4-18
Switch Meshing
Operating Notes for Switch Meshing
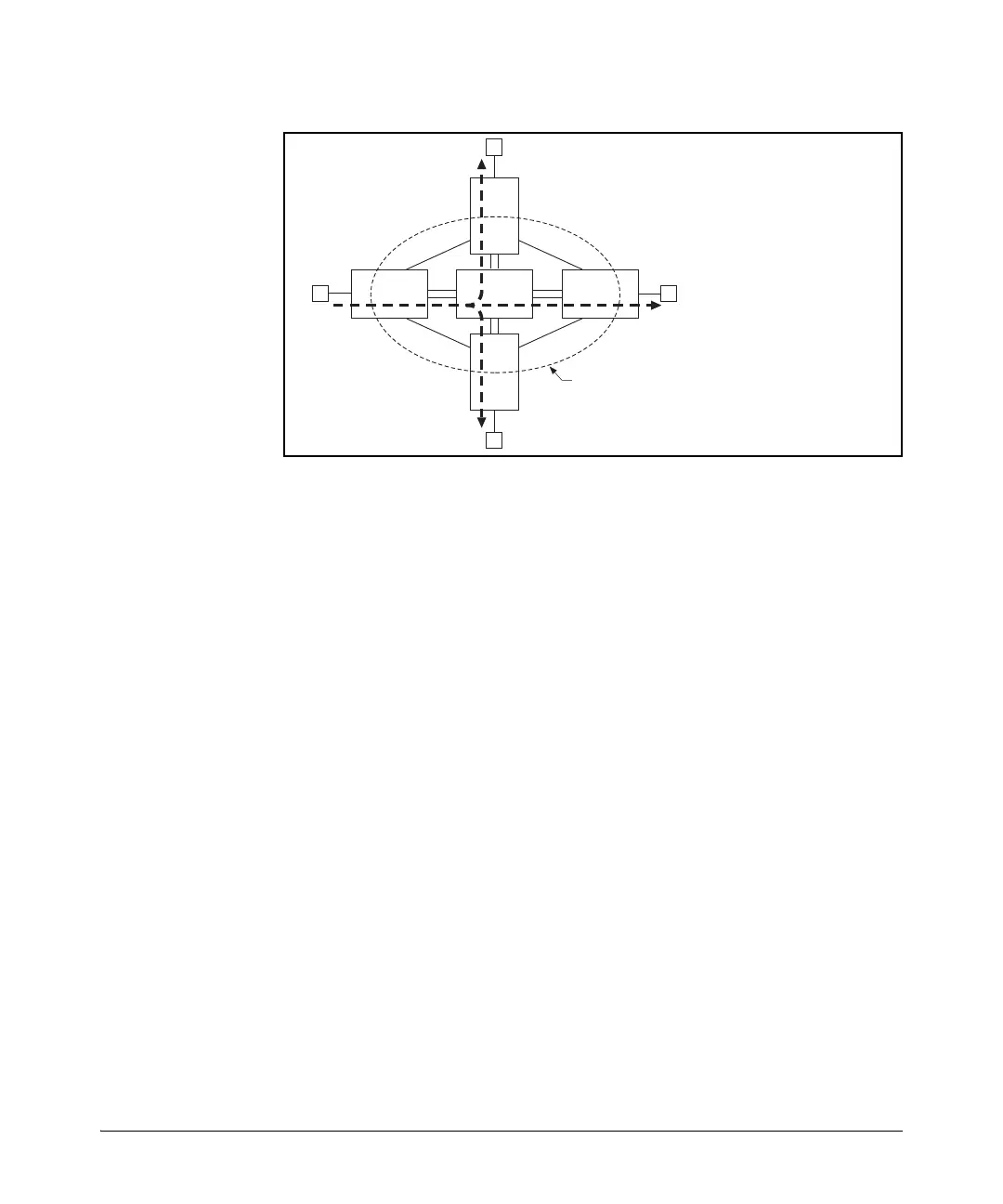
Figure 4-12. Example of a Broadcast Path Through a Switch Mesh Domain
Any mesh switches that are not edge switches will flood the broadcast packets
only through ports (paths) that link to separate edge switches in the controlled
broadcast tree. The edge switches that receive the broadcast will flood the
broadcast out all non-meshed ports. Some variations on broadcast/multicast
traffic patterns, including the situation where multiple VLANs are configured
and a broadcast path through the mesh domain leads only to ports that are in
the same VLAN as the device originating the broadcast.
Unicast Packets with Unknown Destinations
A meshed switch receiving a unicast packet with an unknown destination does
not flood the packet onto the mesh. Instead, the switch sends a query on the
mesh to learn the location of the unicast destination. The meshed switches
then send 802.2 test packets through their non-meshed ports. After the unicast
destination is found and learned by the mesh, subsequent packets having the
same destination address will be forwarded. By increasing the MAC Age Time
you can cause the switch address table to retain device addresses longer. (For
more on MAC Age Time, refer to “System Information” in the chapter titled
“Interface Access and System Information” in the Management and Config-
uration Guide for your switch.) Because the switches in a mesh exchange
address information, this will help to decrease the number of unicast packets
with unknown destinations, which improves latency within the switch mesh.
Also, in an IP environment, HP Networking recommends that you configure
IP addresses on meshed switches. This makes the discovery mechanism more
robust, which contributes to decreased latency.
A
B
C
D
E
Switches A, B, C, & D
are Edge Switches

 Loading...
Loading...











