SWT
GIGABIT/FAST ETHERNET SWITCH TYPE SWT 8/137
USER GUIDE - M0SWTA1903Iv09 - V09 March 2019
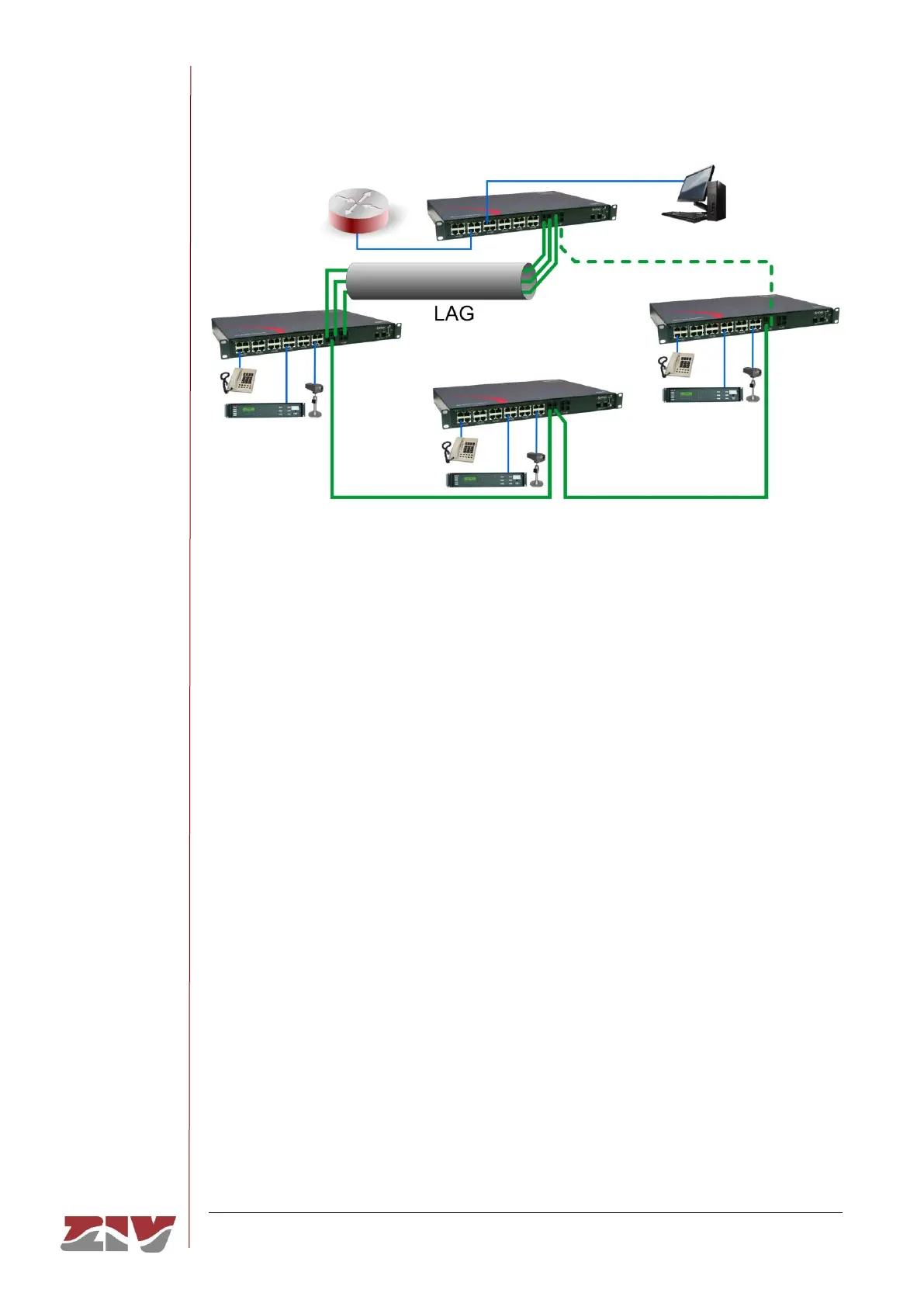
FIGURE 3 Rings
❖ Link Aggregation by LAG function.
The Link Aggregation Group (LAG) function allows grouping several links into a single
aggregated link identifier. Figure 3 illustrates an example of link aggregation. From the
point of view of the STP/RSTP protocol, the connection entity is the LAG group identifier.
In this way, the different links that are part of the LAG are not handled individually and are
not considered a loop, and thus it provides the aggregated bandwidth.
Link aggregation can be created for any of the planned interface functions: user (edge,
untag), inter-switch link (trunk or native) and those associated to the Q-in-Q functionality
(access and core). Once the LAG is established, the set of parameters of the interface
selected as Leader determines the behaviour of the group.
❖ Q-in-Q operation.
The SWT includes two functions that provide Q-in-Q operation (double-tagged). In this
operation mode, the frames include the original tag (C-TAG), either generated by the
client equipment or assigned by the switch itself at the moment is received, and a second
tag, the tag of the provider (S-TAG), which will be the tag used in the network of the
service provider.
The 802.1Q tunnels are a useful tool to reuse the identification VID values of the VLAN,
or for transiting data over third-party networks.
 Loading...
Loading...