n
M,N
Nominal motor speed (nameplate data).
n
s
Synchronous motor speed
n
s
=
2 × par . 1 − 23 × 60s
par . 1 − 39
n
slip
Motor slip.
P
M,N
Rated motor power (nameplate data in kW or hp).
T
M,N
Rated torque (motor).
U
M
Instantaneous motor voltage.
U
M,N
Rated motor voltage (nameplate data).
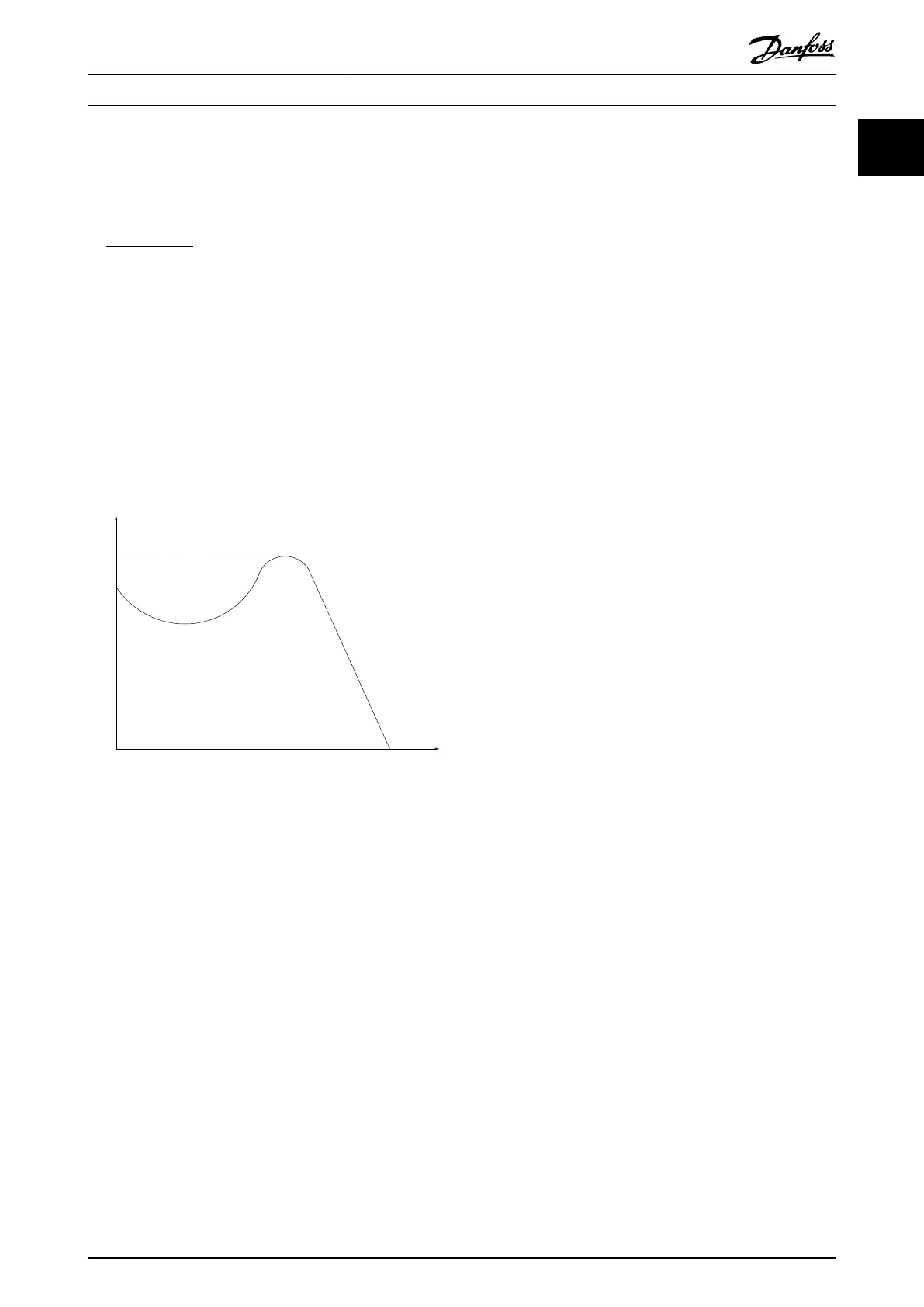
Break-away torque
175ZA078.10
Pull-out
rpm
Torque
Illustration 1.1 Break-away Torque
η
VLT
The eciency of the frequency converter is dened as the
ratio between the power output and the power input.
Start-disable command
A start-disable command belonging to the control
commands in group 1. See Table 1.1 for more details.
Stop command
A stop command belonging to the control commands in
group 1. See Table 1.1 for more details.
1.3.4 References
Analog reference
A signal transmitted to the analog inputs 53 or 54 can be
voltage or current.
Binary reference
A signal transmitted to the serial communication port.
Preset reference
A dened preset reference to be set from -100% to +100%
of the reference range. Selection of 8 preset references via
the digital terminals.
Pulse reference
A pulse frequency signal transmitted to the digital inputs
(terminal 29 or 33).
Ref
MAX
Determines the relationship between the reference input at
100% full scale value (typically 10 V, 20 mA) and the
resulting reference. The maximum reference value is set in
parameter 3-03 Maximum Reference.
Ref
MIN
Determines the relationship between the reference input at
0% value (typically 0 V, 0 mA, 4 mA) and the resulting
reference. The minimum reference value is set in
parameter 3-02 Minimum Reference.
1.3.5 Miscellaneous
Analog inputs
The analog inputs are used for controlling various
functions of the frequency converter.
There are 2 types of analog inputs:
•
Current input: 0–20 mA and 4–20 mA.
•
Voltage input: 0–10 V DC.
Analog outputs
The analog outputs can supply a signal of 0–20 mA, or 4–
20 mA.
Automatic motor adaptation, AMA
The AMA algorithm determines the electrical parameters
for the connected motor at standstill.
Brake resistor
The brake resistor is a module capable of absorbing the
brake power generated in regenerative braking. This
regenerative brake power increases the DC-link voltage,
and a brake chopper ensures that the power is transmitted
to the brake resistor.
CT characteristics
Constant torque characteristics used for all applications
such as conveyor belts, displacement pumps, and cranes.
Digital inputs
The digital inputs can be used for controlling various
functions of the frequency converter.
Digital outputs
The frequency converter features 2 solid-state outputs that
can supply a 24 V DC (maximum 40 mA) signal.
DSP
Digital signal processor.
Introduction Design Guide
MG07B102 Danfoss A/S © 03/2016 All rights reserved. 7
1 1

 Loading...
Loading...

















