C6-2
IM 34M06H62-02E 2nd Edition : June 2008-00
C6.2 Proportional Band
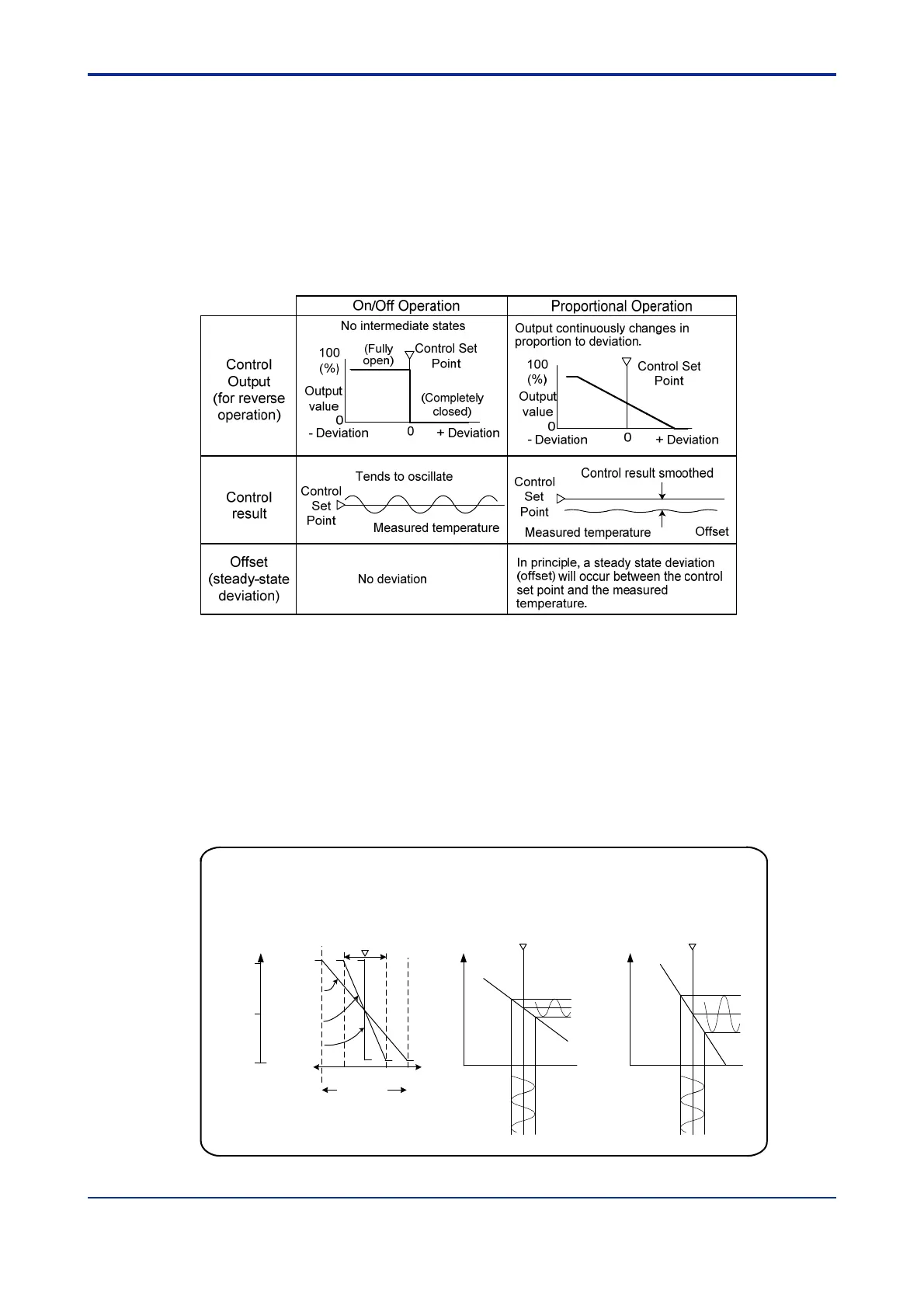
Difference Between On/Off Operation and Proportional Operation
In on/off operation, the control output alternates between “ON” and “OFF” depending on
whether the deviation is positive or negative.
In proportional operation, the control output varies in direct proportion to the deviation,
scaled by the value of the Proportional Band (PB) parameter.
The PB parameter controls the sensitivity of the proportional operation.
Figure C6.2 On/Off Operation Versus Proportional Operation
More about Proportional Band
The proportional band defines the percentage change in input (or deviation) that will
produce a 100% change in the control output, where the percentage change in input is
deemed to be 100% if the PV value changes from PRL to PRH.
Defining a smaller proportional band produces a larger output change for a given
deviation, and reduces the offset. However, it may cause the control output to oscillate.
Therefore the proportional band needs to be tuned within an appropriate range to the
smallest value without causing oscillation. Setting the proportional band to its minimum
value of 0% produces an on/off control.
Proportional Band (n.PB) (n = 1-4)
100(%)
(for reverse operation)
0(%)
PB=100%
PB=50%
(ON/OFF)
PB=0%
PB is small
Control Set Point
Deviation
Proportional band
MR=50% setting
Deviation
Control Set Point
PB is large
Deviation
Control Set Point
Full span
Output value (%)
Output value (%)
Output value (%)
Figure C6.3 Proportional Band

 Loading...
Loading...