62 34405A User’s and Service Guide
3 Measurement Tutorial
Other Primary Measurement Functions
Frequency Measurement Errors
The multimeter uses a reciprocal counting technique to measure
frequency. This method generates constant measurement resolution for any
input frequency. All frequency counters are susceptible to errors when
measuring low–voltage, low–frequency signals. The effects of both internal
noise and external noise pickup are critical when measuring "slow" signals.
The error is inversely proportional to frequency. Measurement errors also
occur if you attempt to measure the frequency of an input following a DC
offset voltage change. You must allow the multimeter's input to fully settle
before making frequency measurements.
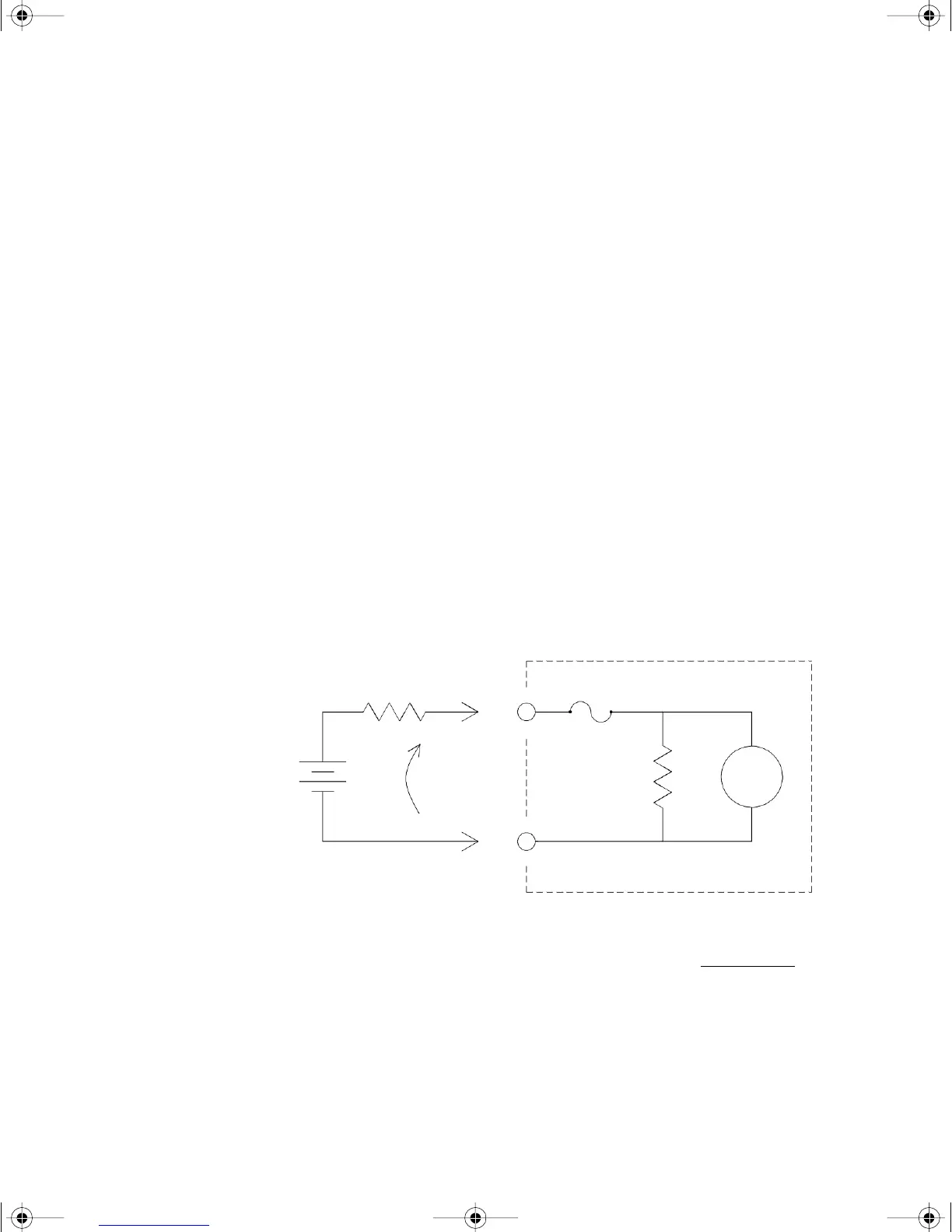
DC Current Measurements
When you connect the multimeter in series with a test circuit to measure
current, a measurement error is introduced. The error is caused by the
multimeter's series burden voltage. A voltage is developed across the
wiring resistance and current shunt resistance of the multimeter, as
shown below.
V
s
= Source Voltage
R
s
= DUT Source Resistance
V
b
= Multimeter Burden Voltage
R = Multimeter Current Shunt
Error (%) =
-100% x V
b
V
s
Ideal
Meter
R
I
LO
V
b
R
s
V
s
34405A users guide.book Page 62 Saturday, September 2, 2006 3:38 PM

 Loading...
Loading...











