2 — INSTALLATION AND WIRING
pg. 17
Return to TOC Curtis AC F4-A Motor Controller – August 2020
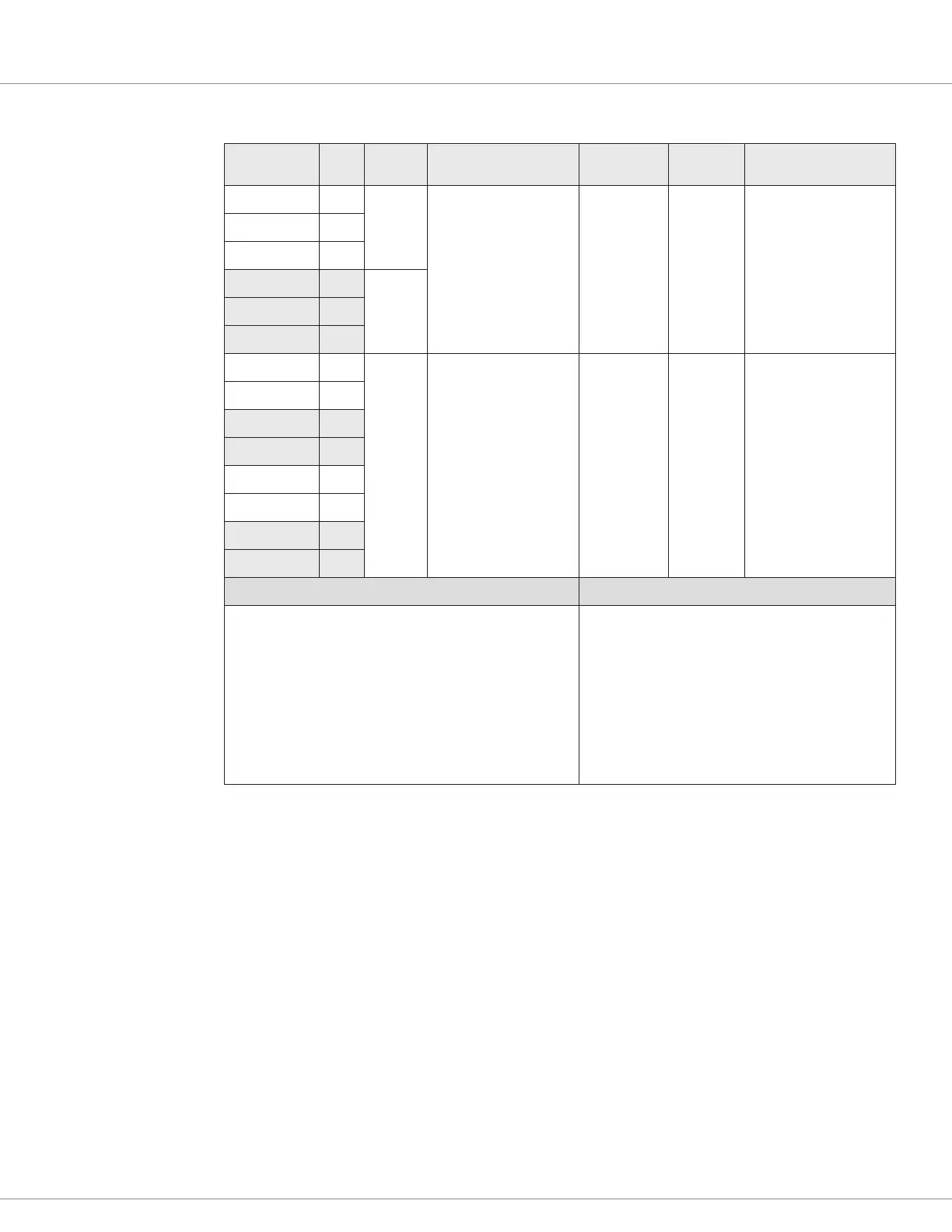
Table 7 Potentiometer Input/Configuration Electrical Specifications
Input
Signal Name
Pin Type
Pot Resistance Range
Available Current
Input
Impedance
Output
Voltage
Fault
Detection
Pot 6 Supply 15
3-Wire
1k – 10k Ω
3 mA supplied, Max.
20k Ω < 15 V
Pot Wiper Open
Pot Resistance Low
Pot Resistance High
Circuit Failure (internal)
Pot 1 Wiper 16
GND 7
1
Pot 19 Supply 27
3-Wire
Pot 18 Wiper 17
GND 7
1
Pot 1 Input 16
2-Wire
1k – 10k Ω
3 mA supplied, Max.
20k Ω < 15 V
Pot Wiper Open
Pot Resistance High
Circuit Failure (internal)
GND 7
1
Pot 6 Input 15
GND 7
1
Pot 18 Input 17
GND 7
1
Pot 19 Input 27
GND 7
1
VCL Functions VCL Monitor variables
Throttle_Pot_Percent
Throttle_Command
Throttle_Multiplier
Mapped_Throttle
Note: similar variables exist for the brake, if
implemented.
Dual_Steer_Pot_Percent
Dual_Steer_Angle
1
Can also use pin 18 as a ground (GND).
PWM and Digital Drivers
Drivers 1 through 5 are low-side pulse-width-modulation (PWM) drivers. ese drivers are for
inductive loads such as contactor coils and electromagnetic brakes. ey can drive a resistive load if
the peak current is within the driver’s current rating. Use caution if the “load” is a RC-type circuit,
however, due to the high (capacitor) inrush current (currents exceeding 120% will cause a Type 2
Driver Overcurrent fault).
Each driver has a settable parameter (checks enable) to detect for an open and shorted coil (e.g.,
vehicle wiring related), and this parameter should be set to O if the driver is not used. e drivers
can withstand shorts to either B+ or B–. Always connect the drivers to the Coil Supply (pin 13)
which is the high side of the driver circuit (i.e., these low-side drivers “sink current” from the coil
supply, via the load). e Coil Supply provides an internal yback-diode for the inductive voltage-
spike protection.
 Loading...
Loading...





