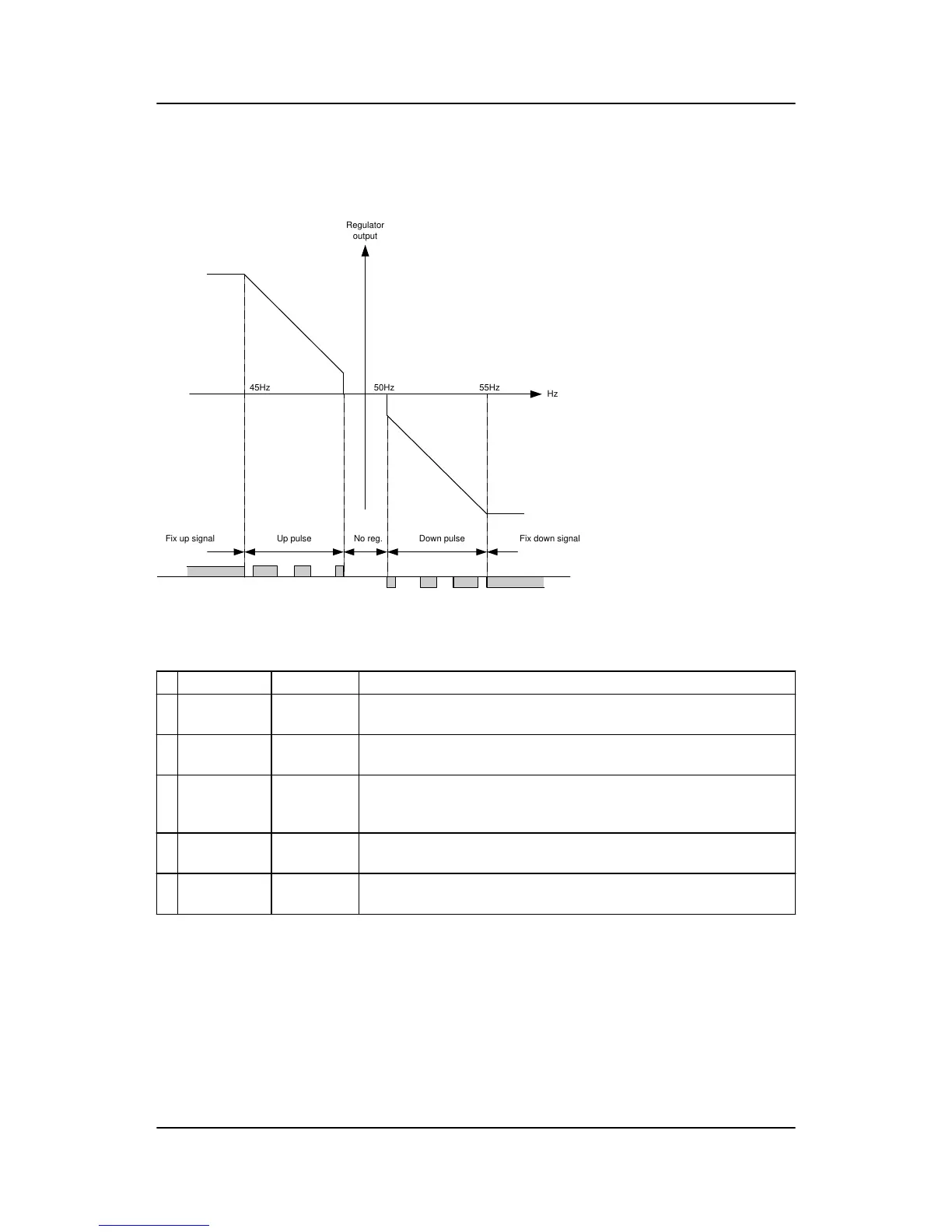
The regulation with relays can be split up into five steps.
# Range Description Comment
1 Static range Fixed up
signal
The regulation is active, but the increase relay will be constantly activa-
ted because of the size of the regulation deviation.
2 Dynamic
range
Up pulse The regulation is active, and the increase relay will be pulsing in order to
eliminate the regulation deviation.
3 Deadband
area
No reg. In this particular range no regulation takes place. The regulation accepts
a predefined deadband area in order to increase the lifetime of the re-
lays.
4 Dynamic
range
Down pulse The regulation is active, and the decrease relay will be pulsing in order
to eliminate the regulation deviation.
5 Static range Fixed down
signal
The regulation is active, but the decrease relay will be constantly activa-
ted because of the size of the regulation deviation.
As the drawing indicates, the relays will be fixed ON if the regulation deviation is big, and they will be pulsing
if it is closer to the set point. In the dynamic range, the pulses get shorter and shorter when the regulation
deviation gets smaller. Just before the deadband area, the pulse is as short as it can get. This is the adjusted
time “GOV ON time”. The longest pulse will appear at the end of the dynamic range (45 Hz in the example
above).
GPC-3 DRH 4189340587 UK
PID controller
DEIF A/S Page 108 of 122

 Loading...
Loading...