SWT
GIGABIT/FAST ETHERNET SWITCH TYPE SWT 74/137
USER GUIDE - M0SWTA1903Iv09 - V09 March 2019
The IGMP is layer 3 protocol, and message exchange of reception requests for multicast
flows takes place between the client equipment and the IGMP routers. In this case, the
messages are spied by the switch to adapt the configuration of each port (IGMP Snooping).
For the IGMP Snooping to be operative, the GARP/GMRP must be inactive.
Activation of any of these mechanisms necessarily implies that the switch shall forward the
multicast traffic only included in the manual configuration or requested by client equipment.
Any other multicast traffic will be discarded.
As an example, FIGURE 40 shows the advantages of using GARP/GMRP or IGMP
Snooping. Figure 40a) shows a network made up by four level-2 switches, which in turn are
connected to a router. Host A is a multicast message emitter, and the Hosts B and C are
multicast receivers belonging to the same group as the Host A. The router will route the
multicast traffic only to the network sections where the Hosts B and C are found, while the
level-2 switches will transmit traffic to all the hosts connected to their interfaces by flood.
Figure 40b) shows a network using the GARP/GMRP or IGMP Snooping mechanism in its
level-2 devices. As shown in the figure, in this case only the hosts that belong to the
diffusion group receive the multicast traffic.
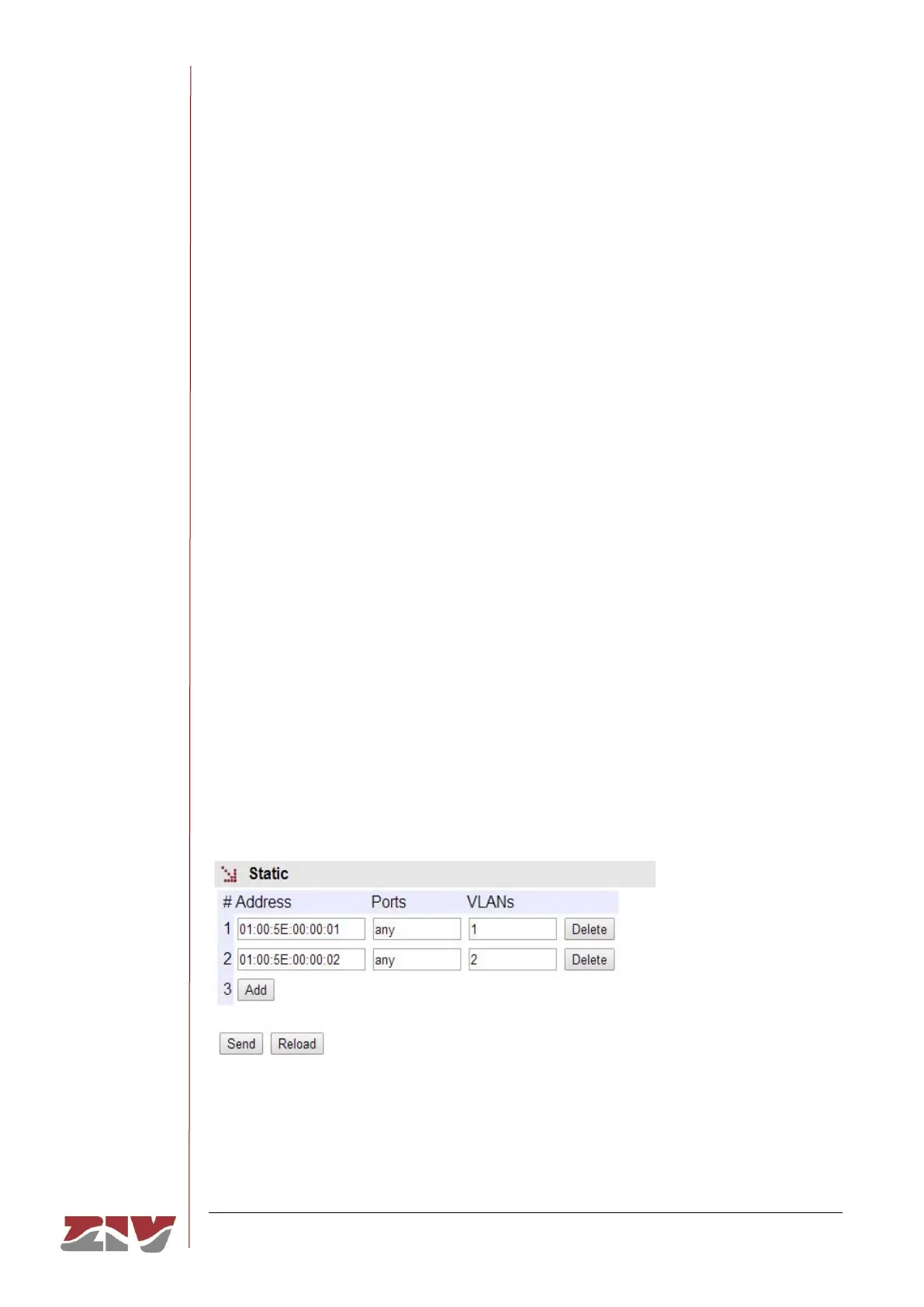
5.13.1 Static
By means of this option, the user can manually configure the interfaces that will propagate
each of the indicated multicast MAC addresses.
In networks with multiple switches, the configuration must be done in each of them.
FIGURE 41 Static configuration page of Multicast menu
 Loading...
Loading...