REGISTER
ALTERED
BIT
access
protection
violation,
and memory
parity
error may
Complete
recoverability
after
a trap may require
that
no
main memory
location,
no fast memory register, and no
part
(or flags)
of
the
PSWs
be
changed
when the trap
occurs.
If
any
of
these registers
or
flags
are
changed,
the Register
Altered
bit
(60)
of
the
old
PSWs
is
set
to 1 and is saved
by
the
trap XPSD.
or
may
not
leave
registers, memory,
and
PSWs
unchanged,
depending
on when
they
occur
during instruction
ex-
ecution.
Generally,
these traps
are
recoverable.
This
is
done
by
checking
for
protection
violations
and
non-
existent
memory
at
the
beginning
of
execution
in case
of
a multiple
operand
access
instruction, restoring the
original
register
contents
if
execution
cannot
be
com-
pleted
because
of
a
trap,
and
not
loading
the
first word
of
the
PSWs
unti I a possible trap condition
due
to
access
of
Changes to
CC1-CC4
cause
the Register Altered
bit
to be
set
only
if
the instruction requires these condition
code
bits
as subsequent inputs.
the second word
could
have
been
detected.
Table 5
con-
tains a list
of
instructions
and
indicates
for these instructions
what
registers, memory locations, and bits
of
the
PSWs,
if
any,
have
been
changed
when a trap
due
to an
operand
ac-
cess memory
cycle
occurs.
Traps caused by conditions
detected
during operand
fetch
and
store memory
cycles,
such as
nonexistent
memory,
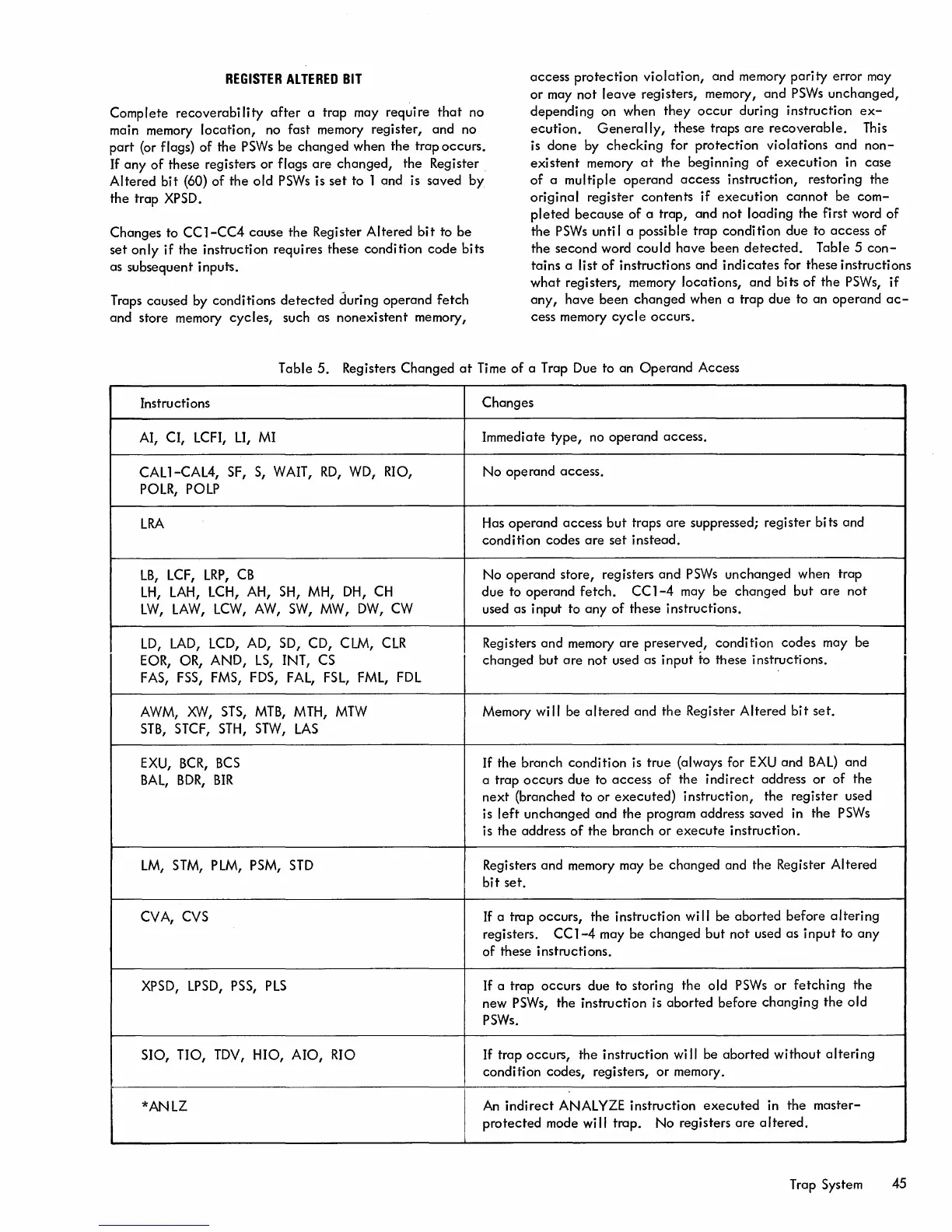
Table
5.
Registers Changed
at
Time
of
a Trap Due to an
Operand
Access
Instructions
Changes
AI, CI, LCFI,
LI,
MI
Immediate
type,
no operand access.
CALl-CAL4,
SF,
S,
WAIT,
RD,
WD,
RIO,
No
operand
access.
POLR, POLP
LRA
Has
operand
