Batteries and Power Management
Managing Power Consumption
52 Corporate Evaluator’s Guide
• Windows XP: Click Start, Control Panel, Performance and Maintenance, Power
Options. On the Power Schemes tab, select a power scheme. This scheme
automatically controls the processor speeds:
• The Max Battery scheme uses the lowest processor speeds while running on
battery power, but uses medium and high processor speeds on AC power.
• The Portable/Laptop option uses medium and high processor speeds on battery
and AC power.
See Windows Help for additional information about power schemes.
To manage power manually
In addition to allowing the computer to enter its power-saving modes automatically, you
can also put it into any of the following three modes whenever you need to.
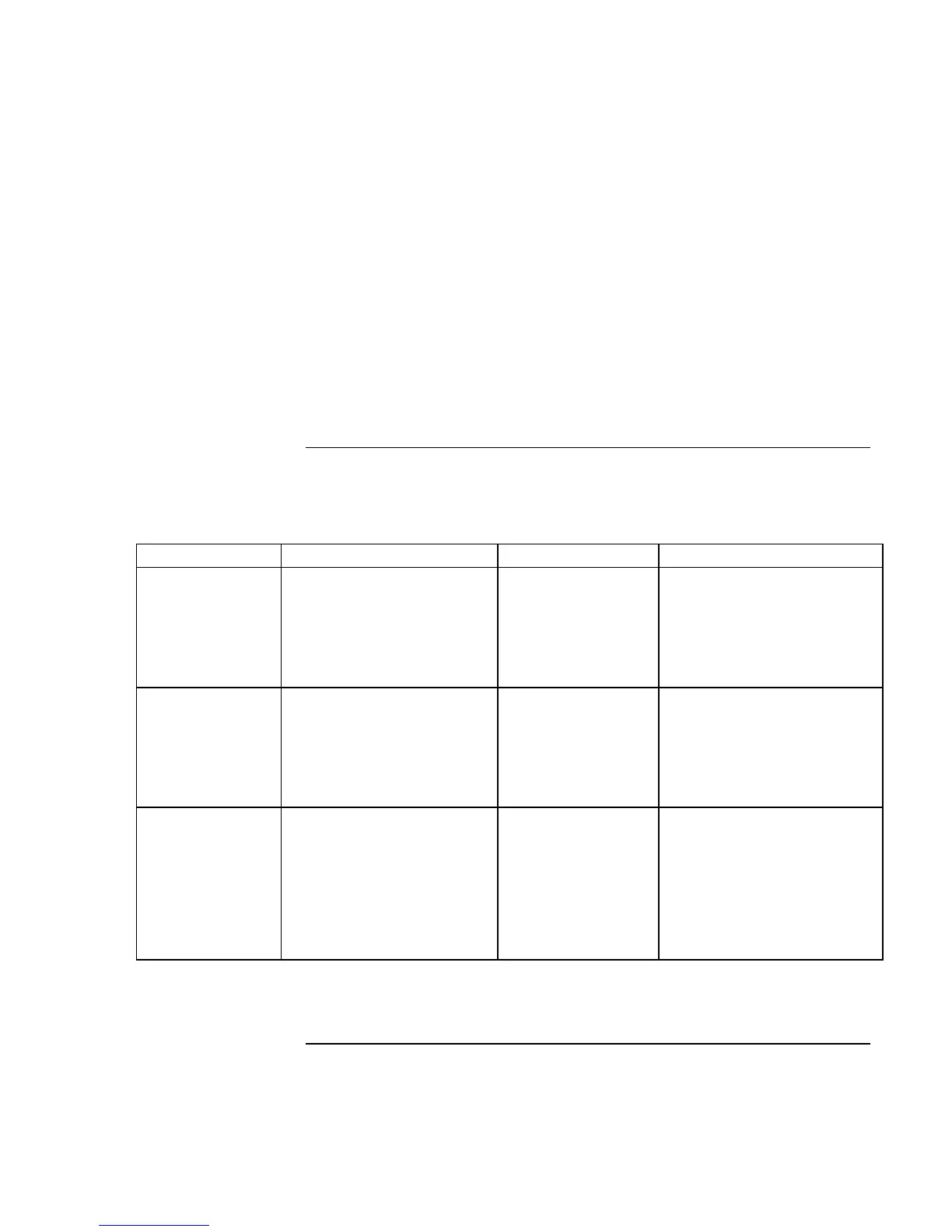
Power mode Does this… Use when… To enter this mode…
Standby Maintains your current
session in RAM, and turns off
the display and other
components.
You will be away
from your computer
for a short time.
Press blue sleep button
–or–
click Start, Shut Down,
Standby (Windows 98 or 2000)
–or–
click Start, Turn Off Computer,
Stand By (Windows XP).
Hibernate Saves the current session to
disk, then shuts down.
Provides maximum power
savings while still allowing you
to recover the current session.
You will be away
from your computer
for several hours, but
want to continue
your session.
Press Fn+F12
–or–
click Start, Shut Down,
Hibernate (Windows 2000)
–or–
click Start, Hibernate
(Windows 98).
Off Turns off your computer,
providing maximum power
savings. The current session
will not be saved, and any
unsaved data will be lost.
You’re done with
your work.
Click Start, Shut Down, Shut
down (Windows 98 or 2000)
–or–
click Start, Turn Off Computer,
Turn Off (Windows XP)
–or–
slide the power button (only if
the Start menu procedure
doesn’t work).

 Loading...
Loading...











