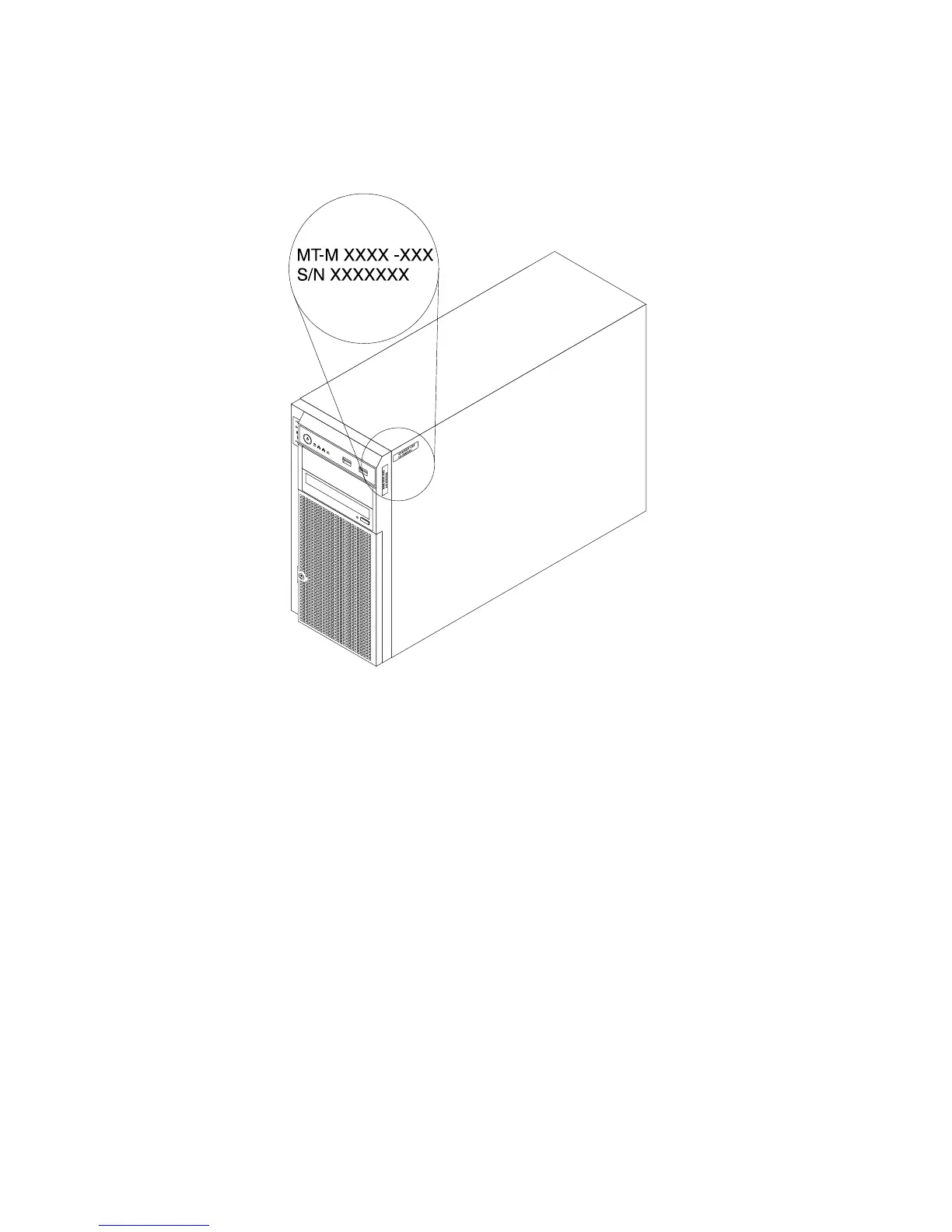
Thefollowingillustrationisasampleofthemachinetype,model,andserialnumberlabelsontheserver.
Note:Dependingonthemodeltype,yourservermightlookslightlydifferentfromtheillustrationinthistopic.
Figure2.Machinetype,model,andserialnumberlabels
14ThinkServerTS430UserGuide
 Loading...
Loading...



















