 0.60 64.7 12
7.3 Formamide 3.76 210.5 3
9.0 Water 1.00 100.0 --
Table B-1 Physical Properties of Eluents (Continued)
Polarity
Index
Eluent
Viscosity [η] CP,
20 °C
Boiling Point °C
(1 atm)
Miscibility
Number (M)
 Loading...
Loading...