3-7
IM 04P01B01-17E
3
Using the RS-422A/485 Communication Interface (/C3 Option)
3.3 The Bit Structure of One Character and the
Operation of the Receive Buffer
The Bit Structure of One Character
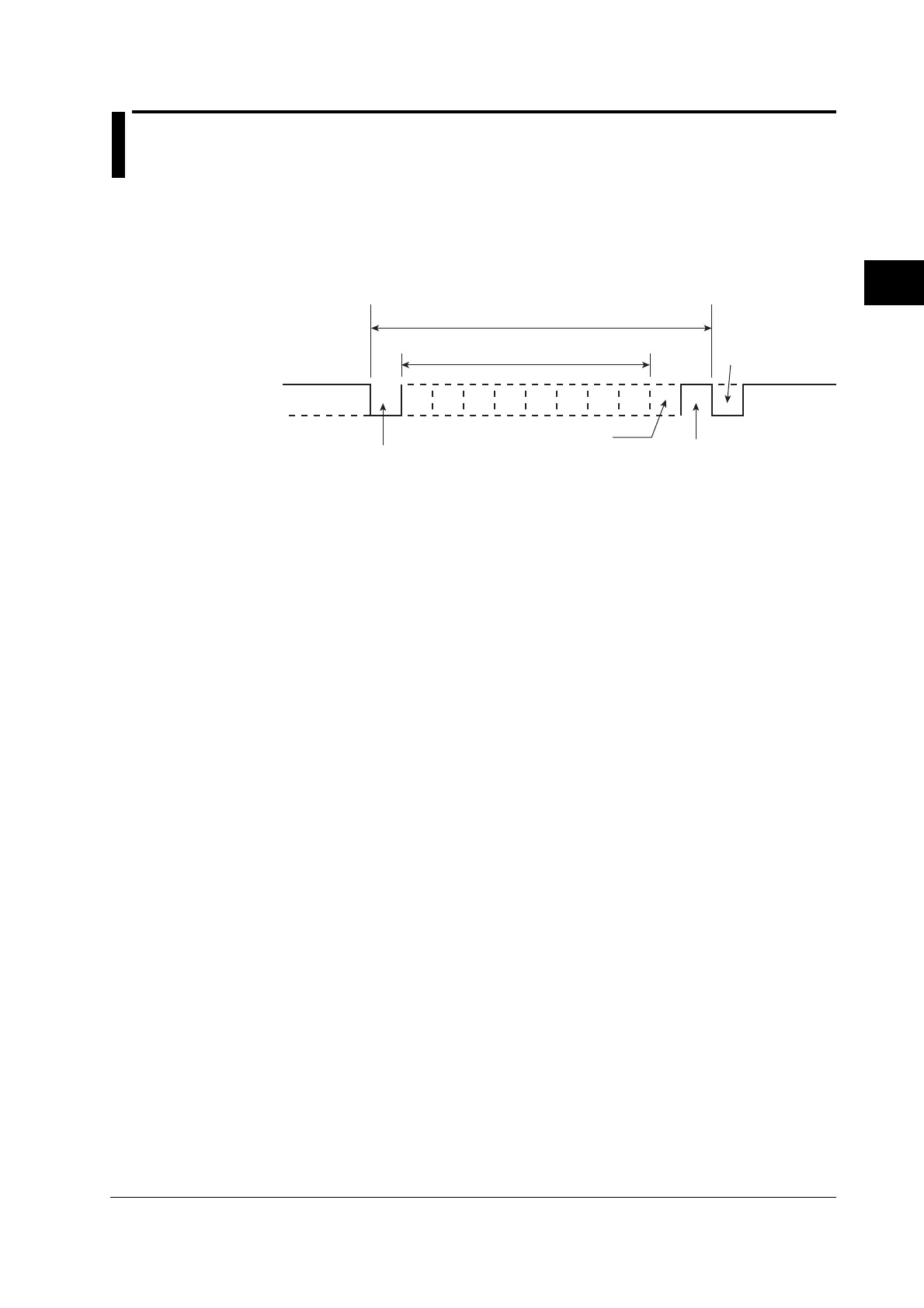
The serial interface on the recorder communicates using start-stop synchronization. In
start-stop synchronization, a start bit is added every time a character is transmitted. The
start bit is followed by the data bits, parity bit, and stop bit. (See the figure below.)
Data bit
(7 or 8 bits)
1 character
Stop bit
Parity bit
Even, Odd,
or None
Start bit
Circuit idle
state
Return to the idle
state (dotted line)
or the start bit of
the next data
character
(solid line)
Receive Buffer and Received Data
The data received from the PC is first placed in the receive buffer of the recorder. When
the received buffer becomes full, all of the data that overflow are discarded.

 Loading...
Loading...