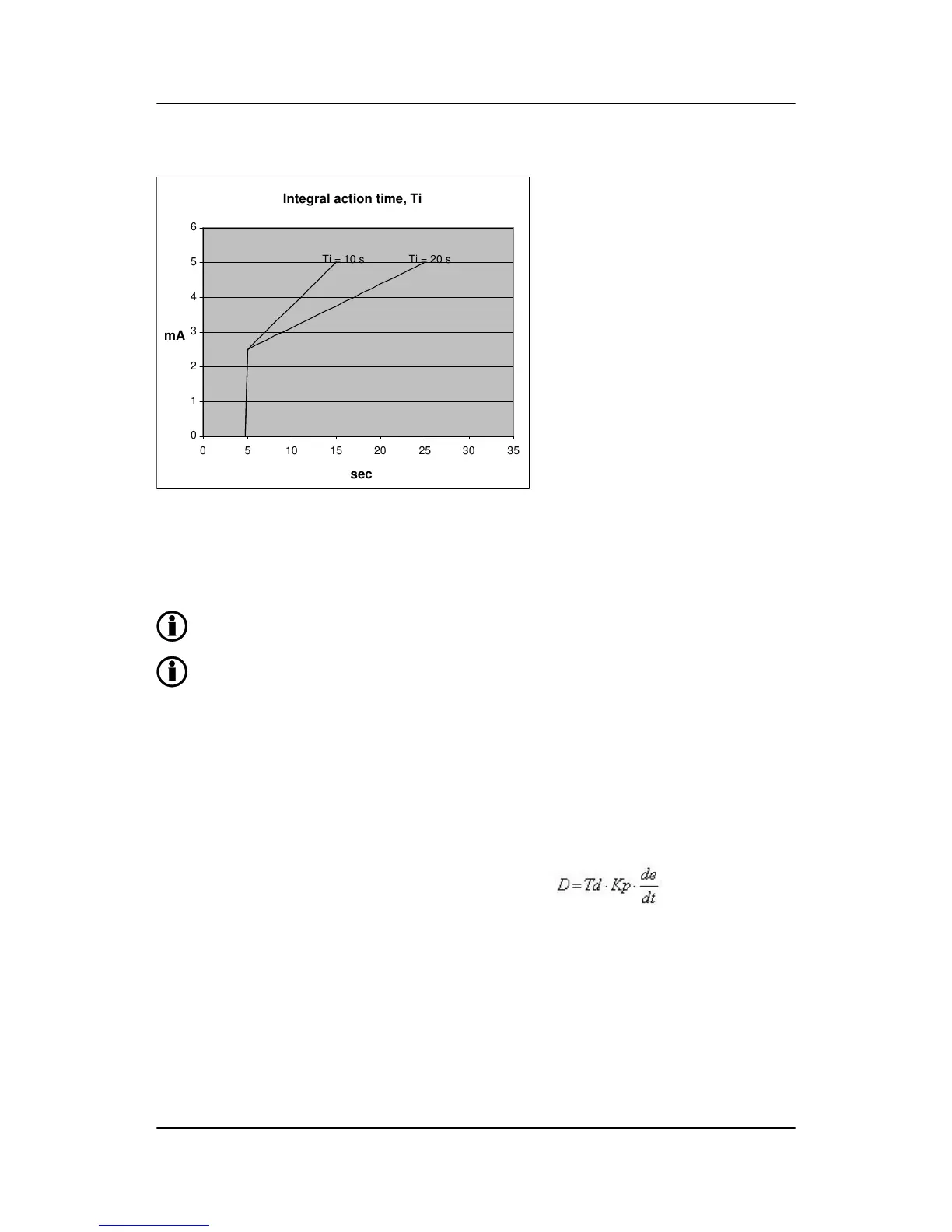
As it appears from the drawing, the output reaches 5 mA twice as fast at a Ti setting of 10 s than with a set-
ting of 20 s.
The integrating function of the I-regulator is increased if the integral action time is decreased. This means that
a lower setting of the integral action time, Ti, results in a faster regulation.
If the Ti is adjusted to 0 s, the I-regulator is switched OFF.
The integral action time, Ti, must not be too low. This will make the regulation hunt, similar to a
too high proportional action factor, Kp.
Differential regulator
The main purpose of the differential regulator (D-regulator) is to stabilise the regulation, thus making it possi-
ble to set a higher gain and a lower integral action time, Ti. This will make the overall regulation eliminate
deviations much faster.
In most cases, the differential regulator is not needed; however, in case of very precise regulation situations,
for example static synchronisation, it can be very useful.
The output from the D-regulator can be explained with the equation:
D = regulator output
Kp = gain
de/dt = slope of the deviation (how fast does the deviation occur)
This means that the D-regulator output depends on the slope of the deviation, the Kp and the Td setting.
Example:
In the following example, it is assumed that Kp = 1.
GPC-3 DRH 4189340587 UK
PID controller
DEIF A/S Page 106 of 122

 Loading...
Loading...