2GZ/2G1
2-1-6
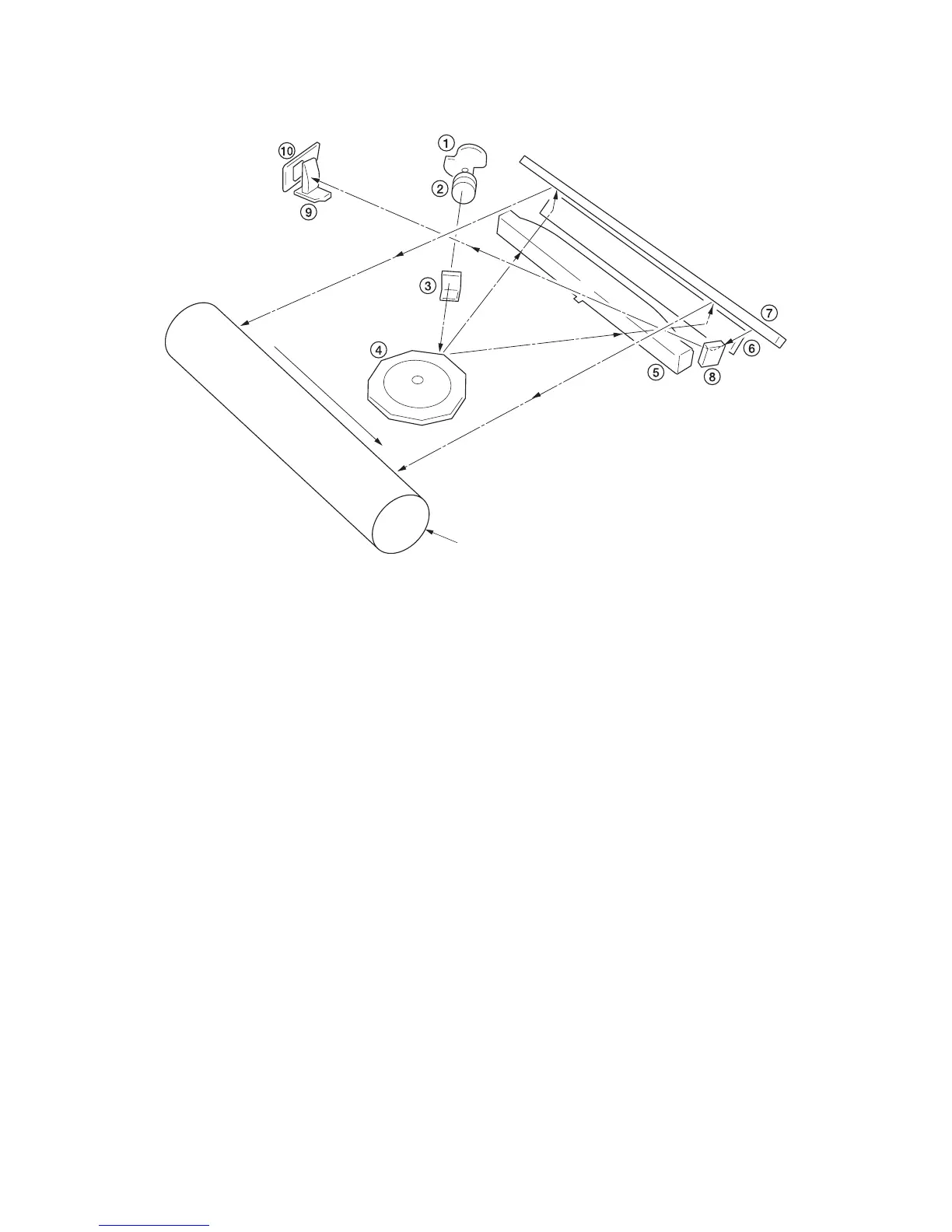
Figure 2-1-8 Laser scanner unit (2)
1. Laser diode: Generates the laser beam which forms a latent image on the drum.
2. Collimator lens: Collimates the diffused laser beam emitted from the laser diode to convert it into a cylindrical
beam.
3. Cylindrical lens: Shapes the collimated laser beam to suit the printing resolution.
4. Polygon mirror: Nine-facet mirror that rotates with each face reflecting the laser beam toward the drum for one
main-direction scan.
5. f
θ lens: Corrects for non-linearity of the laser beam scanning speed on the drum surface, keeps the beam diame-
ter constant and corrects for the vertical alignment of the polygon mirror to ensure that the focal plane of the laser
beam is on the drum surface.
6. Mirror: Reflects the laser beam and changes the irradiation direction.
7. Mirror: Reflects the laser beam and changes the irradiation direction.
8. BD sensor mirror: Reflects the laser beam to the BD sensor to generate the main-direction (horizontal) sync sig-
nal.
9. Cylindrical correcting lens: Corrects for the deviation of the laser beam reflected by the BD sensor mirror to the
BD sensor.
10. BD sensor: Detects the beam reflected by the BD sensor mirror, outputting a signal to the main PWB (MPWB) to
provide timing for the main-direction sync signal.
Drum

 Loading...
Loading...