Configuring VLANs 577
802.1Q (0x8100) EtherType, it allows the traffic to have added security from
misconfiguration while exiting the metro core. For example, if the edge
device on the other side of the metro core is not stripping the second tag, the
packet would never be classified as a 802.1Q tag, so the packet would be
dropped rather than forwarded in the incorrect VLAN.
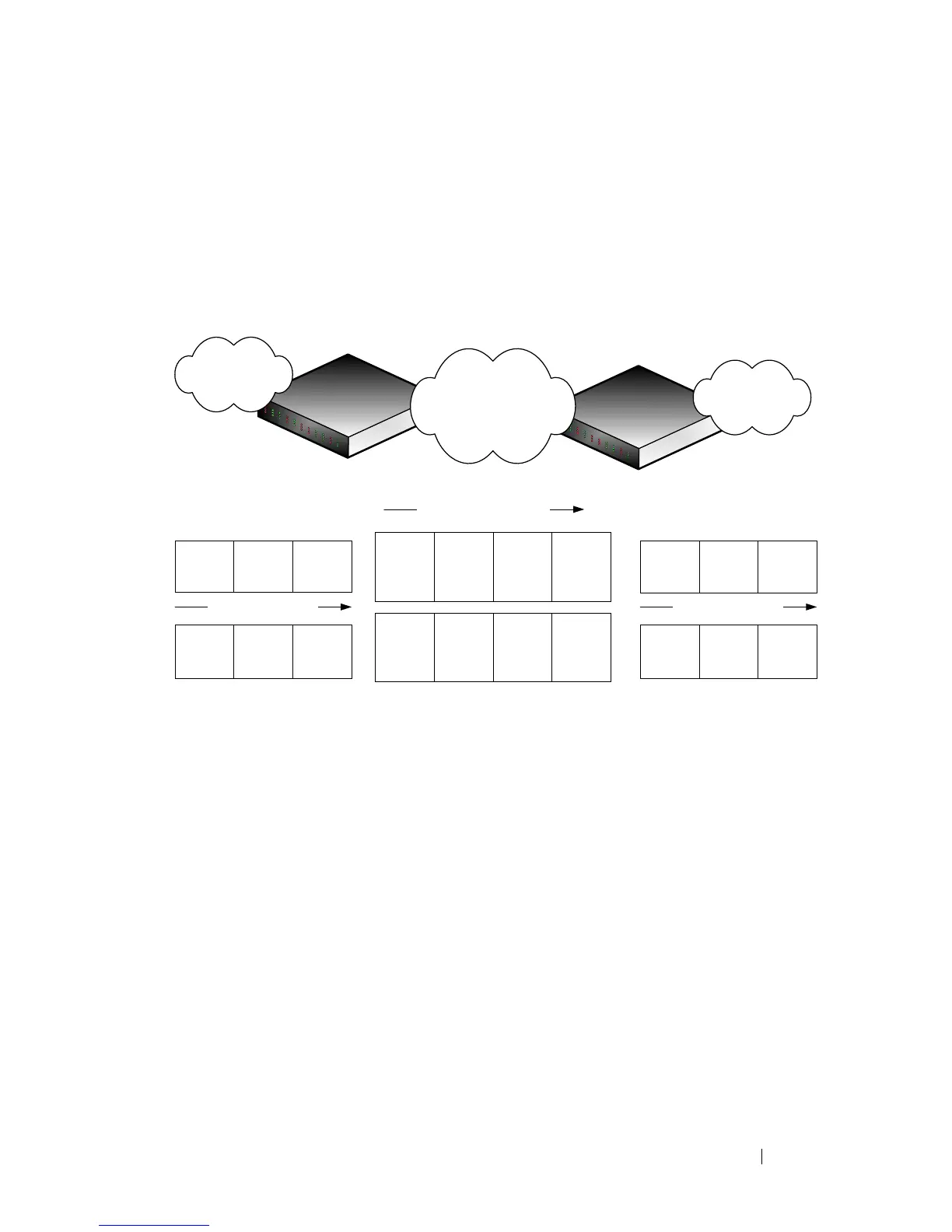
Figure 21-2. Double VLAN Tagging Network Example
Voice VLAN
The Voice VLAN feature enables switch ports to carry voice traffic with
defined priority. When multiple devices, such as a PC and an IP phone, are
connected to the same port, you can configure the port to use one VLAN for
voice traffic and another VLAN for data traffic.
Voice over IP (VoIP) traffic is inherently time-sensitive: for a network to
provide acceptable service, the transmission rate is vital. The priority level
enables the separation of voice and data traffic coming onto the port.
A primary benefit of using Voice VLAN is to ensure that the sound quality of
an IP phone is safeguarded from deteriorating when the data traffic on the
port is high. The switch uses the source MAC address of the traffic traveling
through the port to identify the IP phone data flow.
Data
Link
Header
.1Q Tag
Vlan ID
22
Payload
Data
Link
Header
.1Q Tag
Vlan ID
22
Payload
DVlan
Tag
Vlan ID
50
Data
Link
Header
.1Q Tag
Vlan ID
33
Payload
DVlan
Tag
Vlan ID
60
Data
Link
Header
.1Q Tag
Vlan ID
33
Payload
Customer A
ID = 50
802.1Q Domain
Metro Core
.1Q Tagged Frame
DVLAN Tagged Frame
Edge Device
Edge Device
802.1Q Domain
Data
Link
Header
.1Q Tag
Vlan ID
22
Payload
Data
Link
Header
.1Q Tag
Vlan ID
33
Payload
Customer B
ID = 60
.1Q Tagged Frame

 Loading...
Loading...