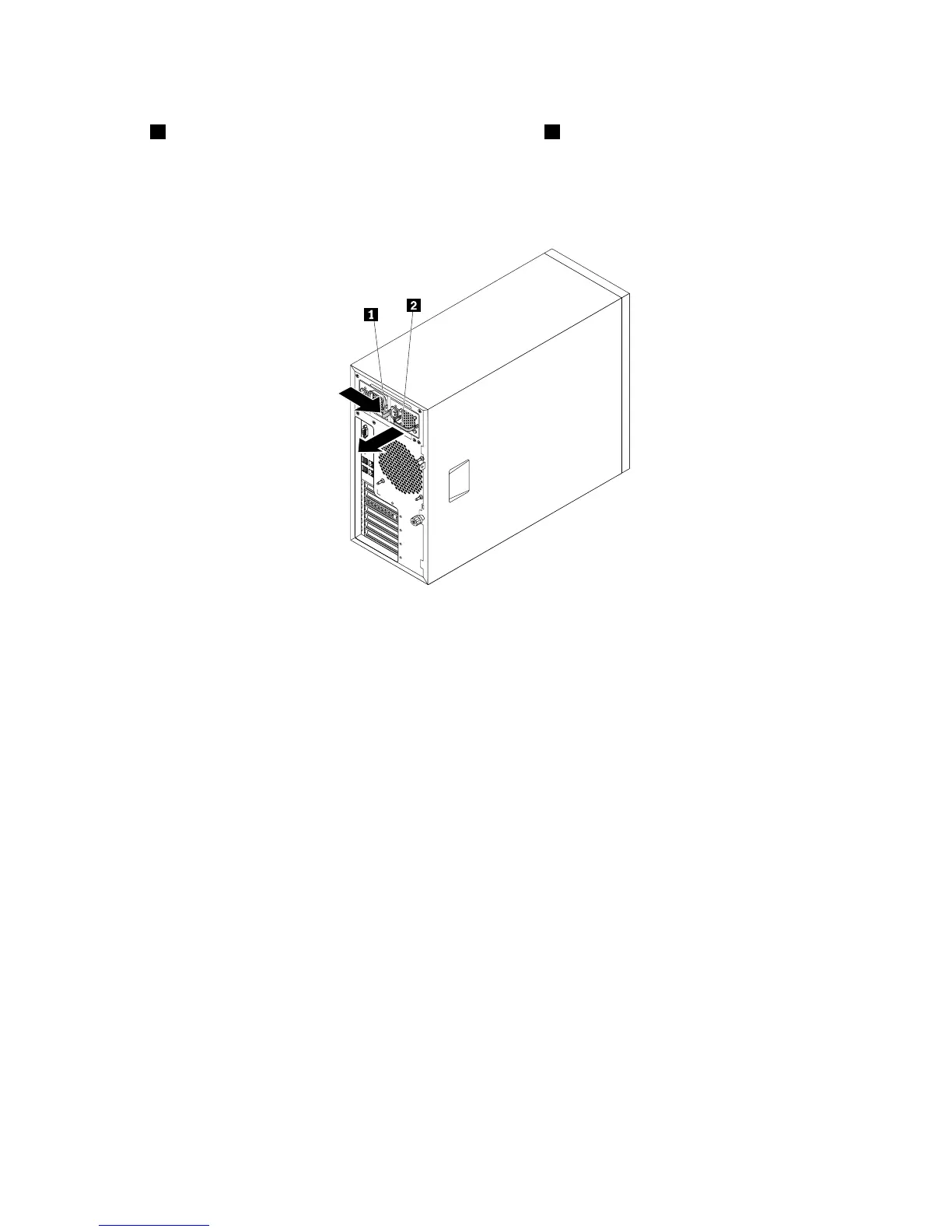
1.Locatethefailinghot-swapredundantpowersupplyontherearofyourserver.Then,presstherelease
tab1inthedirectionasshownandcarefullypullthehandle2atthesametimetoslidetheredundant
powersupplyoutofthechassis.
Note:Donotusetoomuchstrength.Youcanrstcarefullyslidetheredundantpowersupplyalittlebit
outtoreleaseitfromthesecuredposition.Then,completelyslideitoutofthechassis.
Figure88.Removingahot-swapredundantpowersupply
2.Touchthestatic-protectivepackagethatcontainsthenewhot-swapredundantpowersupplytoany
unpaintedsurfaceontheoutsideoftheserver.Then,removethenewhot-swapredundantpower
supplyfromthepackage.
150ThinkServerTS430UserGuide
 Loading...
Loading...



















