34405A User’s and Service Guide 59
Measurement Tutorial 3
True RMS AC Measurements
True RMS responding multimeters, like the Agilent 34405A, measure the
"heating" potential of an applied voltage. Power dissipated in a resistor is
proportional to the square of an applied voltage, independent of the
waveshape of the signal. This multimeter accurately measures true RMS
voltage or current, as long as the wave shape contains negligible energy
above the instrument’s effective bandwidth.
Note that the 34405A uses the same techniques to measure true RMS
voltage and true RMS current.
The multimeter's AC voltage and AC current functions measure the
AC–coupled true RMS value. In this Agilent instrument, the “heating
value” of only the AC components of the input waveform are measured
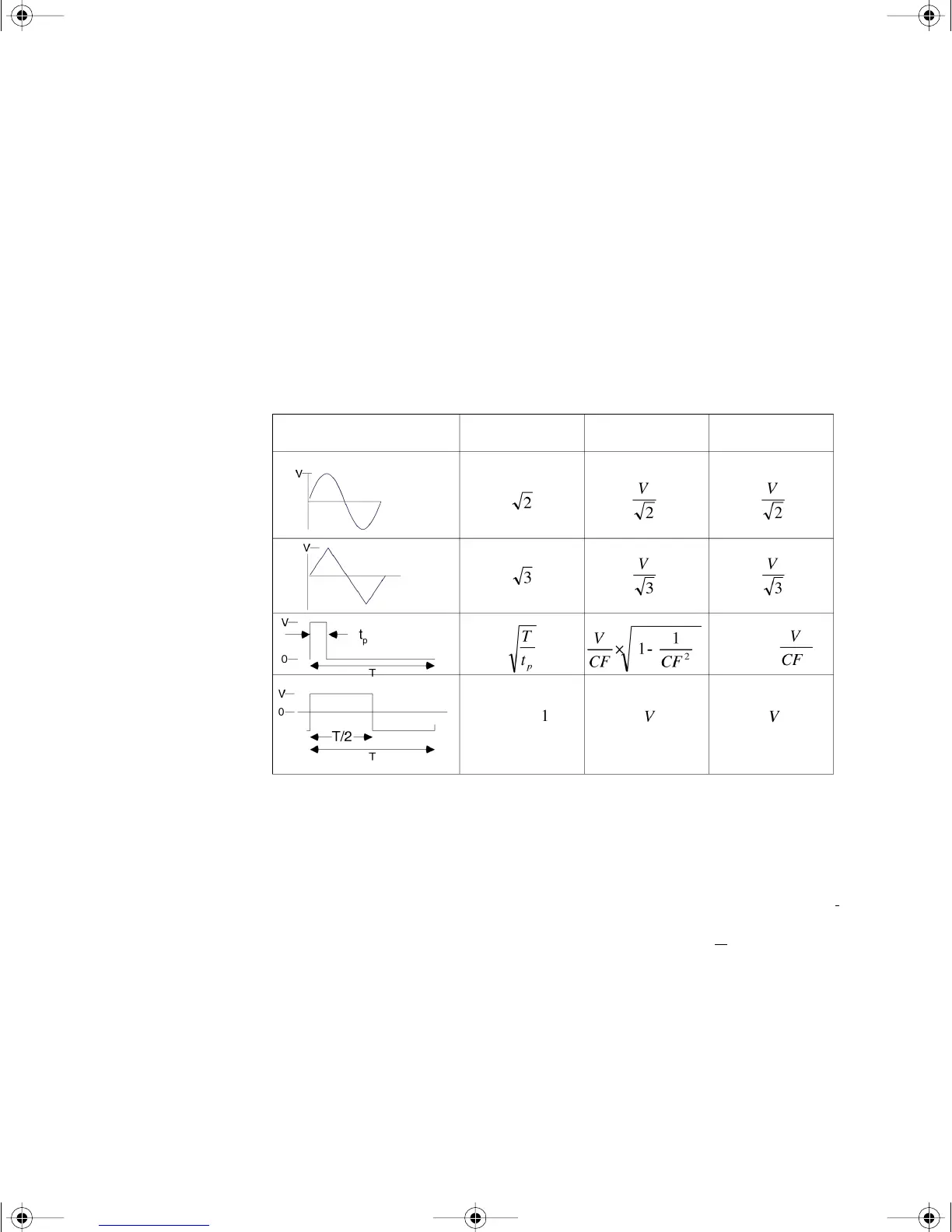
(DC is rejected). As seen in the figure above; for sinewaves, triangle
waves, and square waves, the AC–coupled and AC+DC values are equal,
since these waveforms do not contain a DC offset. However, for
non–symmetrical waveforms, such as pulse trains, there is
a DC voltage
content, which is rejected by Agilent’s AC–coupled true RMS
measurements. This can provide a significant benefit.
An AC–coupled true RMS measurement is desirable when you are
measuring small AC signals in the presence of large DC offsets. For
example, this situation is common when measuring AC ripple present on
Waveform Shape Crest Factor AC RMS AC + DC RMS
34405A users guide.book Page 59 Saturday, September 2, 2006 3:38 PM
 Loading...
Loading...











