• Service provider VLANs (SVLANs)—VLANs assigned for transmitting traffic across the service
provider network.
NOTE:
For more information about QoS policies, see the
ACL and QoS Configuration Guide
.
One-to-one VLAN mapping implementation
This section describes how one-to-one VLAN mapping is implemented on the A3100 v2 EI.
Implementing one-to-one VLAN mapping with a global QoS policy
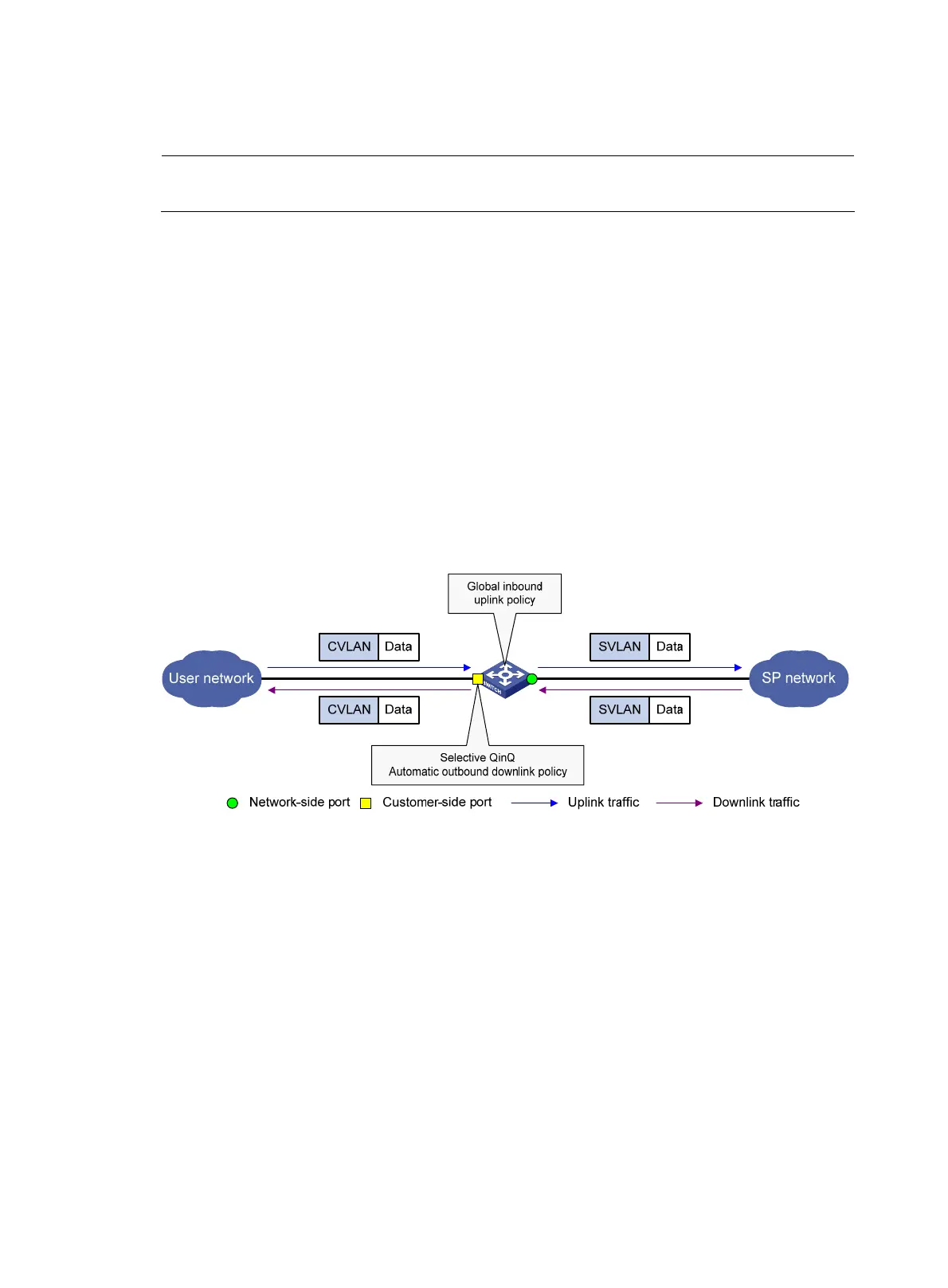
Implement one-to-one VLAN mapping on the customer-side port through the following configurations, as
shown in Figure 52:
• Apply a global uplink policy to the incoming traffic, mapping each CVLAN ID to a unique SVLAN
ID. When a packet arrives, the switch replaces its CVLAN ID with the matching SVLAN ID.
• Enable selective QinQ with the qinq enable downlink command on the customer-side port. The
switch will automatically apply a downlink policy to the outgoing traffic, mapping each SVLAN ID
back to the corresponding CVLAN ID. When forwarding a packet out of the port, the switch
replaces its SVLAN ID with the matching CVLAN ID.
Figure 52 One-to-one VLAN mapping implementation with a globally QoS policy
Implementing one-to-one VLAN mapping with port QoS policies
Implement one-to-one VLAN mapping on the customer-side port through the following configurations, as
shown in Figure 53:
• Apply an uplink policy to the incoming traffic, mapping each CVLAN ID to a unique SVLAN ID.
When a packet arrives, the switch replaces its CVLAN ID with the matching SVLAN ID.
• Apply a downlink policy to the outgoing traffic, mapping each SVLAN ID back to the
corresponding CVLAN ID. When forwarding a packet out of the port, the switch replaces its SVLAN
ID with the matching CVLAN ID.
153

 Loading...
Loading...