12.9 L: Protection Functions
698 YASKAWA SIEPC71061753C GA500 Technical Manual
If deceleration in coordination with more than one drive is necessary, for example textile machinery line systems,
set L2-29 = 2, 3 [System KEB Ride-Thru 1, System KEB Ride-Thru 2].
Table 12.66 KEB Ride-Thru Function Operation Method
L2-29
Kinetic Energy
Backup Method
Operation Configuration Precautions
0 Single Drive KEB
Ride-Thru 1
The drive uses regenerative energy from the motor to keep the DC bus
voltage at the level set in L2-11 [KEB DC Bus Voltage Setpoint] while
it adjusts the rate of deceleration.
The KEB operation continues while the drive adjusts the deceleration
rate with the setting of C1-09 [Fast Stop Time].
• Set C1-09 correctly to prevent Uv1 [DC Bus Undervoltage] and ov
[Overvoltage].
• If the drive detects Uv1 during the KEB operation, decrease the
value set in C1-09.
• If the drive detects ov during the KEB operation, increase the value
set in C1-09.
1 Single Drive KEB
Ride-Thru 2
The drive uses information about the inertia of the connected
machinery to find the deceleration rate necessary to keep the DC bus
voltage at the level set in parameter L2-11.
The drive uses system inertia to calculate the deceleration time. You
cannot adjust this value.
• If the drive detects Uv1 during the KEB operation, increase the
setting value of L3-20 [DC Bus Voltage Adjustment Gain] and L3-
21 [OVSuppression Accel/Decel P Gain].
• If the drive detects ov during the KEB operation, decrease the
setting values of L3-20 and L3-21.
2 System KEB Ride-
Thru 1
The drive does not monitor the DC bus voltage. The drive decelerates
at the KEB deceleration time set in L2-06.
Use L2-06 to set the time necessary to decelerate from the current
frequency reference to 0 Hz. More than one drive can decelerate and
keep a constant speed ratio between drives.
Use the dynamic braking option with System KEB Ride-Thru 1.
3 System KEB Ride-
Thru 2
The drive uses the KEB deceleration time set in L2-06 to decelerate
and it also monitors the DC bus voltage.
If the voltage level increases, the drive momentarily holds the
frequency to prevent an ov before it continues to decelerate.
If you cannot use the dynamic braking option, use System KEB Ride-
Thru 2.
■ KEB Ride Thru Start
When L2-01 = 3, 4, 5 [Power Loss Ride Through Select = Kinetic Energy Backup: L2-02, Kinetic Energy
Backup: CPU Power, Kinetic Energy Backup: DecelStop], the drive starts the KEB operation immediately after it
detects a momentary power loss. When one of these conditions occur, the drive will activate KEB Ride-Thru:
• KEB Ride-Thru 1 set for the MFDI terminal becomes enabled (terminal is deactivated when H1-xx = 65 or
terminal is activated when H1-xx = 66).
The drive uses the mode selected L2-29 [Kinetic Energy Backup Method] to start KEB operation.
• KEB Ride-Thru 2 set for the MFDI terminal becomes enabled (terminal is deactivated when H1-xx = 7A or
terminal is activated when H1-xx = 7B).
The drive automatically starts Single KEB Ride-Thru 2 and it ignores the setting of L2-29.
• The DC bus voltage is less than the level set in L2-05 [Undervoltage Detection Lvl (Uv1)].
The KEB operation will start as specified in L2-29.
Note:
If you try to set KEB Ride-Thru 1 and 2 to the MFDI terminals at the same time, it will trigger oPE03 [Multi-Function Input Setting
Err].
