2 — INSTALLATION AND WIRING
pg. 21
Return to TOC Curtis AC F4-A Motor Controller – August 2020
CAN Ports
Two CAN ports are available. Each CAN port requires a unique Node ID and they can operate at dierent
baud rates. Both isolated CAN and non-isolated CAN port models are available (see Appendix E).
On the non-isolated CAN models, both ports share the controller internal power supply and I/O
ground (B–) reference. On these models, enable the CAN1 port’s internal 120Ω termination by
externally connecting pins 21 and 34 together (See Figures 6 and 7). e CAN2 port does not have
internal 120Ω termination.
e isolated CAN models provide an isolated ground (see Figures 6 and 7a). e isolated CAN
models do not have internal 120Ω terminated. e isolated CAN models do not use pin 21.
e supported protocol is CANopen Physical layer ISO 11898, including the 11-bit and 29-bit
identier protocols. For applications with multiple third party devices, refer to the CANopen Physical
Layer for the recommended bit timing settings and bus lengths based upon baud rate.
Use Port 1 (CAN1) for the communication channel with the Curtis Integrated Toolkit
TM
(CIT) program
and the 1313 HHP programmer. See Appendix D for the CAN port hardware conguration to utilize
these programming tools. is applies to both non-isolated and isolated CAN controller models.
ere are 30 CAN receive mailboxes and 20 CAN transmit mailboxes. ese are shared between
both CAN ports.
Attempting to assign more that this using the Assign_CAN_Mailbox() function will return an error.
See the System Information le.
ere are four TPDO and four RPDO mailboxes, each for CAN Port 1 and Port 2. See the CAN
Interface and CAN Interface 2 menus in Programmer.
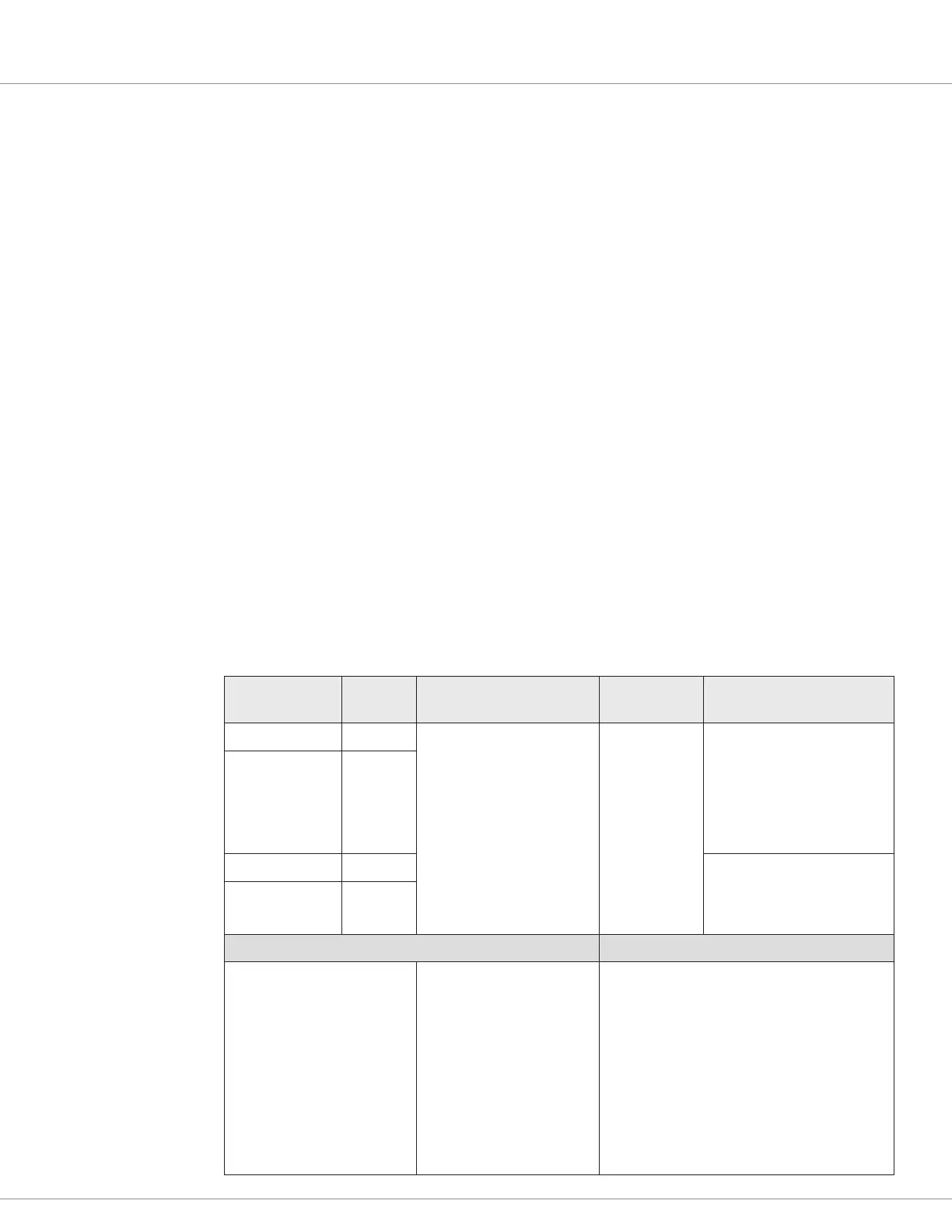
Table 11 CAN Ports Electrical Specifications
CAN Port Pin
Baud Rate
(bps)
Input
Impedance
CAN Termination
CAN1 High 23 –1 = 110k
0 = 125k
1 = 250K
2 = 500K
3 = 800K
4 = 1M
> 1k Ω
<1000pF
Non-isolated CAN:
Internal 120Ω. Requires
connecting pins 21 and 34
together (external jumper).
Else, non-terminated.
Isolated CAN:
No internal termination.
CAN1 Low 35
CAN2 High 21 Non-isolated & isolated CAN:
No internal termination.
CAN2 Low 34
VCL Functions VCL Monitor Variables
Assign_CAN_Mailbox ( )
Setup_CAN_Transmit_Mailbox ( )
Setup_CAN_Transmit_Data ( )
Get_Tramsmit_Counter ( )
Get_Tramsmit_Status ( )
Clear_Transmit_Status ( )
Enable_Transmit_Mailbox ( )
Disable_Transmit_Mailbox ( )
Get_Fault_CAN_Id ( )
Send_Mailbox ( )
Setup_CAN_Receive_
Mailbox ( )
Setup_CAN_Receive_Data ( )
Get_Received_Counter ( )
Get_Received_Status ( )
Clear_Received_Status ( )
Enable_Receive_Mailbox ( )
Disable_Receive_Mailbox ( )
Get_Receive_Timeout ( )
Clear_Receive_Timeout ( )
Get_Receive_ID ( )
CAN_NMT_State
Quick Links:
Fig 6 p.10
Fig 7 p.11
Fig7a p.12
Appendix D p.195
Appendix E p.205
 Loading...
Loading...