access
but
traps
are
suppressed;
register
bits and
condition
codes
are
set
instead.
LB,
LCF,
LRP,
CB
No operand store, registers
and
PSWs
unchanged when trap
LH,
LAH,
LCH, AH, SH, MH,
DH,
CH
due
to operand
fetch.
CC
1-4
may be
changed
but
are
not
LW,
LAW,
LCW,
AW,
SW,
MW,
DW,
CW
used as input to
any
of
these instructions.
LD,
LAD,
LCD,
AD, SD, CD, CLM,
CLR
Registers
and
memory
are
preserved,
condition
codes may
be
EaR,
OR,
AND,
LS,
INT, CS
changed
but
are
not used as
input
to these instructions.
FAS, FSS, FMS, FDS,
FAL,
FSL,
FML,
FDL
AWM,
XW,
STS,
MTB,
MTH,
MTW
Memory wi
II
be
altered
and
the
Register
Altered
bit
set.
STB,
STCF,
STH,
STW,
LAS
EXU,
BCR,
BCS
If
the branch condition is true (always for
EXU
and
BAL)
and
BAL,
BDR,
BIR
a trap occurs
due
to
access
of
the
indirect
address
or
of
the
next
(branched to or
executed)
instruction,
the
register
used
is
left
unchanged and the program address saved in the
PSWs
is
the
address
of
the branch or
execute
instruction.
LM,
STM, PLM, PSM,
STD
Registers and memory may be
changed
and the Register
Altered
bit
set.
CVA,
CVS
If a trap occurs, the instruction
wi
II
be
aborted
before
altering
registers.
CC
1-4
may be
changed
but
not
used as
input
to
any
of
these instructions.
XPSD,
LPSD,
PSS,
PLS
If
a trap occurs due to storing the old
PSWs
or
fetching
the
new
PSWs,
the instruction is
aborted
before
changing
the
old
PSWs.
SIO,
no,
TDY,
HIO,
Ala,
RIO
If
trap occurs, the instruction
wi"
be
aborted
without
altering
condition
codes, registers,
or
memory.
*ANLZ
I
An
indirect
ANALYZE instruction
executed
in
the
master-
protected
mode wi
II
trap.
No registers
are
altered.
Trap System 45

 Loading...
Loading...











