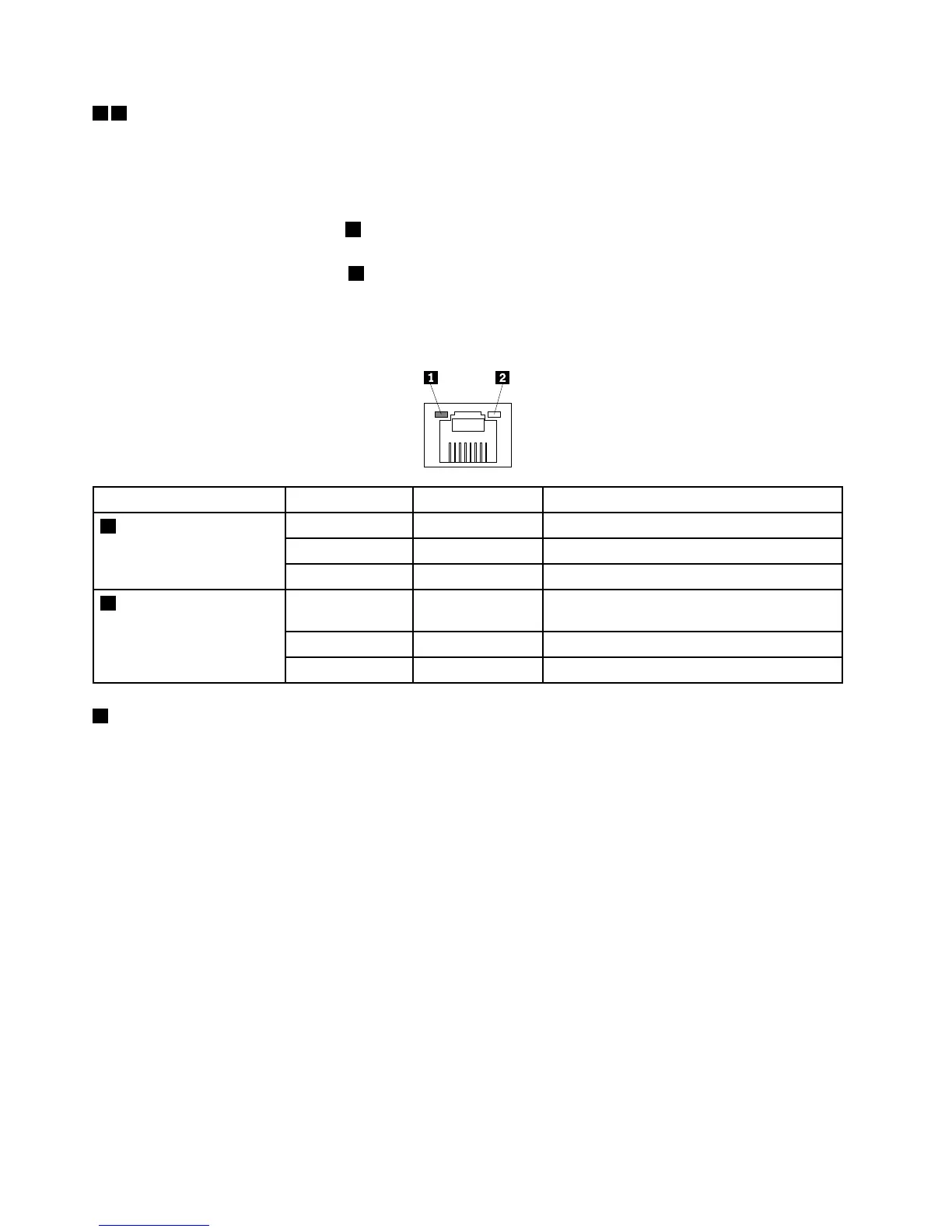
67Ethernetconnectors
UsedtoattachanEthernetcableforaLAN.EachEthernetconnectorhastwostatusLEDstohelpyou
identifytheEthernetconnectivity,activity,andconnectionspeed.
Notes:
•TheEthernetconnector2(callout7)markedwith“MGMT”isforsystemmanagement.Ifyouwanttouse
remotemanagementfunctions,youneedtoconnectanEthernetcabletotheEthernetconnector2.
•TheEthernetconnector2(callout7)markedwith“MGMT”doesnotsupporttheLinkAggregation
ControlProtocol(LACP)teamingincludingNICfailovercapabilities.Iftheteamingfunctionisenabled,
theTMMmanagementcapabilitywillbedisabled.
Note:
EthernetstatusLED
ColorStatus
Description
GreenOn
TheserverisconnectedtoaLAN.
None
Off
TheserverisdisconnectedfromaLAN.
1Left
Green
BlinkingTheLANisconnectedandactive.
Amber
On
Theconnectionspeedis1000Mbps
(megabitspersecond).
GreenOn
Theconnectionspeedis100Mbps.
2Right
None
Off
Theconnectionspeedis10Mbps.
8Frontdoorkey
Usedtoopenorlockthefrontdoor.
Note:Carefullysavethefrontdoorkeytoavoidloss.
Serverlocks
Lockingtheservercoverhelpspreventunauthorizedaccesstotheinsideofyourserverandlockingthefront
doorhelpspreventunauthorizedaccesstotheinstalledharddiskdrives.
Note:Dependingonthemodel,yourservermightlookslightlydifferentfromtheillustrationsinthistopic.
22ThinkServerTS430UserGuide
 Loading...
Loading...



















