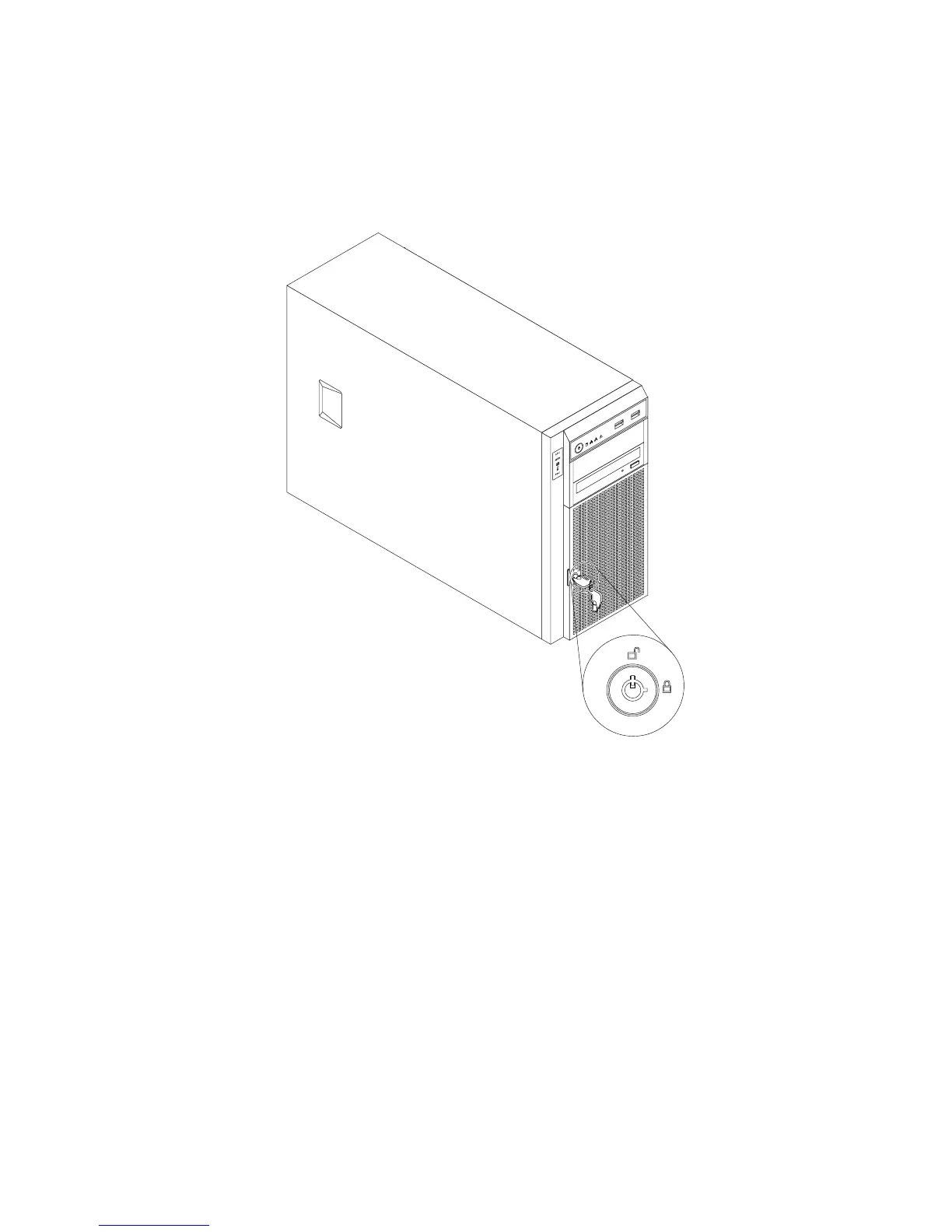
Frontdoorlock
Youcanremovethekeyattachedontheserveranduseittoopenorlockthefrontdooroftheserver.
Thefrontdoorhelpsprotecttheharddiskdrivecagestopreventunauthorizedaccesstotheinstalled
harddiskdrives.
Figure10.Frontdoorlock
Servercomponents
Thistopicprovidesinformationtohelpyoulocatethecomponentsofyourserver.
Toremovetheservercoverandgainaccesstotheinsideoftheserver,see“Removingtheservercover”
onpage87.
Thechassiscongurationvariesbymodel.Thefollowingillustrationsshowthefourmainchassis
congurationsbasedonthesupportedharddiskdrives.
Chapter3.Productoverview25
 Loading...
Loading...



















