2.10 Conditions
56 YASKAWA SIEPC71061753C GA500 Technical Manual
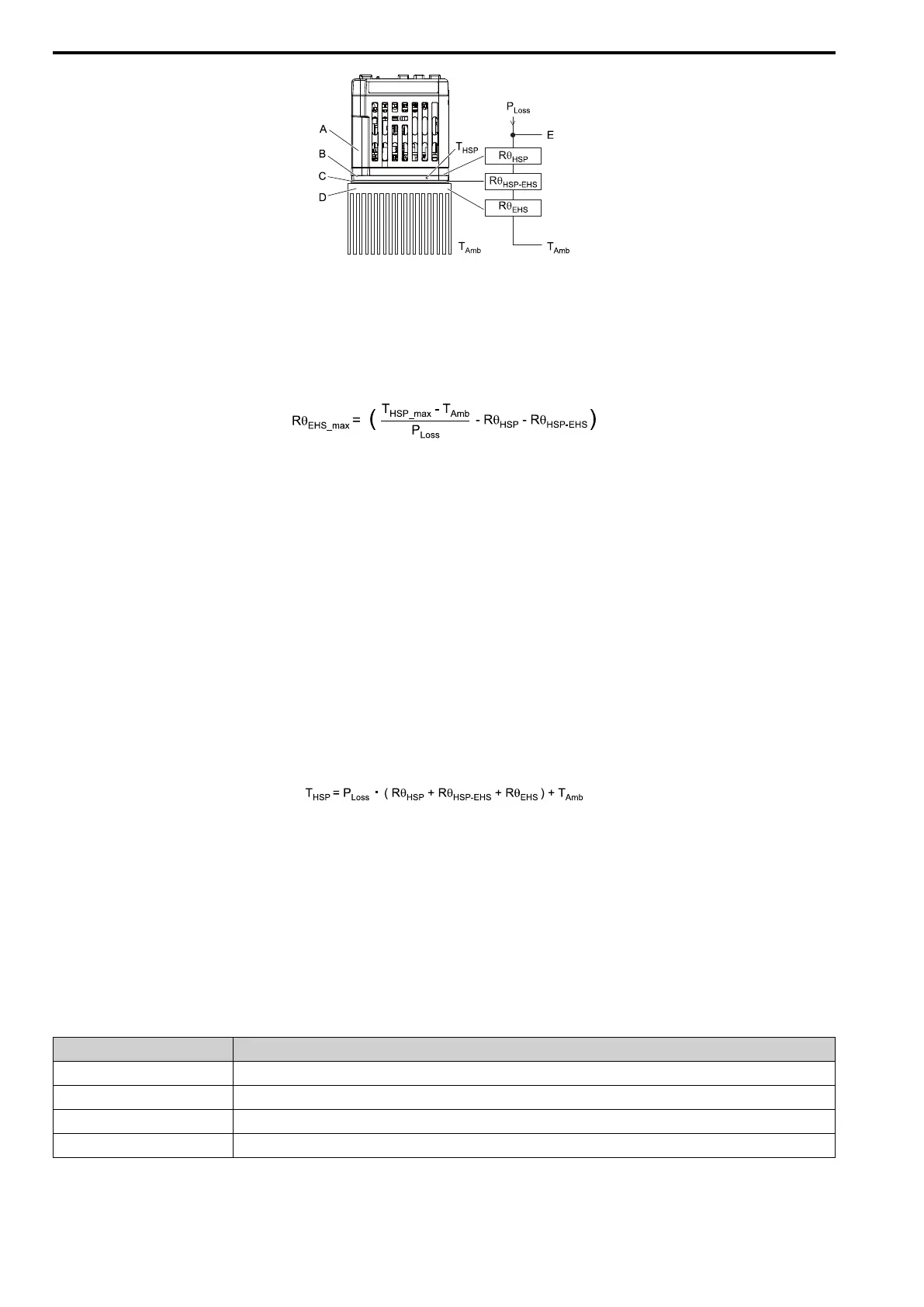
A - Drive
B - Heatsink Plate
C - Thermal Compound
D - External Heatsink
E - Heatsink Plate Temperature
Figure 2.19 Thermal Equivalent Circuit Diagram
Select External Heatsink by Thermal Resistance
Use this formula to calculate the maximum thermal resistance Rθ
EHS_max
of the external heatsink.
Select an external heatsink with a smaller thermal resistance than Rθ
EHS_max
.
Make sure that the dimensions of the external heatsink are close to the drive dimensions (H × W). If the thermal
resistance of the external heatsink is large, but the dimensions of the external heatsink are near the external
dimensions of the drive, select one of these external heatsinks:
• External heatsink with more fins
• External heatsink with longer fin shape
Consider the installation environment of the drive and correct the thermal resistance Rθ
EHS
of the external
heatsink. Dust and unwanted material can decrease the cooling capacity of the external heatsink.
Note:
Apply correction factors to the thermal resistance values listed in the specification of the external heatsink in these cases. For details,
contact the external heatsink manufacturer.
• The heatsink height and width dimensions are much larger than the drive heatsink plate dimensions.
• You are installing multiple drives on one heatsink.
Examine Feasibility of the Selected External Heatsink
If installation conditions, for example installation space, limit your external heatsink selection, use this formula to
calculate the heatsink plate temperature and examine the external heatsink:
If T
HSP
value is lower than the maximum temperature of the heatsink, you can use the selected external heatsink.
Refer to Monitor Heatsink Plate Temperature on page 49 to monitor drive heatsink plate temperature.
■ External Heatsink Selection
These examples show an applicable heatsink selection for drive model 2006 when C6-01 = 1 [Normal / Heavy
Duty Selection = Normal Duty Rating].
These are examples of calculations for the external heatsink from MIZUTANI ELECTRIC IND.CO., LTD.
• Universal Type Heat Sink EF Series, EF (98) L:150 (thermal resistance Rθ
EHS
= 1.6 K/W)
• Universal Type Heat Sink EK Series, EK (95) L:150 (thermal resistance Rθ
EHS
= 1.1 K/W)
Table 2.35 External Heatsink Selection
Symbol Value
P
Loss
25.0 W
T
HSP_max
90 °C (194 °F)
T
Amb
40 °C (104 °F)
Rθ
HSP
0.05 K/W

 Loading...
Loading...