Rockwell Automation Publication MOTION-RM003I-EN-P - February 2018 253
protection method. When a motor thermal model is employed, the motor
overload condition occurs when the motor thermal model indicates that the
Motor Capacity has exceeded the Motor Overload Limit. In the case of the I
2
T
overload protection method, the motor overload condition occurs when the
motor current, in percent of rated continuous motor current, exceeds the Motor
Overload Limit. The Motor Overload Action provides opportunities to mitigate
the overload condition without stopping operation.
Motor Overload Action functionality is independent of the motor overload
exception action functionality.
No explicit action is taken by the device in the overload condition if None is the
selected overload action. Selecting the Current Foldback action, however, results
in a reduction of the motor current command in proportion to the percentage
difference between Motor Capacity and the Motor Overload Limit,, or in the case
of the I
2
T overload protection method, in proportion to the difference between
the motor current, in percent of rated continuous motor current, and the Motor
Overload Limit.
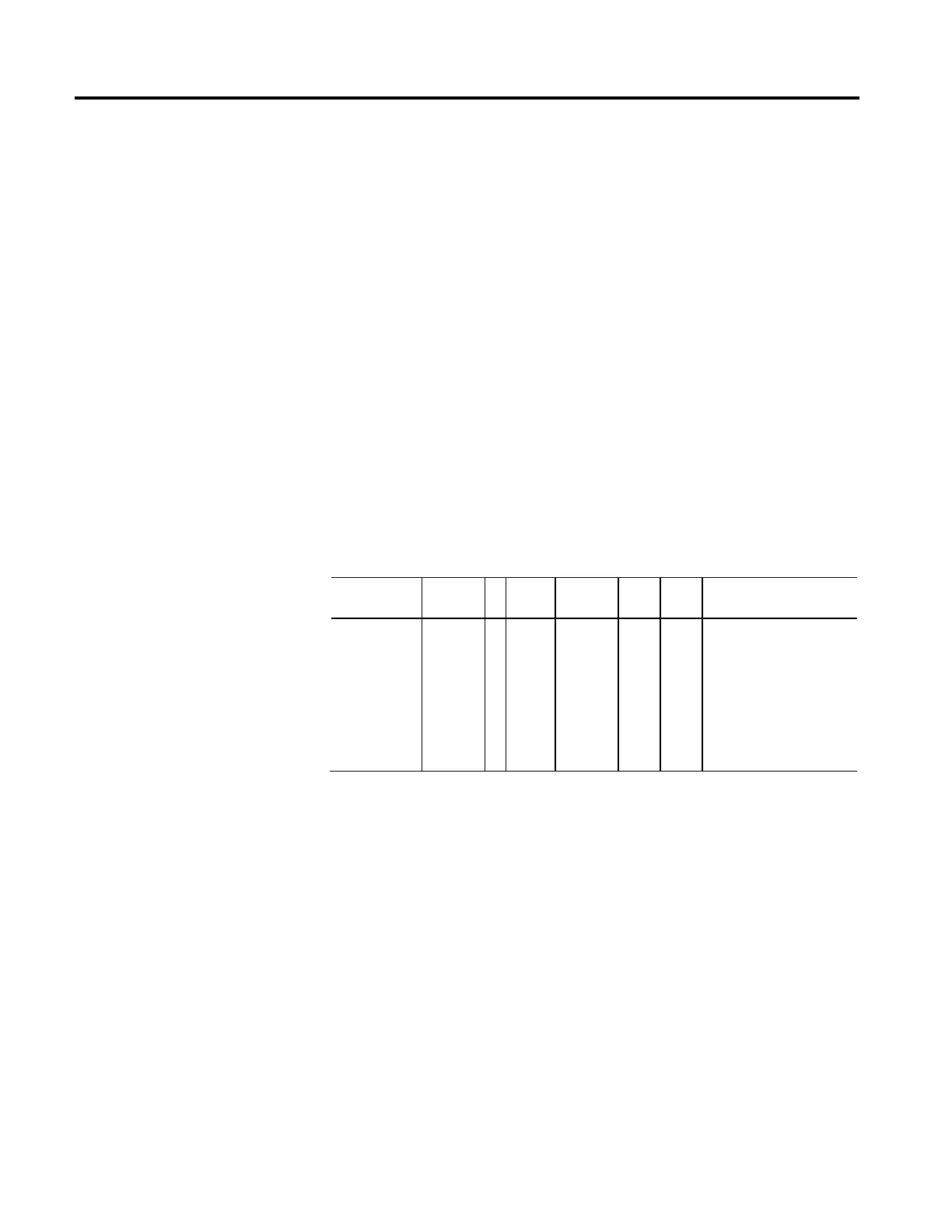
Inverter Overload Action
Usage Access T Data
Type
Default Min Max Semantics of Values
Optional - D Set/SSV
USINT 0 - - Enumeration
0 = None (R)
1 = Current Foldback (O)
2...127 = Reserved
128...255 = Vendor Specific
128 = Reduce PWM Rate
129 = PWM - Foldback
The Inverter Overload Action attribute selects the device's response to an inverter
overload condition based on an I
2
t or inverter thermal model based overload
protection method. When an inverter thermal model is employed the inverter
overload alarm condition occurs when the inverter thermal model indicates that
the Inverter Capacity has exceeded the Inverter Overload Limit. In the case of the
I
2
T overload protection method, the inverter overload condition occurs when the
inverter current, in percent of rated continuous inverter current, exceeds the
Inverter Overload Limit.
The Inverter Overload Action provides opportunities to mitigate the overload
condition without stopping operation. Inverter Overload Action functionality is
independent of the motor overload exception action functionality.
An overload alarm condition can also be generated by exceeding the limits of the
device's power block thermal model that includes switching losses that have a
dependency on the PWM Frequency.

 Loading...
Loading...











