Rockwell Automation Publication MOTION-RM003I-EN-P - February 2018 429
Guard Faults
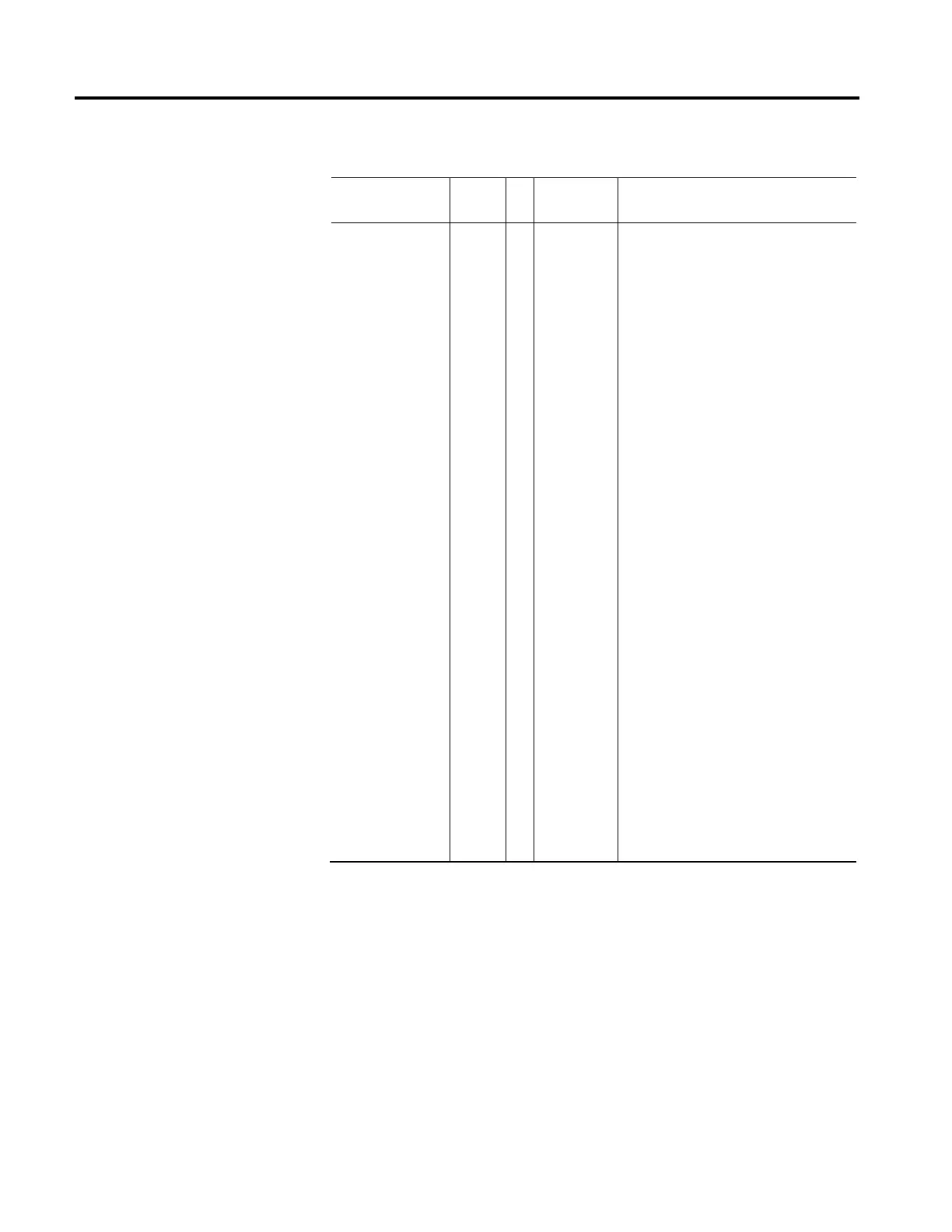
Usage Access T Data Type Semantics
Optional - D GSV T DWORD Bitmap
0 = (Reserved - Combined Faults)
1 = Guard Internal Fault
2 = Guard Configuration Fault
3 = Guard Gate Drive Fault
4 = Guard Reset Fault
5 = Guard Feedback 1 Fault
6 = Guard Feedback 2 Fault
7 = Guard Feedback Speed Compare Fault
8 = Guard Feedback Position Compare Fault
9 = Guard Stop Input Fault
10 = Guard Stop Output Fault
11 = Guard Stop Decel Fault
12 = Guard Stop Standstill Fault
13 = Guard Stop Motion Fault
14 = Guard Limited Speed Input Fault
15 = Guard Limited Speed Output Fault
16 = Guard Limited Speed Monitor Fault
17 = Guard Max Speed Monitor Fault
18 = Guard Max Accel Monitor Fault
19 = Guard Direction Monitor Fault
20 = Guard Door Monitor Input Fault
21 = Guard Door Monitor Fault
22 = Guard Door Control Output Fault
23 = Guard Lock Monitor Input Fault
24 = Guard Lock Monitor Fault
25 = Guard Enabling Switch Monitor Input Fault
26 = Guard Enabling Switch Monitor Fault
27 = Guard Feedback 1 Voltage Monitor Fault
28 = Guard Feedback 2 Voltage Monitor Fault
29 = Reserved (RLM Reset Fault)
30...31 = Reserved
The Guard Faults attribute is a collection of bits indicating the safety faults of the
drive axis. When a safety fault condition occurs the safety core processor always
requests a Safe Stop operation and notifies the drive controller to set the
appropriate Guard Faults bit. This bit remains latched even if the safety fault
condition is cleared in the safety core. A Fault Reset Request to the associated axis
clears the safety fault bits, but the bits set again immediately if the underlying
safety fault condition is still present.

 Loading...
Loading...