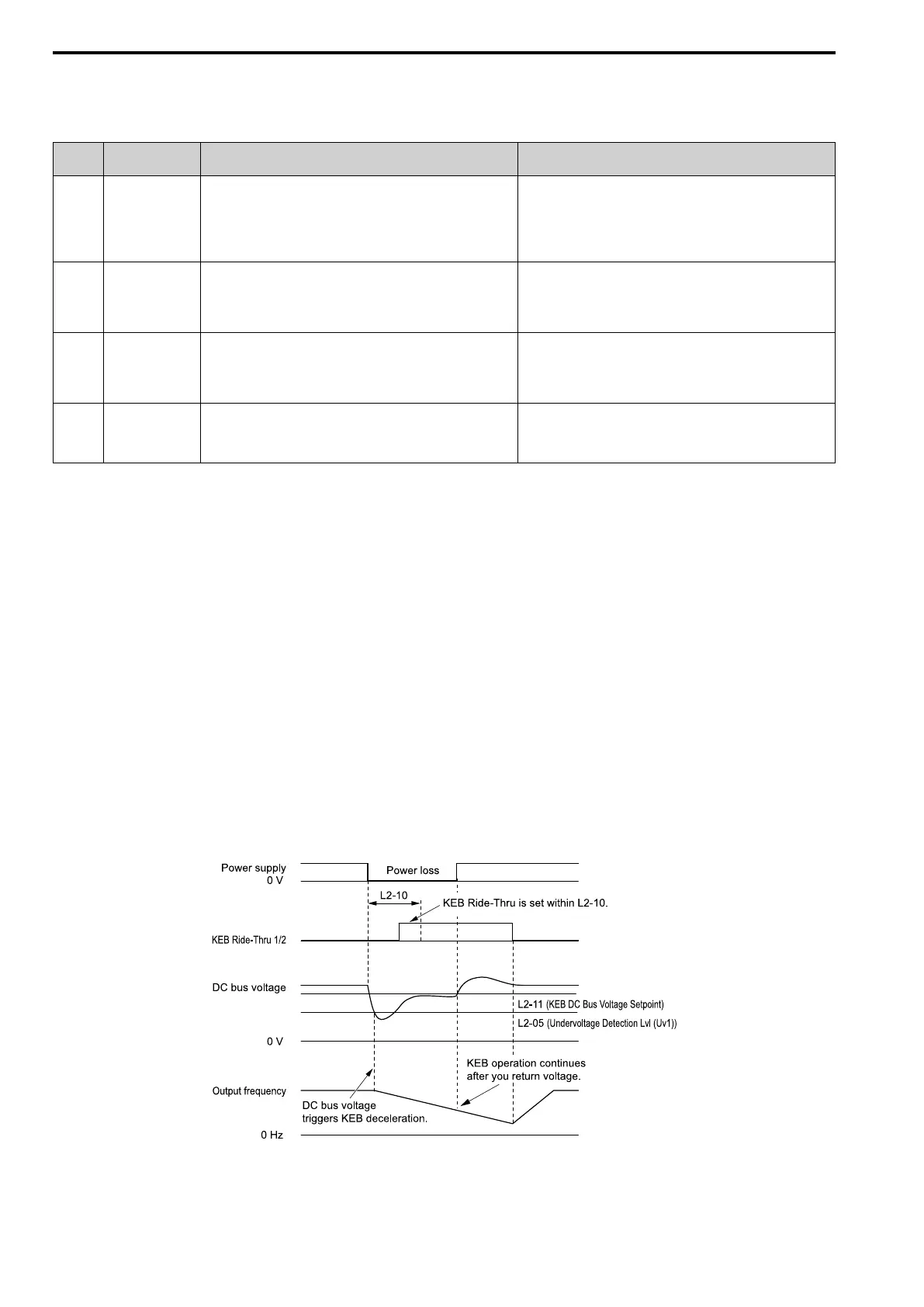
n this example, the drive detects that the DC bus voltage is less than the level set in L2-05 and starts the KEB
operation. When you return power during KEB operation, the drive will continue KEB operation when the KEB
Ride-Thru is input, although the time set in L2-10 [Minimum KEB Time] expired. The motor accelerates again
after you cancel the KEB Ride-Thru.
Figure 12.112 KEB Operation through KEB Ride-Thru Input

 Loading...
Loading...